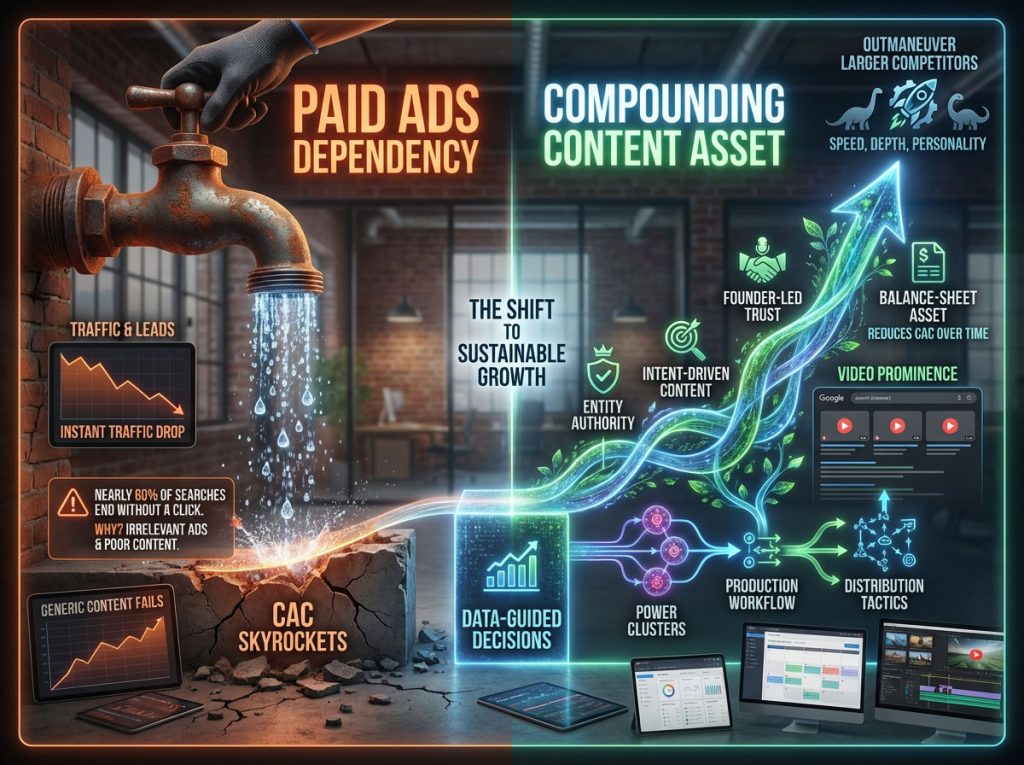
Stopping paid ads usually means stopping traffic. This is the harsh reality for most founders and small business owners who rely exclusively on performance marketing to keep the lights on. You turn off the tap on Google Ads or Meta, and the leads vanish instantly. It is a precarious way to build a business, yet it remains the default playbook for many early-stage companies operating in the US market.
Table of Contents
The only way to escape this expensive cycle is to build an asset that compounds over time. That asset is a robust, data-backed content marketing plan.
For US-based startups and small businesses, the goal is no longer just “more traffic.” With nearly 60% of searches now ending without a click due to AI overviews and instant answers, your strategy must pivot. You cannot win by writing generic 500-word blog posts about broad topics or resharing industry news that everyone else has already covered.
You win by establishing Entity Authority.
A successful content marketing plan for small businesses shifts the focus from chasing volume to chasing intent. It leverages the founder’s voice to build trust. It uses video to capture attention in search results. It uses data to make decisions rather than guessing. Most importantly, it treats content not as a marketing expense, but as a balance sheet asset that lowers your Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) over time.
This guide outlines a specific, data-backed content marketing strategy for startups. We will move beyond theory and give you the exact “Power Clusters,” production workflows, and distribution tactics needed to grow startup traffic and revenue without a massive budget. We will explore how to compete with incumbents who have ten times your budget by out-maneuvering them with speed, depth, and personality.
The New Reality of Startup SEO Strategy: Entity Authority vs. Keyword Stuffing
To understand how to rank today, you must understand how Google has changed. In the past, you could stuff a page with the keyword “startup SEO strategy,” mention it fifteen times, and rank on the first page. Today, Google’s algorithms look for “Entities.”
Building Entity Authority: How Google Ranks B2B Content
An “Entity” is a concept, brand, or person that Google understands as a distinct object in its Knowledge Graph. It does not just look for matching text strings. It looks for Experience, depth, and the relationships between concepts.
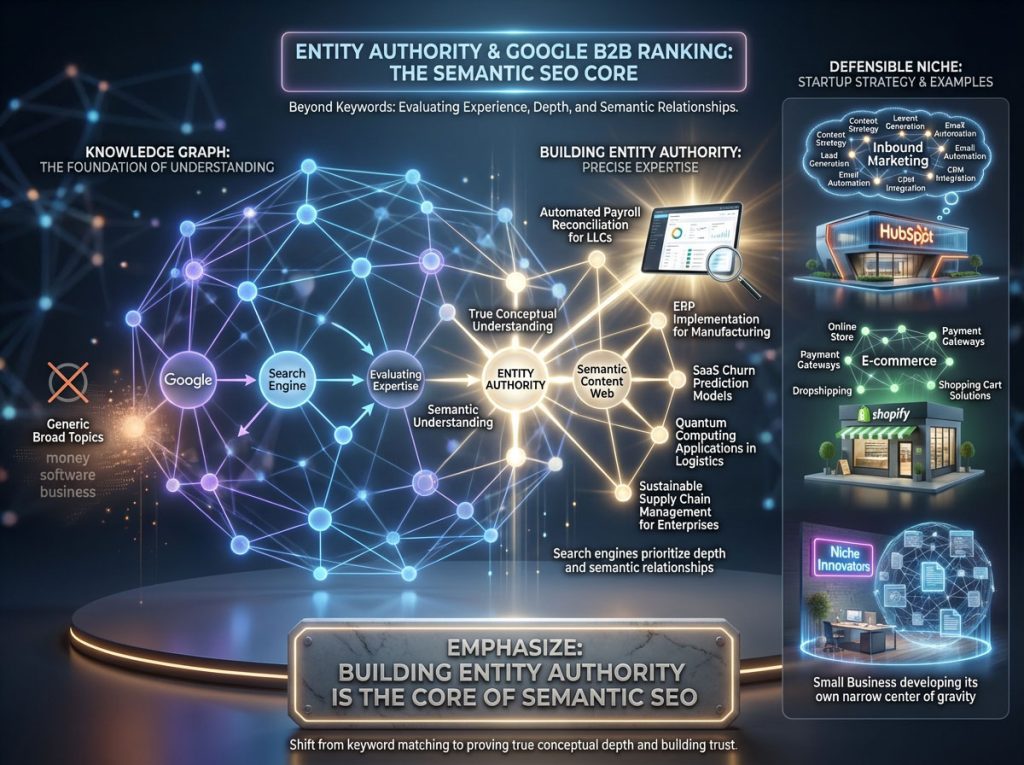
When you create a content marketing plan for startups, your goal is to prove to search engines that your brand is the “Entity” that owns a specific topic.
If you are a fintech startup, you do not just write about “money.” You write about “automated payroll reconciliation for LLCs” with such depth and expertise that Google recognizes you as the authority. This is the core of Semantic SEO. You are building a web of content that signals to the search engine that you are not just using the words; you understand the underlying concepts.
This approach filters out generic, low-quality content. Major SaaS brands like HubSpot or Shopify dominated their markets not by writing about everything, but by owning specific entities like “Inbound Marketing” or “E-commerce” respectively. They created a center of gravity around these terms. For a small business, you must do the same but on a narrower, more defensible scale.
Why High-Volume Keywords Fail to Grow Startup Traffic
Many founders make the mistake of targeting keywords with high search volume but low intent. They write articles like “What is marketing?” hoping to capture everyone.

This is a waste of a low budget content marketing allocation.
A keyword with 10,000 monthly searches might bring you zero customers if those searchers are just students looking for definitions. Conversely, a keyword with only 50 searches per month, such as “best CRM for plumbing small business,” might bring you 10 high-value customers. The volume is irrelevant if the intent does not match your business goals.
Your content marketing strategy for small business must prioritize commercial intent over vanity metrics. You are not a media company selling eyeballs to advertisers; you are a business selling a product or service. Therefore, 100 qualified visitors are worth infinitely more than 10,000 random passersby.
Leveraging E-E-A-T Principles to Boost Content Marketing for Small Businesses
Google’s guidelines on Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) are not just suggestions; they are the filter through which your content is judged. For a startup, “Experience” is your greatest weapon. Large corporations often outsource content to generalist writers who have never used the product or suffered the problem it solves.
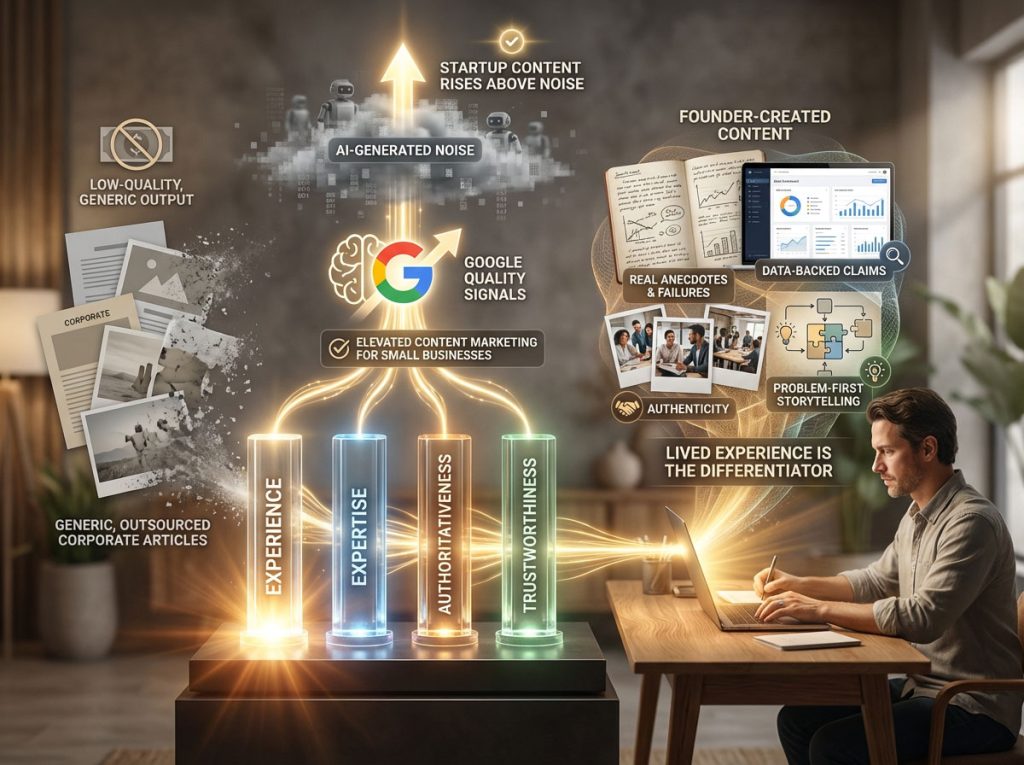
As a founder or early employee, you have lived the problem. You have deep, visceral experience. When you write from that perspective, sharing specific anecdotes, failures, and data points, you signal “Experience” to Google. This human element is what separates successful startup blogs from the infinite sea of AI-generated slush.
Phase 1: Strategic Content Pillars for Low Budget Content Marketing
Startups cannot afford to scatter their energy. You need to focus your budget on the areas that generate the highest ROI. Based on current search data and user behavior, we have identified four “Power Clusters” that should form the foundation of your plan. These clusters are designed to bypass the “awareness” stage and go straight to the users who are ready to engage.
Cluster 1: “Best Alternatives” & Comparison Posts for High-Intent Lead Generation
This is where the money is. Users searching for comparisons are at the bottom of the funnel. They have a credit card in hand and are deciding which software to buy. They are aware of their problem, they are aware of the solutions, and they are looking for a reason to choose one over the other.

Your content marketing plan for startups should explicitly target high-conversion keywords like:
- “[Competitor] alternative”
- “[Your Brand] vs [Competitor]”
- “Best [Industry] software for small business”
- “[Competitor] pricing analysis”
Do not shy away from mentioning competitors. Many startups fear that mentioning a competitor gives them free publicity. The reality is that if a user is searching for “[Competitor] alternative,” they already know the competitor exists. Your job is to intercept that search.
Create a comparison matrix that honestly highlights where you win. Be objective. If your competitor has a feature you lack, admit it, but explain why your alternative approach is better for a specific type of user. This honesty builds immense trust and captures high-intent traffic that is ready to convert.
Cluster 2: Problem-Solving “How-To” Guides to Drive Organic Traffic
These are not generic guides. These are detailed solutions to expensive problems your customers face. The difference between a “Topic” and a “Pain Point” is urgency. A topic is “Time Management.” A pain point is “How to stop paying overtime due to scheduling conflicts.”
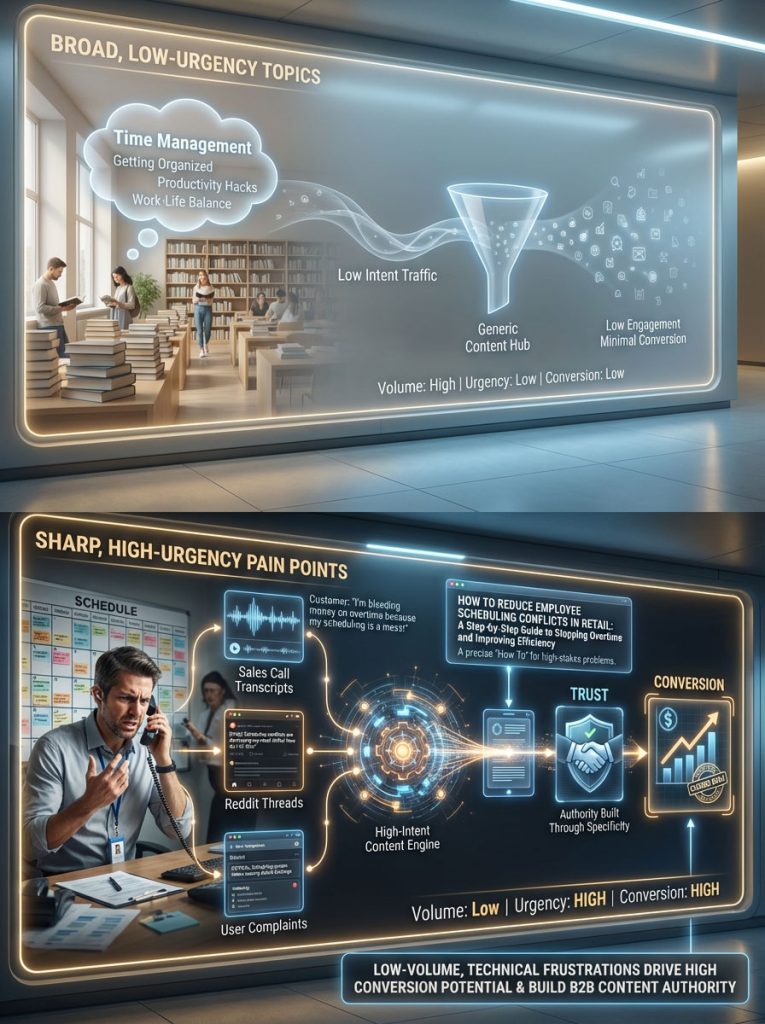
If you sell scheduling software, do not write “Why time management is good.” Write “How to reduce employee scheduling conflicts in retail.”
This establishes your B2B content marketing authority. You are helping the user solve a specific pain point. When they see you understand their problem, they will trust your solution.
To find these pain points, look at your sales call transcripts. What are the specific complaints prospects make? Look at Reddit threads in your industry. What are people venting about? These specific, often technical frustrations are gold mines for content. They have lower search volume but incredibly high conversion potential.
Cluster 3: Video Marketing Strategy to Capture Zero-Click Searches
Google search results now feature “Short Video” carousels and YouTube embeds prominently. If your startup SEO strategy ignores video, you are invisible to a massive segment of users.

Certain queries inherently demand a visual answer. If someone searches for a tutorial, a review, or a walkthrough, they likely do not want to read a 2,000-word essay. They want to see the product in action.
Target keywords that imply a visual answer:
- “How to install…”
- “… tutorial”
- “… review”
- “… walkthrough”
By creating content for these queries, you can leapfrog competitors who only have text articles. You do not need a studio. A simple screen recording with a voiceover, solving the user’s problem in three minutes, can often rank higher than a text article from a massive incumbent.
Cluster 4: Local Content Marketing for Small Businesses & Brick-and-Mortars
For a local business, the content marketing strategy for small business must focus on “Near Me” intent. This is the battleground for brick-and-mortar businesses.
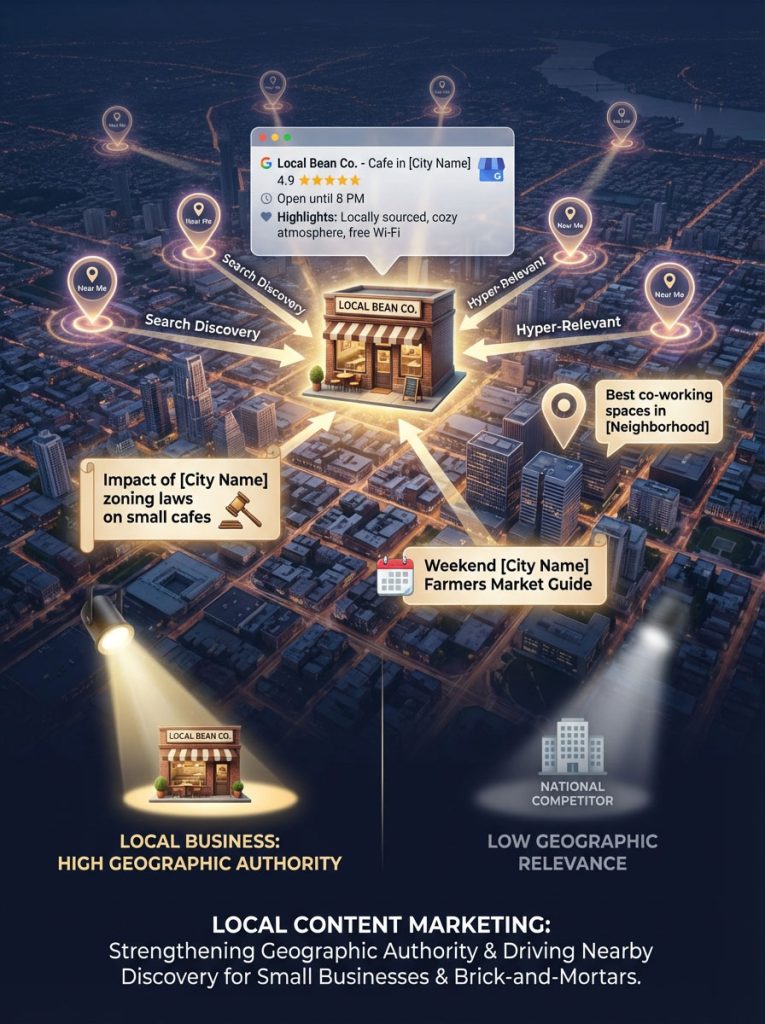
This involves optimizing your Google Business Profile and creating content about local events, local regulations, or local customer stories. This signals relevance to search engines for any user in your geographic area.
Write about “The impact of [City Name] new zoning laws on small cafes” or “Best co-working spaces in [Neighborhood].” These articles signal to Google that you are hyper-relevant to that specific location. When someone in that area searches for your service, your geographic authority gives you a significant edge over national competitors.
Analyzing the ROI: Content Marketing vs. Paid Ads for Startups
To understand why this investment is necessary, look at the structural difference between organic traffic growth strategy and paid acquisition.
| Metric | Content Marketing (Organic) | Paid Advertising (PPC) |
| Cost Profile | High upfront effort, near-zero marginal cost long-term. | High continuous cost; expenses rise linearly with traffic. |
| Speed to Results | Slow (6–18 months for compounding growth). | Instant (Traffic starts the moment you pay). |
| Trust Factor | High (Users trust organic results 4x more). | Low (Users often ignore “Sponsored” tags). |
| Asset Value | Compounding (Articles bring traffic for years). | Renting (Traffic stops immediately when budget stops). |
| Best For | Lowering CAC, Brand Authority, Long-term Scale. | Testing offers, Short-term promos, Retargeting. |
The table above illustrates the fundamental shift in thinking required. Paid ads are essentially renting attention. You are a tenant on Google’s land. Content marketing is building equity. You are constructing digital real estate that you own. While the initial construction phase is labor-intensive, the long-term maintenance costs are low, and the asset appreciates over time.
Phase 2: The “Cyborg” Workflow: AI Tools for Efficient Startup Content Creation
A common question is: “How can we produce enough content with a small team?” The answer lies in the Hybrid Model, often called the “Cyborg” workflow.
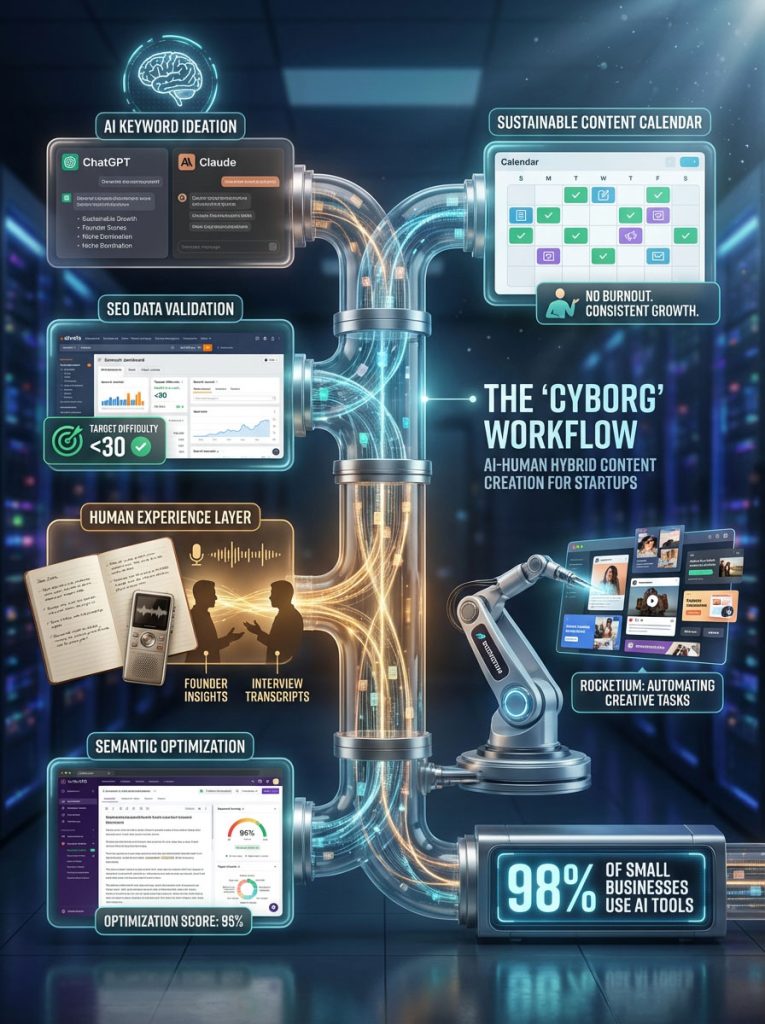
This approach uses AI for efficiency and humans for experience. It is the secret weapon of efficient low budget content marketing. It allows a team of one or two to output the volume and quality of a team of ten.
Implementing the AI-Human Hybrid Model for B2B Startups
The goal here is not to let AI write your content. Pure AI content is often bland, repetitive, and lacks the unique insights required to rank. The goal is to use AI to handle the robotic parts of the process so the human can focus on the creative parts.
1. AI-Assisted Keyword Research & Ideation
Use tools like ChatGPT or Claude to brainstorm topics and build audience personas. Ask the AI to identify gaps in your competitors’ content. This speeds up the ideation phase significantly.
- Example Prompt: “Act as a marketing manager for a B2B SaaS in the logistics space. List 20 painful problems a fleet manager faces daily that they might search for on Google. Focus on problems that cost them money.”
2. Data Validation with SEO Tools
Once you have ideas, you must validate them. Use Ahrefs or Semrush to verify that people are actually searching for these topics. Ensure the keyword difficulty is manageable for a new site. Look for keywords with a difficulty score under 30 if your domain is new. This ensures you are not fighting battles you cannot win.
3. Drafting: The Human Experience Layer
This is non-negotiable. AI cannot replicate human experience. A founder or subject matter expert must write the core insights, stories, and emotional hooks. This “Experience” is the first “E” in Google’s E-E-A-T framework.
If the founder is too busy to write, interview them. Record a 20-minute conversation where they explain the topic. Then, have a writer turn that transcript into an article. The voice, the opinions, and the expertise remain authentic, even if the founder didn’t type every word.
4. Semantic Optimization with Content Intelligence Tools
Once the human draft is done, run it through a tool like SurferSEO or Clearscope. These tools analyze the top-ranking results and suggest semantic keywords to ensure your content marketing plan for startups is technically sound. They act as a guardrail, ensuring you haven’t missed any sub-topics that Google expects to see.
Real-World Example: How Rocketium Scaled Content with AI
Consider Rocketium, a creative automation platform. They faced the challenge of needing to produce vast amounts of creative variations for their marketing but had a small team. They used programmatic tools—essentially a form of automation similar to our Cyborg workflow—to help SMBs launch campaigns 8x faster than traditional methods.
By automating the repetitive formatting and resizing tasks, they allowed their human designers to focus on the core creative concepts. This mirrors the trend across the industry. According to data from the AP and U.S. Chamber of Commerce, approximately 98% of small businesses now use AI-enabled tools to level the playing field against larger competitors.
Adopting this workflow allows you to maintain a consistent content calendar for startups without burning out your core team. It changes the equation from “Can we afford to write this?” to “Can we afford not to?”
Phase 3: Content Distribution Strategy for Startups: Video & Personal Branding
Creating content is only 20% of the job. The other 80% is distribution. A content marketing plan for startups that lacks a distribution strategy will fail to grow startup traffic. You cannot simply hit “publish” and hope the world finds you. You must aggressively push your content into the channels where your audience hangs out.
Video SEO Tactics: Repurposing Content for YouTube and TikTok
Video is no longer optional. Video marketing strategy is now SEO strategy. The lines between search and video are blurring.
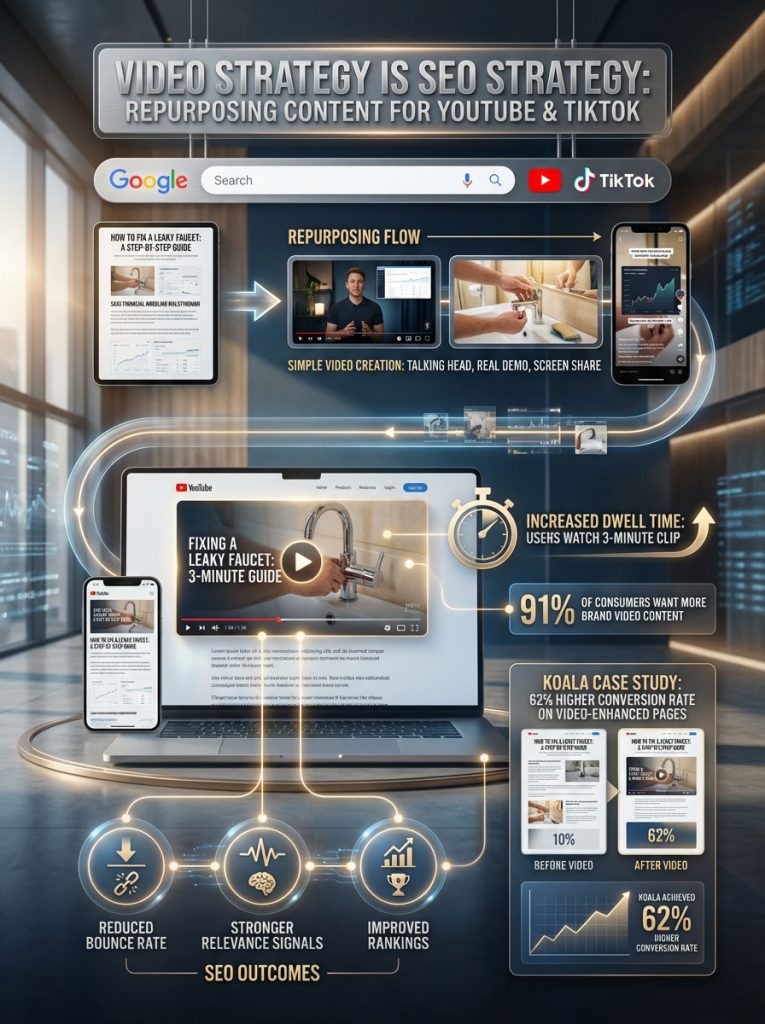
The Repurposing Tactic:
Record your blog post as a YouTube video. It does not need high production value; a simple screen share or “talking head” video works. If you wrote a guide on “How to fix a leaky faucet,” stand in front of a sink and film it. If you wrote about “SaaS financial modeling,” record your screen as you walk through a spreadsheet.
Embed this video at the very top of your blog post.
The SEO Result:
This significantly increases “Dwell Time” (how long a user stays on the page). When a user clicks your result and immediately watches a three-minute video, Google interprets this as a massive signal of quality and relevance. It reduces your bounce rate and signals that your page solved the user’s query.
Data-Driven Proof:
According to HubSpot and Wyzowl, 91% of consumers want to see more online video content from brands. Furthermore, Koala (an e-commerce mattress brand) used humorous, relatable video ads to differentiate themselves. By integrating video deeply into their landing pages and content, they drove a 62% higher conversion rate on pages featuring video.
Founder-Led Growth Hacking: Building Trust via LinkedIn and X
People trust people, not corporate logos. This is why founder-led brand building is becoming a dominant channel for B2B content marketing. In a world of sterile corporate speak, a founder who speaks plainly and authentically stands out.

The “Building in Public” Strategy:
The founder should document the journey of building the company. Share the wins, the losses, and the lessons learned on platforms like LinkedIn or X (formerly Twitter). This is often called “Building in Public.”
Execution of Personal Branding:
Take the key insight from your “Pillar Blog Post” and turn it into a LinkedIn thread. Do not just post the link. Rewrite the core lesson as a standalone social post. Hook the reader with a strong opening line, deliver value in the body of the post, and then link back to the full article in the comments or bio for those who want to go deeper.
Founders like Tyler Denk (Beehiiv) and Adam Robinson (RB2B) utilized this exact strategy. They grew their startups largely through personal brand authority, bypassing the need for massive ad spend. They became the primary distribution channel for their own companies. This is organic growth hacking at its finest because it builds an audience that you own, rather than one you rent.
The Content Waterfall Distribution Model
Think of your content as a waterfall. It starts at the top with a heavy, research-backed “Pillar Piece.” This takes the most effort. From there, it flows down into lighter, easier-to-consume formats.

- The Pillar: A 3,000-word guide on your website regarding content marketing for startups.
- The Video: A 10-minute YouTube walkthrough of that guide.
- The Audio: The audio from the video becomes a podcast episode.
- The Social Threads: The guide is broken into 5 LinkedIn threads and 5 Twitter threads.
- The Shorts: The video is cut into 5 vertical clips for TikTok/Reels.
- The Newsletter: The guide is summarized for your email list.
One idea, executed once, provides weeks of distribution material across every relevant channel.
Phase 4: A 90-Day Content Marketing Plan Template for Execution
To make this content marketing plan for startups actionable, we break it down into a 90-day sprint. This roadmap ensures you build momentum without getting overwhelmed. Most startups fail because they try to do everything at once. This plan focuses on sequential progress.
Month 1: Establishing Authority and Technical Foundations
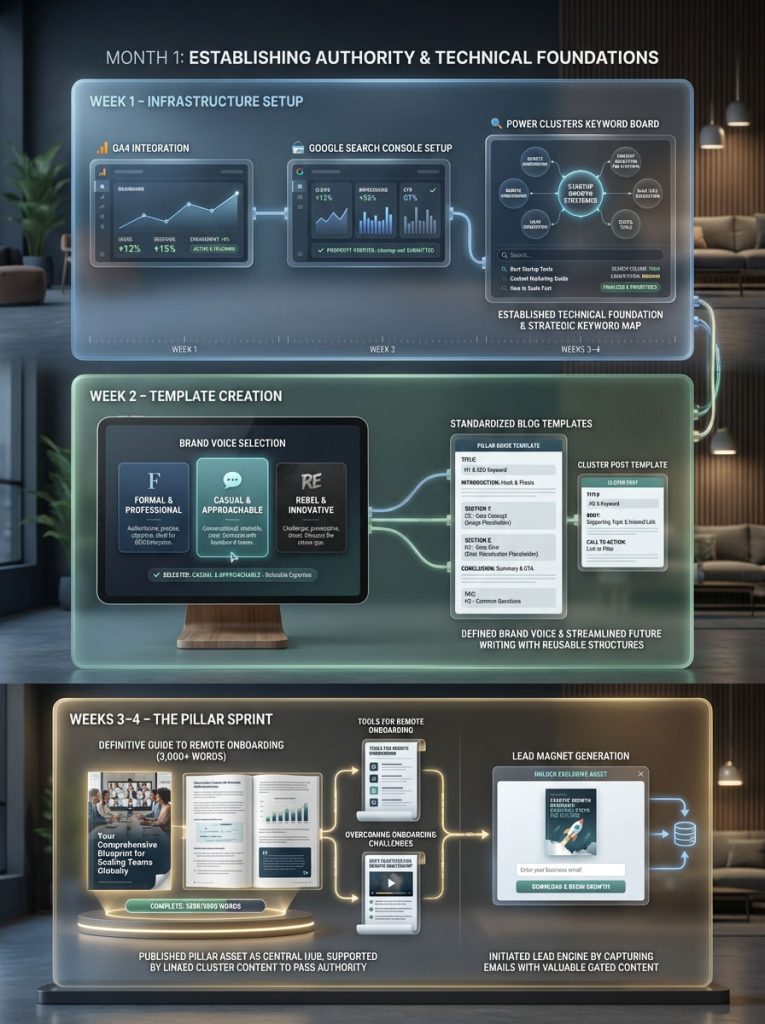
Week 1: Infrastructure Setup
Set up your infrastructure. Ensure Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and Google Search Console are installed and verifying data. Create your list of “Power Clusters.” Do the keyword research now so you don’t have to stop writing later to find topics.
Week 2: Template Creation
Develop your templates. Create a standard structure for your blog posts. This speeds up writing. Decide on your brand voice. Are you formal? Casual? Rebel? Define this now.
Week 3-4: The Pillar Sprint
Produce one massive “Pillar Asset” (3,000+ words) that covers a core topic exhaustively. If you are in HR tech, write “The Definitive Guide to Remote Onboarding.” This asset will be the anchor for your authority. Then, produce three smaller supporting articles that link back to the pillar. These “Cluster” posts support the main argument and pass link equity to the main page.
Lead Magnet Generation:
Create a downloadable template (e.g., “Startup Growth Checklist” or “Onboarding Excel Sheet”) and gate it to capture emails. This begins your lead generation engine immediately.
Month 2: The Video & Distribution Layer
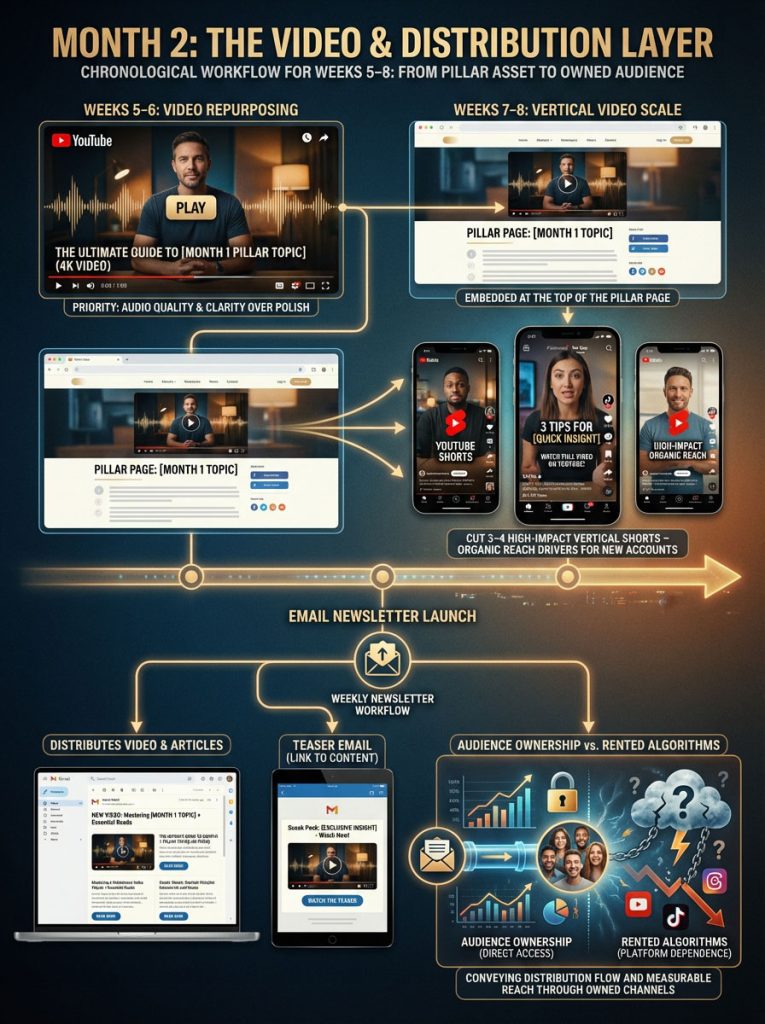
Week 5-6: Video Repurposing
Take your Pillar Asset from Month 1 and repurpose it. Record it as a YouTube video. Do not worry about perfection; worry about audio quality and clarity of information.
Week 7-8: Vertical Video Scale
Cut the highlights into 3-4 vertical shorts for TikTok and YouTube Shorts. These platforms offer massive organic reach for new accounts. Even if you have zero followers, a good Short can get thousands of views.
Email Newsletter Launch:
Launch a weekly newsletter. Use this to distribute your content directly to your audience. This owns the relationship, protecting you from algorithm changes. Send a “Teaser” email that links to your new video and articles.
Month 3: Optimization, Scale, and Paid Amplification
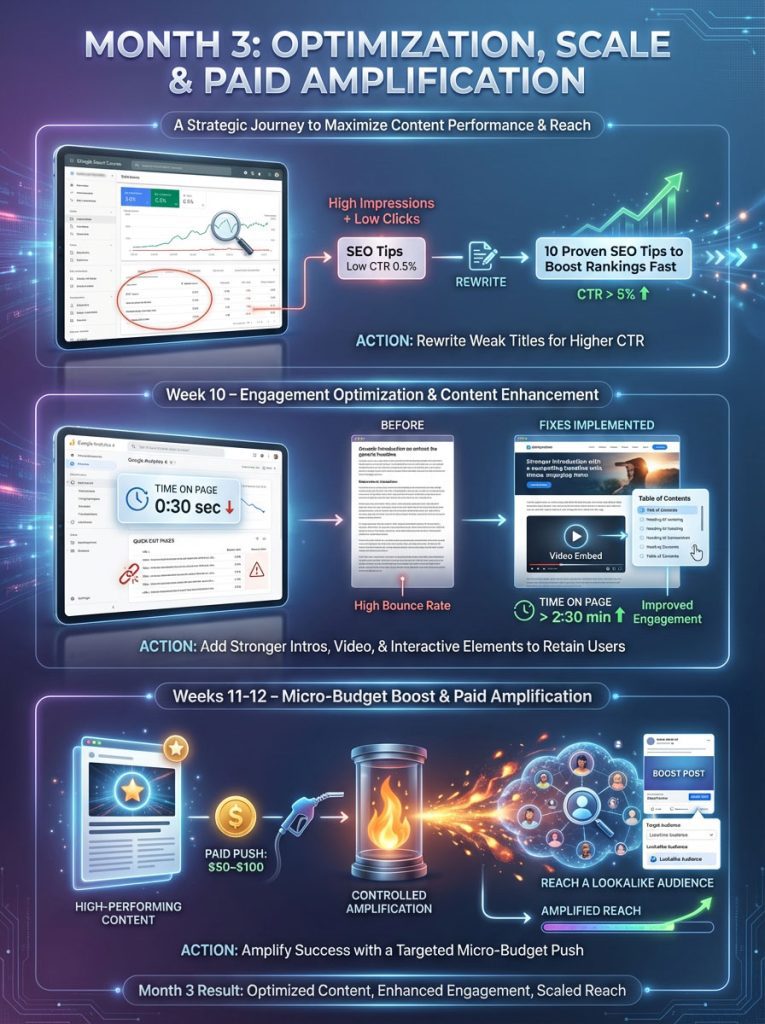
Week 9: Search Console Audit
Analyze your data in Google Search Console. Look for keywords where you have high impressions but low clicks. This means you are ranking, but your title isn’t enticing enough. Rewrite the titles for those pages to improve Click-Through Rate (CTR).
Week 10: Engagement Optimization
Look at “Time on Page” in GA4. If people are leaving a certain page quickly, rewrite the introduction. Add a video embed. Add a table of contents.
Week 11-12: The Micro-Budget Boost
Paid Boost. If one piece of content is performing exceptionally well organically, put a small budget (50−100) behind it to amplify reach to a lookalike audience. This is like pouring gasoline on a fire that is already burning.
Strategic Priority by Startup Stage
Your content marketing strategy for small business should evolve as you grow. A Seed stage company has different needs than a Series B company.
| Startup Stage | Primary Goal | Content Priority | Key Channels |
| Seed / Launch | Validation & Trust | Founder Stories, “Building in Public,” Problem-Aware Blogs. | LinkedIn, X (Twitter), Substack. |
| Growth (Series A) | Lead Generation | “Alternatives” Pages, In-depth “How-to” Guides, Webinars. | Organic Search (SEO), YouTube, Email. |
| Scale (Series B+) | Market Dominance | Original Data Reports, Brand Media, High-Production Video. | Multi-channel, PR, Paid Amplification. |
| Local SMB | Foot Traffic/Calls | Local SEO, Google Business Profile Updates, Community Stories. | Google Maps, Facebook, Instagram. |
Measuring Content ROI: Tracking KPIs and CAC for Small Businesses
You must move beyond vanity metrics. Likes and pageviews do not pay the bills. A robust content marketing plan for startups tracks business outcomes. You need to know if your effort is actually moving the needle on revenue.
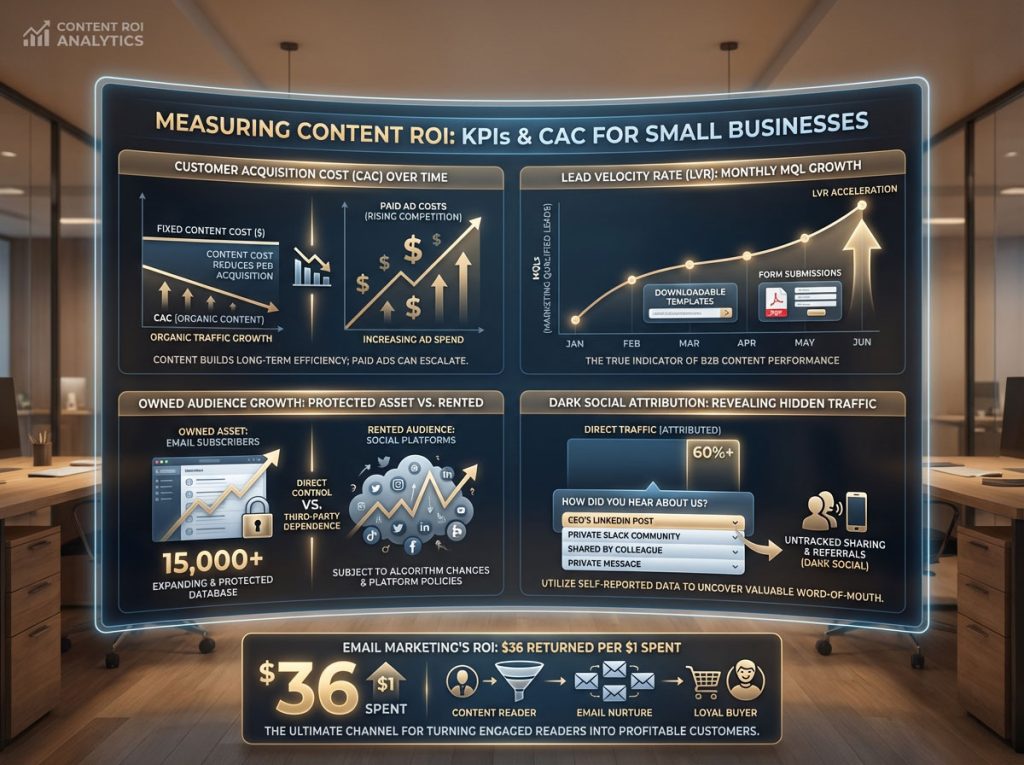
Critical KPIs for Tracking Content Performance
1. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC):
Content production is largely a fixed cost. You pay for the article once, but it drives traffic forever. As your organic traffic growth increases, the cost per visitor drops. Over time, your CAC should trend downward, unlike paid ads where it usually rises as competition increases.
2. Lead Velocity Rate (LVR):
Track the number of Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs) generated by your content each month. This is the true measure of whether your B2B content marketing is working. Are people filling out the form? Are they downloading the template?
3. Owned Audience Growth (Email List):
Social media platforms rent you an audience; email allows you to own it. Track the growth of your subscriber base. This is your insurance policy against platform changes.
4. Dark Social Attribution:
Much of content sharing happens in private channels—Slack DMs, WhatsApp, email forwards. Analytics software cannot track this; it shows up as “Direct” traffic. To measure this, add a simple field to your sign-up form: “How did you hear about us?” You will be surprised how many people say “Saw your CEO’s post on LinkedIn” or “A friend sent me your guide.”
The Multiplier Effect of Email Marketing
Email marketing remains the king of ROI for SMBs, generating approximately $36 for every $1 spent. It is the most efficient way to nurture leads captured by your content. It turns a “reader” into a “buyer” over time.
Summary & Key Takeaways
Building a content marketing plan for startups & small businesses is a game of patience and precision. It is not about shouting the loudest; it is about answering the best questions. It is about showing up consistently with value when your competitors are showing up with sales pitches.

Key Takeaways:
- Prioritize Commercial Intent: Ignore vanity volume. Focus on “Power Clusters” like comparisons and specific how-to guides that target buyers, not browsers.
- Embrace the Cyborg Model: Use AI for speed (research, outlining), but rely on human experience for authority and trust (drafting, storytelling).
- Video is Mandatory: Integrate video marketing strategy into your SEO efforts to capture modern search traffic and increase dwell time.
- Founder-Led Distribution: Use the founder’s personal brand to drive initial traction and trust. Be the face of your company until the brand is big enough to stand on its own.
By following this roadmap, you build an asset that works for you while you sleep, compounding your traffic and revenue for years to come. You move from being a renter of attention to an owner of authority.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the best content marketing strategy for startups in the US?
The most effective strategy combines Semantic SEO with Founder-Led distribution. It focuses on high-intent, bottom-of-funnel keywords (like “alternatives” or “comparisons”) to generate revenue early, rather than chasing broad traffic volume. It leverages the founder’s personal experience to build trust in a market skeptical of AI content.
How much does content marketing cost for a small business?
A lean content marketing plan for small businesses can be executed for 500
–500–
1,500 per month using a DIY approach. This covers tools like Ahrefs, hosting, and perhaps freelance editing support. Agency support typically starts at $3,000+ per month, which may be out of reach for seed-stage startups.
How long does it take for content marketing to work?
Generally, SEO efforts show compounding results in 12–18 months. However, by targeting low-competition, long-tail keywords (the “Power Clusters” mentioned above), a startup can begin seeing relevant organic traffic growth in as little as 3-4 months.
Is blogging still relevant for business in the age of AI?
Yes, but the style has changed. Generic blogs are obsolete. Deep, experience-based guides that establish Entity Authority and answer specific user questions are critical for ranking in Google. The blog post is no longer just text; it is a container for video, data, and tools.
How can small businesses measure the ROI of content marketing?
Calculate ROI by subtracting production costs from the revenue generated by content leads, then dividing by production costs. Use attribution in tools like Google Analytics 4 (GA4) or HubSpot to track which articles drive conversions. Do not forget to account for “Dark Social” by asking customers where they found you.
Should a small business hire a content marketing agency or do it in-house?
Early-stage startups (Seed/Series A) should often keep it in-house or founder-led to establish a unique voice. Agencies often struggle to replicate the nuanced expertise of a founder. Outsourcing to an agency is more effective once you have a proven playbook, a clear voice, and need to scale production volume.
What tools do startups use to manage a content marketing plan?
Essential tools include a CMS like WordPress or Webflow, SEO tools like Ahrefs or Semrush for research, optimization tools like SurferSEO or Clearscope, and AI assistants like ChatGPT or Claude for research and outlining.
How often should a startup publish blog posts?
Consistency beats frequency. Publishing one high-quality, comprehensive article every two weeks is far superior to publishing four thin, low-value posts per week. Google rewards depth and freshness, but depth is currently the stronger signal for new domains.
What is “Founder-Led” content and why does it matter?
It is a strategy where the founder actively shares insights and stories on social platforms. It matters because it builds “Personal Monopoly” and trust (E-E-A-T) that nameless corporate accounts cannot match. It humanizes the brand and creates an emotional connection with early adopters.
How do I choose the right topics for my startup blog?
Talk to your sales and support teams. The specific questions prospects ask during sales calls (e.g., “How does X compare to Y?” or “Can I do Z with this tool?”) are your highest-value blog topics. These questions represent real market demand.
What is the difference between “Content Strategy” and “Content Marketing”?
Content strategy is the “Why” and “How”—the planning, audience mapping, and goal setting. It is the architectural blueprint. Content marketing is the “What”—the creation, publishing, and distribution of the assets. It is the construction work. You need a strategy before you start marketing.
How does AI fit into a startup content workflow without hurting SEO?
AI should be used for research, outlining, and brainstorming, but not for the final draft. Google rewards unique human experience and insights, which pure AI content lacks. Using AI to assist the human writer is a force multiplier; using AI to replace the human writer is a race to the bottom.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional financial or business advice. Implementation of these strategies may vary based on your specific industry and market conditions.









