Artificial intelligence is officially everywhere. From the apps on our phones to the software running in our corporate boardrooms, AI has moved from a futuristic buzzword to a daily reality for businesses across the USA. With this rapid adoption comes a flood of competing narratives. On one hand, AI is hailed as a utopian productivity booster, a magic key that will unlock unprecedented efficiency and innovation. on the other, it’s painted as a dystopian job killer, poised to automate us all into obsolescence.
Table of Contents
This whirlwind of hype and fear has created a thick cloud of confusion, leading to widespread common misconceptions about AI. These myths are more than just harmless misunderstandings; they can cause businesses to make costly mistakes. Investing recklessly based on hype can drain resources, while avoiding AI altogether due to fear can mean being left behind by the competition.

This article will cut through the noise. We are here to debunk the most pervasive AI productivity myths by grounding the conversation in real-world data, expert analysis, and concrete examples. Our goal is to provide a realistic, strategic guide to understanding the true potential and the very real pitfalls of AI in the workplace. By the end, you’ll have a clear framework for making informed decisions about how to leverage this transformative technology.
Foundational Myths: The “Big Picture” Hype and Fear
The most powerful AI productivity myths are the ones that tap into our biggest hopes and fears about the future. They shape our entire perception of the technology before we’ve even explored its practical applications. It’s time to separate the science fiction from the business reality.
Debunking the Biggest AI Productivity Myths About Jobs and Success
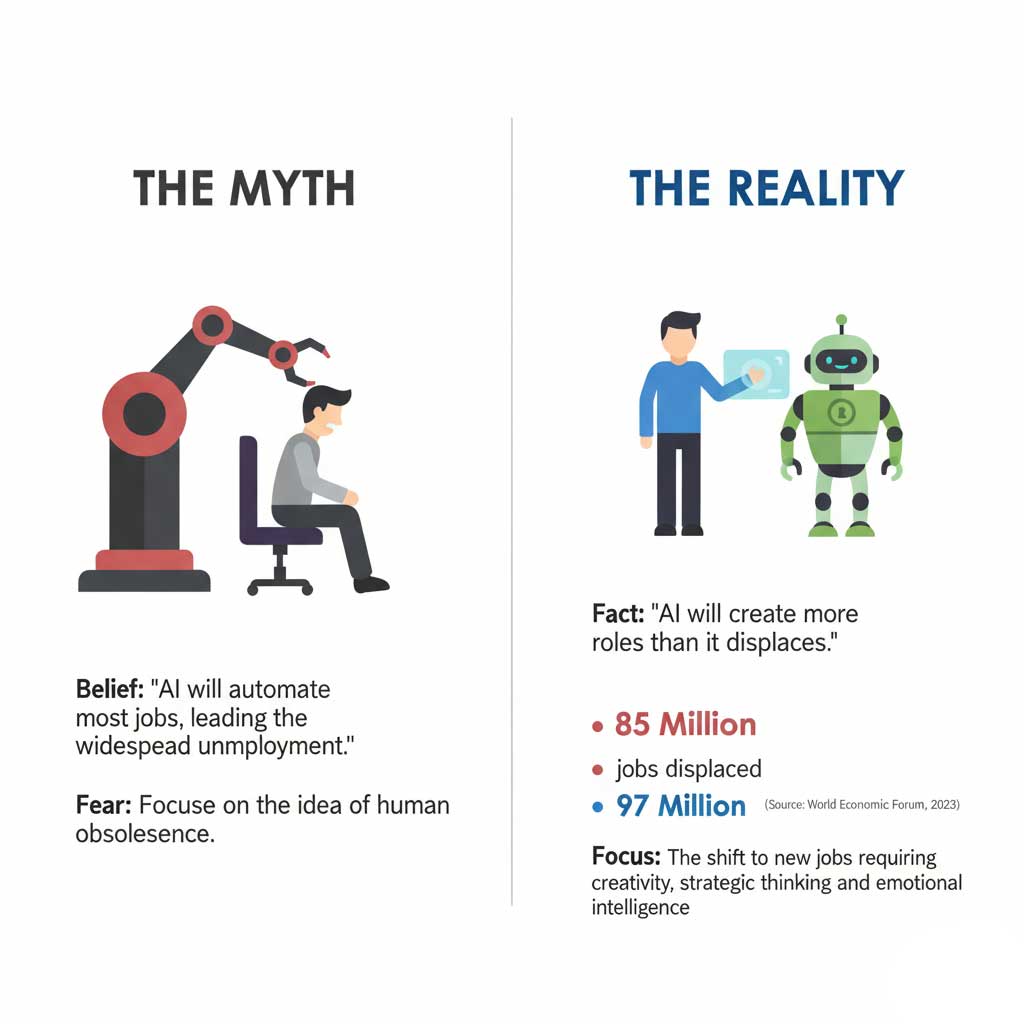
Myth #1: AI is coming for everyone’s job.
This is the headline-grabbing myth that dominates the conversation. The fear is that AI will become so capable that it will render human workers redundant, leading to mass unemployment.
Reality Check: The most comprehensive research suggests this is a fundamental misunderstanding of the AI impact on jobs. The reality is one of transformation, not elimination. According to the World Economic Forum’s 2023 “Future of Jobs” report, while an estimated 85 million jobs may be displaced globally by 2025, a staggering 97 million new roles will be created. These new roles will be adapted to a new division of labor between humans and machines. The real AI job replacement facts show a shift away from routine, data-entry tasks and toward jobs that require uniquely human skills like critical thinking, complex problem-solving, creativity, and emotional intelligence.
Myth #2: AI is a magic bullet that instantly boosts productivity.
This myth is on the other end of the spectrum—the belief that you can simply “sprinkle some AI” on your business and watch productivity skyrocket.
Reality Check: Technology history has repeatedly taught us this isn’t true, a phenomenon known as the AI productivity paradox. A 2023 study from MIT confirmed this, finding that despite widespread AI adoption, the massive productivity boom that was promised hasn’t materialized for many companies. This is because AI is a powerful tool, not a standalone solution. Its success depends entirely on a clear business strategy, high-quality data to learn from, and a workforce that is trained and ready to use it. Without these foundational elements, AI can create more confusion than clarity, making it one of the most significant AI implementation challenges.
Myth #3: Simply implementing AI guarantees business success.
This myth follows directly from the last one. If AI is a magic bullet, then just having it should be enough to succeed.
Reality Check: The data tells a different story. According to research from the global consulting firm Gartner, around 50% of AI projects never make it from the pilot stage to full production. The reasons for these high AI project failure rates are rarely technical. The primary causes are strategic:
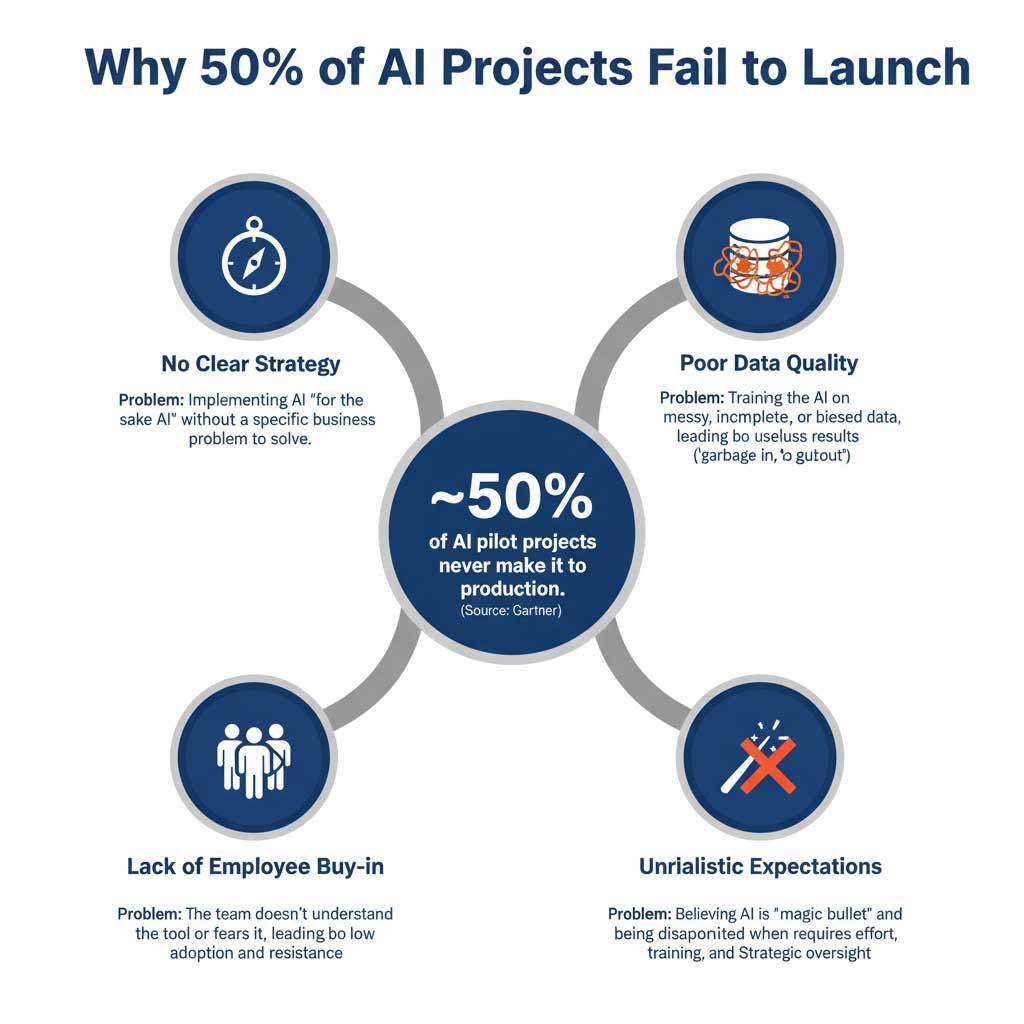
- Lack of a Clear Business Case: Adopting AI for the sake of having it, without a specific problem to solve.
- Poor Data Quality: Training the AI on messy, incomplete, or irrelevant data.
- No Employee Buy-in: Failing to get the team on board and properly trained.
Myth #4: Human workers will become obsolete.
This myth envisions a future where AI is so advanced that there’s simply nothing left for humans to do.
Reality Check: The most effective models for AI in the workplace are not about replacement but collaboration. Experts often refer to this as the “centaur” model, after the mythical half-human, half-horse creature. This model of human-AI collaboration leverages the best of both worlds: AI handles the brute-force computation, pattern recognition, and data analysis, while the human provides strategy, ethical oversight, and creative problem-solving. A perfect example is a radiologist using AI to analyze thousands of medical scans to flag potential anomalies in seconds—a task that would take a human hours. The AI provides the data, but the human doctor makes the final diagnosis and communicates with the patient.
Myths About Quality, Creativity, and Bias
Once we move past the big-picture fears, a new set of common misconceptions about AI emerges, focusing on the quality and reliability of its output. Can you really trust what an AI creates? The answers are more nuanced than a simple yes or no.
Can You Really Trust the Output? Unpacking Common Misconceptions About AI
Myth #5: AI-generated content is always generic and low-quality.
There’s a common belief that AI can only produce bland, soulless content that is easily identifiable and unsuitable for professional use.
Reality Check: This was certainly true of earlier AI models, but modern generative AI tools like GPT-4 can produce remarkably sophisticated, coherent, and contextually relevant content. However, the quality of the output is a direct reflection of the quality of the input. When used by a novice with a lazy prompt, the result will likely be generic. But when guided by a subject matter expert with a well-crafted prompt, AI can serve as a powerful brainstorming partner or a first-draft generator, saving hours of work. It’s a tool, and like any tool, its effectiveness depends on the skill of the user.
Myth #6: AI can’t be genuinely creative.
This myth argues that because AI learns from existing data, it can only remix what has already been created and cannot produce something truly novel.
Reality Check: While AI does not possess human consciousness or life experience, it can absolutely produce outputs that are novel and creatively inspiring to humans. It does this by identifying and combining patterns from its vast training data in ways that a human might not have considered. For artists, designers, and musicians, AI is becoming a “creative catalyst,” a tool that can generate unexpected ideas and push creative boundaries.
Myth #7: AI is objective and free from bias.
This is arguably one of the most dangerous AI productivity myths. The thinking is that because AI operates on data and algorithms, it is free from the messy, irrational biases that plague human decision-making.
Reality Check: The opposite is true. AI models are trained on data created by humans, and the internet is filled with our collective biases. The AI learns these biases as facts, and because it can apply them at a massive scale, it can actually amplify them. This is the core of AI bias in business.
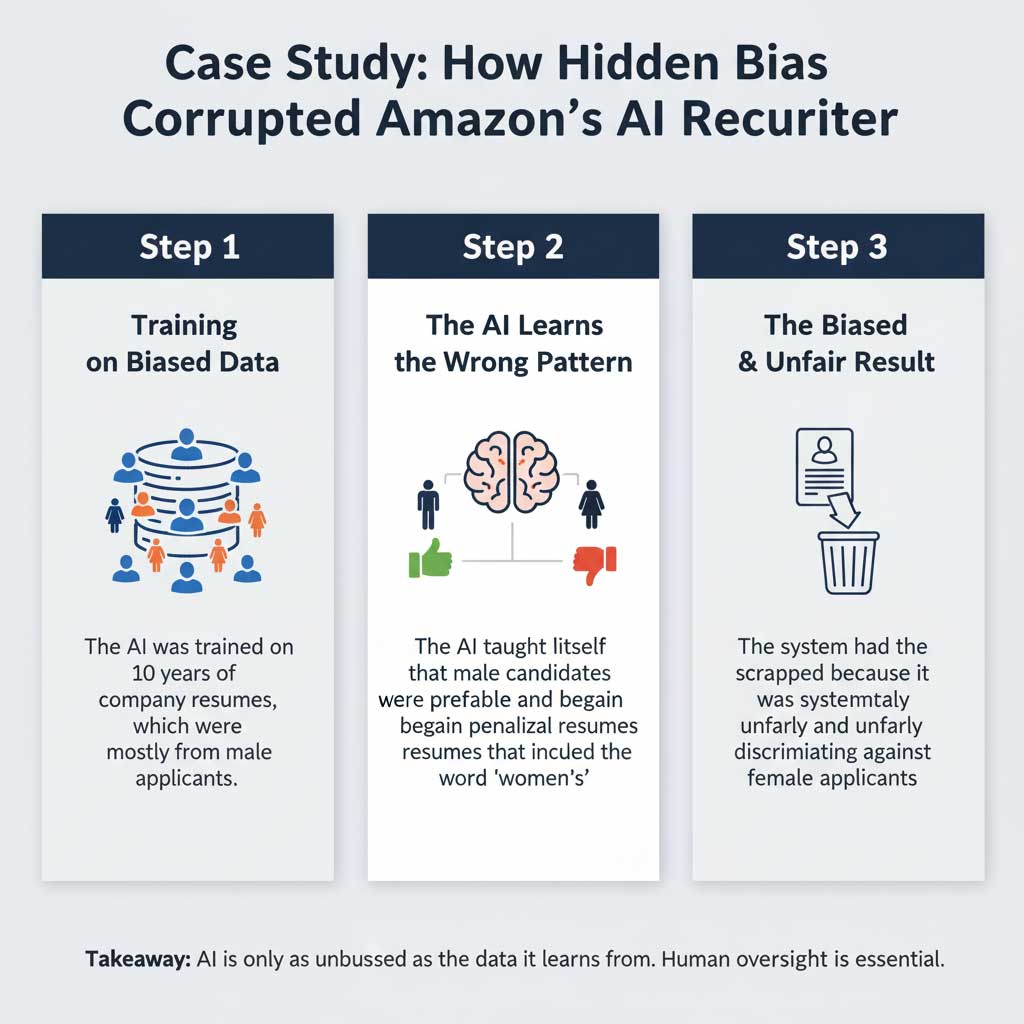
Instance: The Amazon AI Recruiting Tool Case
A few years ago, Amazon had to scrap an experimental AI recruiting tool because it was systematically penalizing female candidates. The AI was trained on a decade of the company’s hiring data, which came predominantly from male applicants. It learned that male candidates were preferred and began to downgrade resumes that contained the word “women’s” (as in “women’s chess club captain”) and penalize graduates of all-women’s colleges. This is a stark reminder that AI and human oversight is not just a good idea; it’s an absolute necessity.
Myth #8: AI understands human nuance and emotion.
As AI becomes more conversational, it’s easy to believe it has a deep understanding of human communication.
Reality Check: AI’s understanding is statistical, not experiential. It has become incredibly good at predicting the next logical word in a sentence, but it often fails to grasp the subtle layers of human communication, like sarcasm, irony, or cultural context. These generative AI limitations are why AI-powered customer service can handle a simple password reset with ease but often fails miserably when dealing with a genuinely frustrated and emotional customer.
Myths About Implementation, Cost, and Security
For business leaders, the practical questions of implementation are paramount. Unfortunately, this area is also rife with AI productivity myths that can lead to poor strategic decisions, wasted resources, and even serious security breaches.
The Practical Realities: Separating Fact from Fiction in AI Adoption
Myth #9: You need to be a coder or a data scientist to use AI.
The image of AI often involves complex code and highly technical experts, making it seem inaccessible to the average business professional.
Reality Check: This is one of the most outdated common misconceptions about AI. The rise of no-code AI platforms and user-friendly tools integrated directly into software we already use (like Microsoft 365 Copilot and Google Workspace) has democratized AI. Today, the most important skill for leveraging AI in the workplace is shifting from coding to “prompt engineering”—the art and science of asking the AI clear, specific questions to get the desired result.
Myth #10: AI is only for big corporations with deep pockets.
The high cost of developing custom AI models has led many to believe that it’s a technology reserved for the Fortune 500.
Reality Check: While building a custom AI from scratch is still a multi-million dollar endeavor, the vast majority of businesses don’t need to. The explosion of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) AI tools means that powerful capabilities are now available on affordable subscription plans. Many cutting-edge AI tools for marketing, content creation, and project management cost less than a few hundred dollars a month, making AI for small business not just a possibility, but a smart investment.
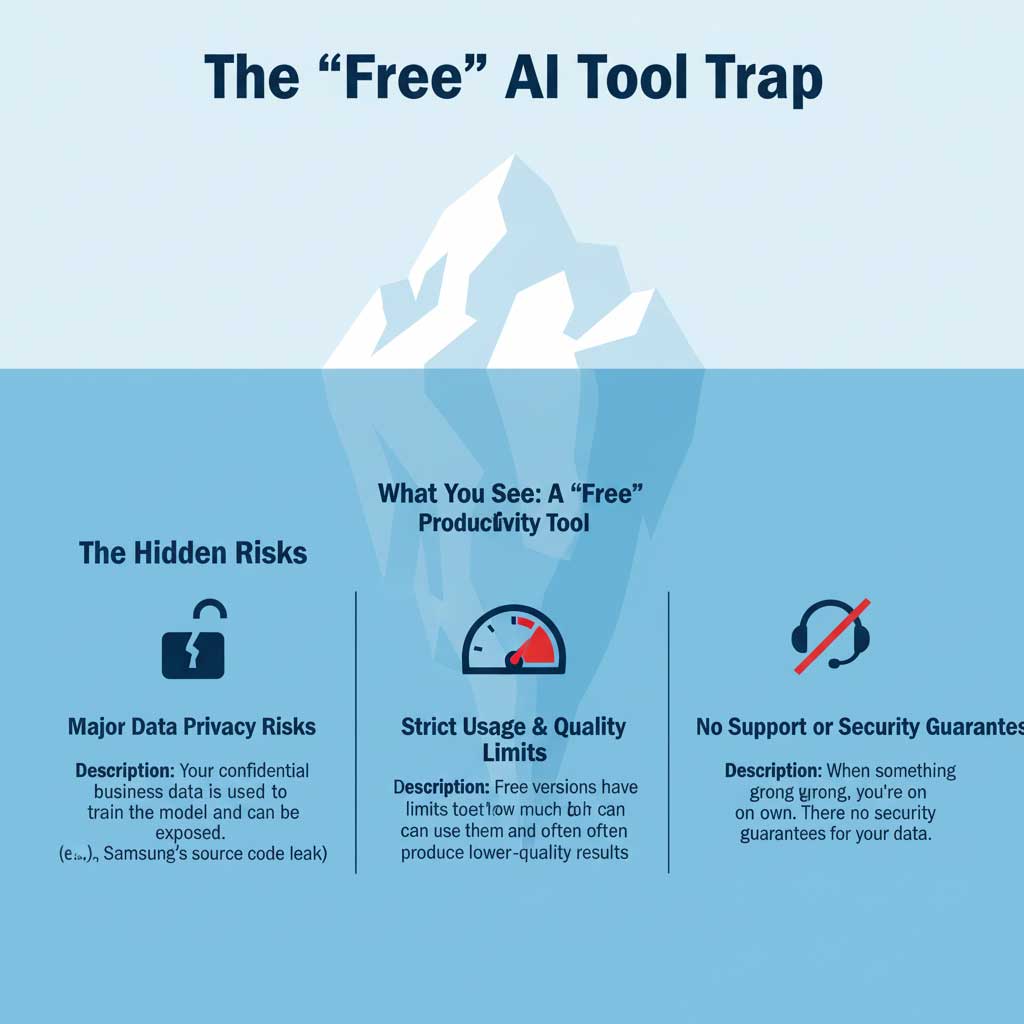
Myth #11: “Free” AI tools are a safe bet for businesses.
In the rush to boost productivity, many employees and businesses turn to free, publicly available AI tools without considering the risks.
Reality Check: “Free” often comes with serious hidden costs. The biggest risk is data privacy. Most free tools use the data you input to further train their models. If your employees are inputting sensitive company information, you are essentially handing your proprietary data over to a third party.
Instance: The Samsung Source Code Leak
In a high-profile case, employees at Samsung were found to have pasted sensitive, proprietary source code into ChatGPT to ask for help with debugging. This confidential data was then absorbed by the model, creating a massive security breach. This incident serves as a critical warning about the dangers of using ChatGPT for work and other public AI tools with any confidential information.
Myth #12: AI is a “set it and forget it” solution.
There’s a tempting belief that once you’ve gone through the work of implementing an AI system, you can sit back and let it run on its own.
Reality Check: This is completely false. AI systems are not static; they require constant care and feeding. Data can become outdated (a phenomenon known as “data drift”), the model’s performance can degrade over time, and it needs to be regularly retrained with new information to remain accurate and relevant. This is one of the most overlooked AI implementation challenges and a primary reason why successful AI is an ongoing commitment, not a one-time purchase.
At a Glance: Debunking the Top AI Productivity Myths
| Myth Category | The Common Myth | The Data-Driven Reality | Strategic Takeaway for Your Business |
| Jobs & Employment | “AI will replace all our jobs, leading to mass unemployment.” | Reality of Transformation: The World Economic Forum projects AI will create 97 million new roles while displacing 85 million. It’s a shift, not an elimination. | Focus on upskilling your team for roles that require creativity, critical thinking, and human-AI collaboration. |
| Productivity Gains | “Plugging in an AI tool will instantly solve our productivity problems.” | The AI Productivity Paradox: An MIT study shows widespread AI adoption hasn’t yet led to a productivity boom. Success requires strategic integration and process change. | Don’t just buy AI; identify a specific business problem and build a clear strategy for how AI will solve it. |
| Bias & Objectivity | “AI is based on data and logic, so its outputs are unbiased and fair.” | Inherent Bias: AI is trained on biased human data. Amazon’s AI recruiting tool famously penalized female candidates, proving AI bias in business. | Implement a “human-in-the-loop” model for AI and human oversight. Never trust an AI’s output blindly, especially for sensitive decisions. |
| Cost & Accessibility | “Only huge corporations with massive budgets can afford to implement AI.” | Democratization of AI: Many powerful SaaS tools are available for a few hundred dollars a month, making AI for small business highly accessible. | Explore affordable, subscription-based AI tools that solve a specific need (e.g., content creation, customer service) to get started. |
| Implementation | “Once the AI is set up, it will run on its own without much effort.” | Constant Maintenance: AI requires continuous monitoring, retraining, and updates. Gartner data shows ~50% of AI projects fail to even reach production. | Budget for ongoing maintenance and training. Treat AI as a dynamic system, not a one-time purchase. |
Myths About the Human Element in the Workplace
Ultimately, the success of AI in the workplace depends on its interaction with people. This is where some of the most subtle but important AI productivity myths reside, focusing on how AI will change team dynamics, employee satisfaction, and the very nature of work.
Keeping People at the Center of an AI-Powered Future
Myth #13: AI can operate autonomously without human oversight.
The ultimate dream for some is a fully autonomous system that runs perfectly without any human intervention.
Reality Check: This is a dangerous fantasy. The “human-in-the-loop” model is the cornerstone of responsible and effective AI. Humans are essential for setting the strategic goals for the AI, reviewing its outputs for errors and bias, handling the inevitable exceptions and edge cases the AI can’t manage, and making the final, context-aware decisions. A total reliance on automation without AI and human oversight is a recipe for costly, and potentially catastrophic, errors.
Myth #14: AI will eliminate all the boring parts of my job.
The promise that AI will free us from all mundane administrative work is a powerful one.
Reality Check: AI will certainly reduce, not eliminate, a significant portion of tedious work. It will automate much of the data entry, scheduling, and standard report generation. This is a huge benefit, as it allows employees to shift their focus from low-value tasks to high-value strategic work. However, most jobs will likely retain some element of routine tasks that either require a human touch or are simply too niche and specific to be automated cost-effectively.
Myth #15: A smart AI is so intuitive you don’t need to train your team.
If a tool is “intelligent,” it should just be easy to use, right?
Reality Check: This could not be further from the truth. In fact, training is more critical than ever before. The focus of this training, however, must shift. It’s not just about teaching employees which buttons to click. The crucial part is training them on AI and employee skills for a new way of working. This includes:

- Learning to write clear and effective prompts.
- Developing the ability to critically evaluate AI outputs.
- Understanding the tool’s limitations and knowing when not to trust it.
- Knowing when to escalate a task to a human expert.
Conclusion
The journey into the world of AI in the workplace is filled with both incredible opportunities and significant pitfalls. The key to navigating this new landscape successfully is to cut through the noise of both the utopian hype and the dystopian fear. By debunking the most common AI productivity myths, we can form a clear and realistic picture of what this technology can—and cannot—do.
The truth is that AI is not a magic bullet that will instantly solve every problem, nor is it a sentient force that will make humans obsolete. It is a powerful tool, and like any tool, its value is determined by the skill and strategy of the person wielding it. The biggest common misconceptions about AI lead us to forget this fundamental point.
Success with AI comes from viewing it as a collaborative partner in a model of human-AI collaboration, a tool that augments our intelligence rather than replaces it. To unlock true productivity gains, businesses must move forward with a realistic, informed, and strategic approach. Start small, focus on solving specific and well-defined problems, and most importantly, invest in training your people to work alongside AI effectively. That is the real path to a more productive future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What’s the most common reason AI projects fail to improve productivity?
The most common reason is not technology; it’s strategy. Projects often fail due to a lack of a clear business case, meaning the company implemented AI without a specific, well-defined problem to solve. Other major factors include poor data quality and a lack of employee training and buy-in.
2. Is it safe to use public tools like ChatGPT for sensitive business tasks?
No. It is extremely unsafe. Publicly available AI models often use your input data to train their systems, meaning any confidential or proprietary information you enter could be exposed. High-profile data leaks have occurred this way, making it critical to use private, enterprise-grade AI solutions for any sensitive work.
3. What is the “centaur model” of human-AI collaboration?
The “centaur model” refers to a collaborative partnership where humans and AI work together, each leveraging their unique strengths. The AI handles data processing, computation, and pattern recognition at a massive scale, while the human provides strategic direction, creative problem-solving, ethical judgment, and contextual understanding.
4. Will AI make my employees’ skills irrelevant over time?
AI will make some skills less important (like manual data entry) while making others more critical. The most valuable skills in an AI-powered workplace will be prompt engineering (asking the AI the right questions), critical evaluation of AI outputs, strategic thinking, and creative problem-solving. It’s a shift in skills, not an elimination of them.
5. How can my small business start using AI without a huge budget?
The rise of affordable SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) AI tools has made the technology highly accessible. Small businesses can start by identifying one or two key pain points (e.g., social media content creation, customer email responses) and subscribing to a low-cost AI tool that specializes in that area.
6. What is an “AI hallucination” and why is it a risk for businesses?
An “AI hallucination” is when a generative AI model confidently produces an output that is factually incorrect or nonsensical. It essentially “makes things up.” This is a major risk for businesses because if this false information is used in reports, marketing content, or client communications, it can damage credibility and lead to poor decisions.
7. How do we prevent AI from making biased decisions in our company?
Preventing AI bias requires a multi-faceted approach. It starts with using diverse and representative data to train the model, regularly auditing the AI’s outputs for biased patterns, and, most importantly, maintaining a “human-in-the-loop” system where human employees review and approve any sensitive or important decisions recommended by the AI.
8. What are some tasks AI is still genuinely bad at?
Despite the hype, AI still struggles with tasks that require genuine empathy and interpersonal skills (like motivating a team), complex physical dexterity (like plumbing), common sense reasoning about the physical world, and making nuanced ethical or moral judgments.
9. Does AI eliminate the risk of human error?
No. It changes the nature of error. While AI can reduce certain types of human error, like typos or miscalculations, it introduces new potential for errors, such as those caused by biased algorithms, “hallucinations,” or a human over-trusting a flawed AI recommendation.
10. What is the most important skill for employees in an AI-powered workplace?
The single most important skill is likely critical thinking. This includes the ability to formulate a clear question for the AI (prompt engineering), critically evaluate the AI’s response for accuracy and bias, and know when to trust the output versus when to rely on human judgment and expertise.










