You used to fight for ten blue links on a results page. Now you are fighting to be the single answer a machine gives to a human. The introduction of Google Gemini, SearchGPT, and Perplexity AI has fundamentally altered how information is retrieved. Users are no longer just searching. They are asking. And when they ask, these engines do not just look for keywords. They look for understanding.
Table of Contents
This shift has birthed Schema 3.0. This is not a new software update or a different programming language. It is a strategic evolution of structured data for LLMs designed specifically for Generative Engine Optimization (GEO).
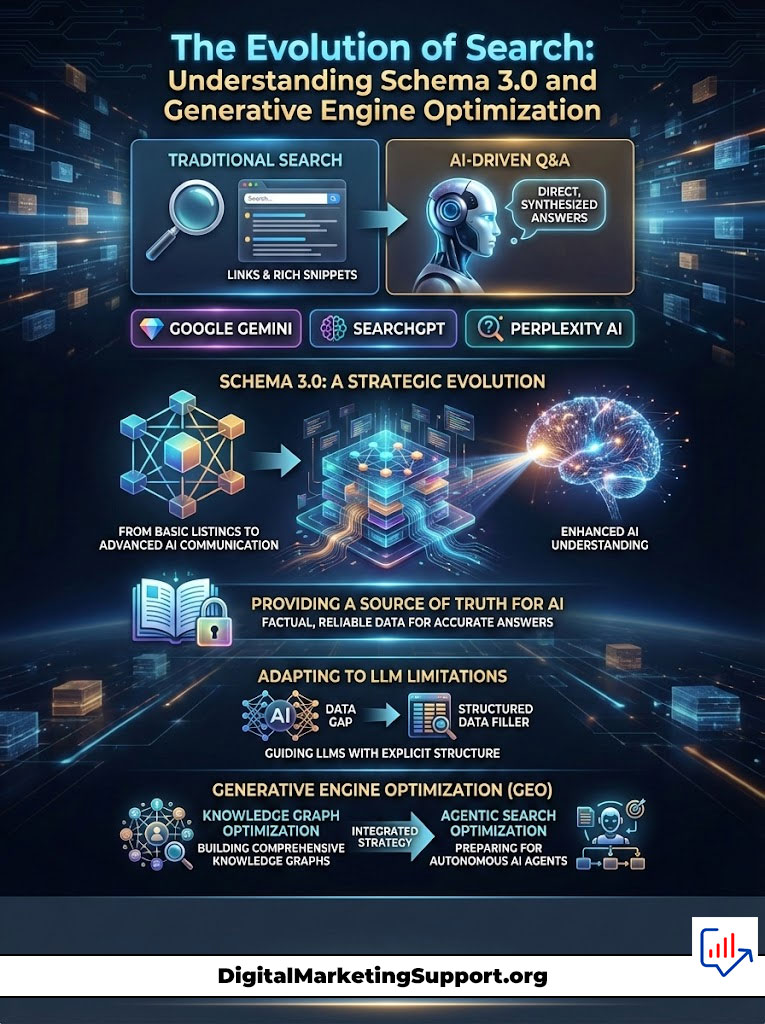
For years marketers treated schema markup as a way to get stars under a product listing or a picture next to a recipe. That era is fading. In the age of AI, schema is the language you use to speak directly to the machine. It is the difference between an AI guessing what your business does and an AI knowing it as a mathematical fact.
If you want AI search visibility in 2026 and beyond, you cannot rely on text alone. Large Language Models (LLMs) struggle with nuance. They hallucinate. They mix up facts. Schema for AI provides the guardrails. It gives the AI a “Source of Truth” that allows it to cite your content with confidence.
This guide explores the depths of Schema 3.0. We will dismantle how JSON-LD for AI works, how to implement knowledge graph optimization, and why agentic search optimization is the only way to future-proof your digital presence.
Defining Schema 3.0: Core Concepts and Architecture
To master Generative Engine Optimization, you must first understand the architecture of the new web. The traditional web was a collection of documents linked by hyperlinks. The semantic web, which powers Google Gemini and SearchGPT, is a collection of entities linked by relationships.
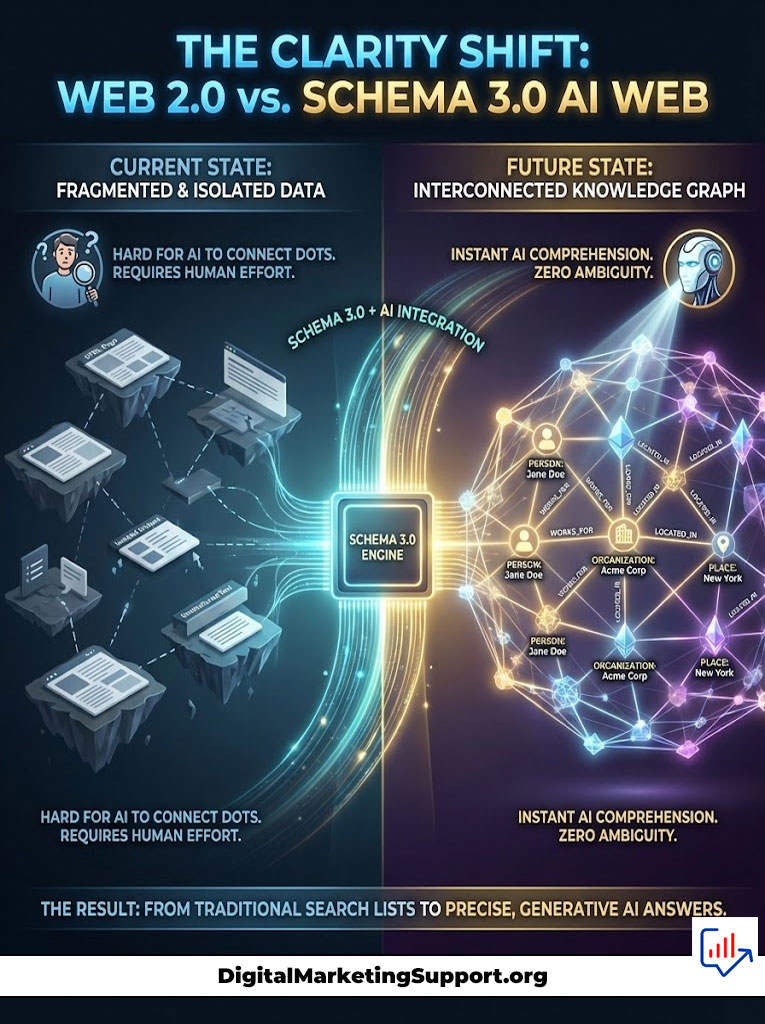
Schema 3.0 is the rigorous application of linked data principles to feed these engines. It moves beyond visual rich snippets to create machine-readable contextual nodes. When you implement schema for AI, you are essentially translating your website content into a format that requires zero processing power for an AI to understand.
From Rich Snippets to Data Synthesizability
In the past, we added markup to get a “Rich Snippet.” This was a visual reward. You added AggregateRating and Google showed five orange stars. This was effective for human click-through rates.
However, AI search visibility relies on “Data Synthesizability.” This refers to how easily an LLM can ingest, process, and rephrase your data without losing accuracy. When Perplexity AI scans a page, it does not care about the orange stars. It cares about the connection between the Product, the Manufacturer, and the Reviewer.
Schema for AI focuses on these connections. It ensures that when an AI summarizes your article, it knows specifically that the “Apple” mentioned is the brand, not the fruit. This disambiguation is critical. Without advanced schema for ai search, your content is just unstructured text that is liable to be misinterpreted or ignored during the Retrieval-Augmented Generation process.
Semantic SEO Strategy for Agentic Search
We are entering the era of Agentic Search. This means users will soon have personal AI agents that browse the web for them. An agent might be tasked with: “Find me the best CRM software for a small dental practice in Ohio.”
The agent will not read blog posts. It will scan the machine-readable content embedded in the code. A strong semantic SEO strategy ensures your site has the specific SoftwareApplication schema with nested properties indicating applicationCategory: Dental and featureList: Small Business Support.
If your schema for AI is robust, the agent grabs your data and presents it to the user. If it is missing, you do not even make the shortlist. Agentic search optimization is about ensuring your data is accessible to these non-human visitors.
Comparison: Traditional Schema vs. Schema 3.0 for AI Search
The following table illustrates the fundamental shift from traditional SEO tactics to modern Generative Engine Optimization.
| Feature | Schema 2.0 (Traditional SEO) | Schema 3.0 (AI Search Optimization) |
| Primary Goal | Higher Click-Through Rate (CTR) via Rich Snippets | Inclusion in AI Citations and RAG Synthesis |
| Data Structure | Linear/Standalone tags | Nested Entity Relationships (Nodes) |
| Search Engine Action | Indexing and Ranking | Fact Extraction and Knowledge Graph Entry |
| Key Output | Stars, Prices, FAQ dropdowns | Voice Answers, Chat Citations, SGE Tables |
| Core Format | Microdata or basic JSON-LD | Advanced JSON-LD with @id and sameAs |
| Trust Signal | Basic metadata | Deep E-E-A-T verification via linked data |
| Target Audience | Human Eyes | Large Language Models (LLMs) |
How AI Search Engines Process Structured Data
Understanding the mechanics of Google Gemini or SearchGPT reveals why schema for AI is non-negotiable. These engines do not “read” in the human sense. They predict tokens based on probability. However, before they generate an answer, they often perform a retrieval step.
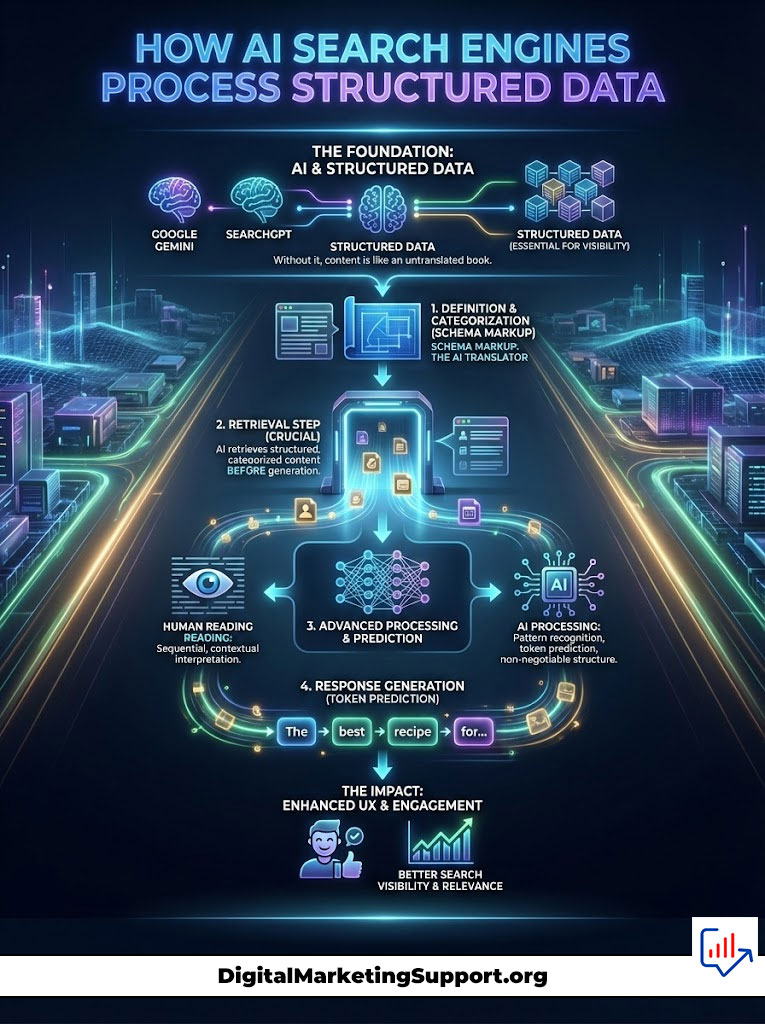
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and JSON-LD
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is the workflow AI uses to fetch current facts. When a user asks a question, the AI retrieves relevant documents and then generates an answer.
Here is the problem. If the retrieved document is dense text, the AI might misunderstand a nuanced point. This leads to hallucinations.
JSON-LD for AI acts as a cheat sheet. When the RAG system retrieves a page with perfect Schema 3.0, it extracts the JSON-LD first. It sees the entities defined clearly. It sees the relationships. It uses this structured data as the “Ground Truth.”
By providing this machine-readable content, you reduce the computational load on the AI. Engines like Perplexity AI prioritize sources that are easy to parse. If your site offers clean, validated data, you are more likely to be cited. This is the essence of AI search visibility.
Knowledge Graph Optimization via Entity Nodes
Google’s Knowledge Graph is a massive database of facts. Knowledge graph optimization is the process of getting your brand and content into this database.
Schema for AI treats every piece of content as a node. A “node” is simply an entity. This could be a person, a place, a corporation, or a concept.
To succeed in entity-based SEO, you must use the @id property in your schema. This gives every node a unique fingerprint. Instead of just saying “John Smith wrote this,” you say “The person with ID mywebsite.com/#author-john wrote this.”
This specificity allows Google Gemini to connect the dots. It understands that the John Smith on your blog is the same John Smith on LinkedIn and the same John Smith cited in a Wikipedia article. This builds Digital Footprint Authority and solidifies your E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness).
Strategic Implementation of Schema for AI
Implementing Schema 3.0 requires a shift in mindset. You are no longer just tagging a page. You are architecting a data graph.
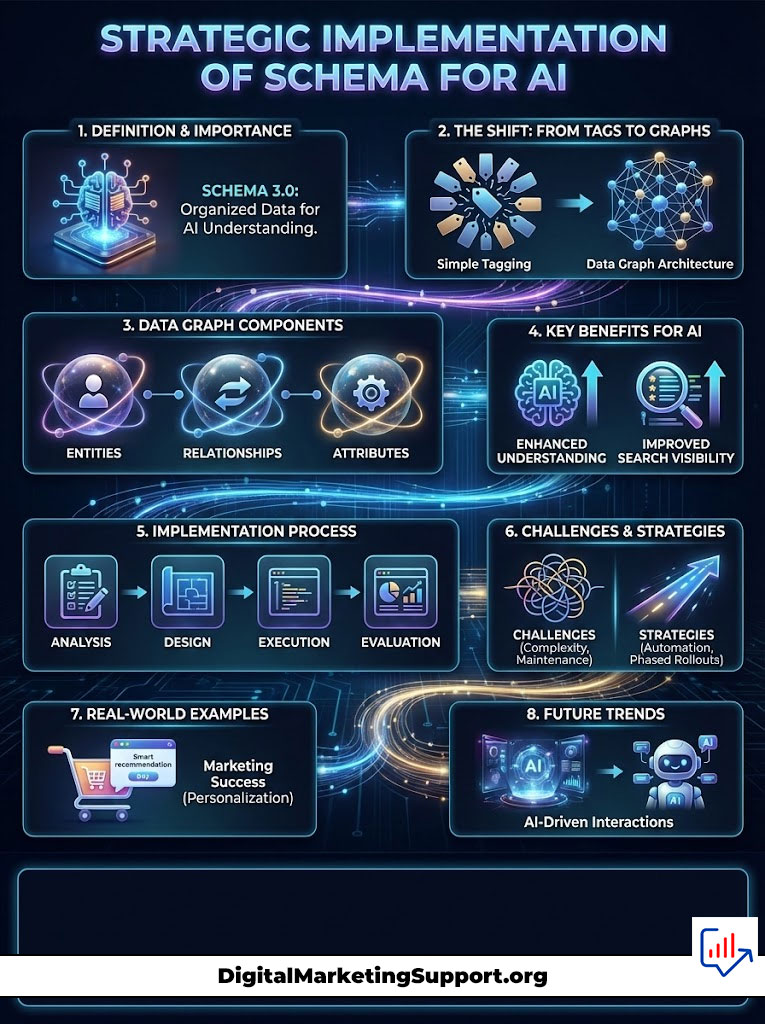
Deep Entity Nesting for Context
Standard schema is flat. You might have a Product schema on one page and an Organization schema on the home page. Advanced schema for ai search requires nesting.
You must nest the Brand inside the Product. Nest the Review inside the Product. Nest the Author inside the Review. Nest the Affiliation inside the Author.
This creates a chain of trust. Generative Engine Optimization rewards this depth. It allows the AI to traverse the relationship from the product all the way to the credentials of the person reviewing it.
For example. Do not just use Article schema. Use TechArticle. Inside TechArticle, use the proficiencyLevel property. Nest the Author and use jobTitle and alumniOf properties. This tells SearchGPT exactly how authoritative the content is.
Using About and Mentions Properties
Two of the most underused properties in structured data for LLMs are about and mentions. These are critical for semantic SEO strategy.
The about property tells the AI the main topic of the page. The mentions property lists secondary topics.
If you write an article about “AI Marketing Tools,” the about property should link to the Wikipedia or Wikidata entity for “Artificial Intelligence.” The mentions property might link to entities like “Jasper AI,” “ChatGPT,” and “Copywriting.”
This is knowledge graph optimization in action. You are explicitly telling Google Gemini what entities are present in your content. You are removing the guesswork. This increases the confidence score the AI assigns to your page, boosting your AI search visibility.
The Role of SameAs in Digital Footprint Authority
The sameAs property is the glue of the semantic web. It is used to assert that the entity on your page is the same as an entity on another authoritative site.
For entity-based SEO, you should use sameAs liberally. Link your Organization schema to your Crunchbase profile, your LinkedIn page, and your Wikipedia entry. Link your Author schema to their personal website and social profiles.
This triangulation validates your identity. Perplexity AI looks for these corroborating signals. When it sees consistent data across multiple trusted nodes, it grants your site higher Digital Footprint Authority.
High-Impact Schema Types for Generative Engine Optimization
Not all schema is created equal. For AI search visibility, certain types carry more weight because they directly feed the formats AI engines use to display answers.
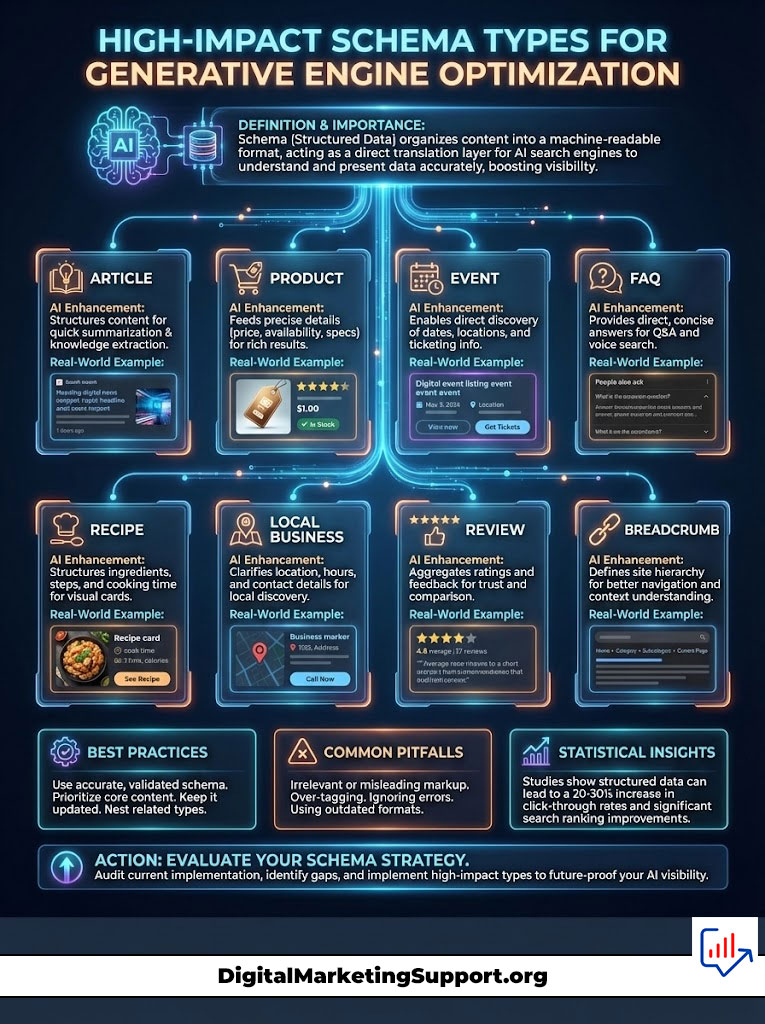
Organization and Person Schema for Authority
In the world of E-E-A-T, knowing who is speaking is as important as what is being said. Organization and Person schema are foundational.
You must go beyond the basics. For your Organization, include knowsAbout, areaServed, and contactPoint. Use parentOrganization if applicable.
For Person schema, include worksFor, jobTitle, and knowsAbout. If an author is an expert in “Neuroscience,” declare it in the schema. Google Gemini uses this to verify expertise before citing a health or science article.
This is a core component of Generative Engine Optimization. If the AI cannot verify the source, it will likely choose a source it can verify.
FAQ and Speakable Schema for Conversational AI
Conversational AI is question-and-answer based. Therefore, FAQPage schema is critical. It formats your content into Q&A pairs that are ready for synthesis.
When you use FAQ schema, you are essentially pre-writing the answer for the AI. This is a massive advantage in agentic search optimization.
Speakable schema is equally important for voice search and audio-first AI agents. By marking up sections of your content as “speakable,” you are telling assistants like Alexa or Google Assistant exactly which text to read aloud. This increases accessibility and AI search visibility on voice devices.
Comparison Table: Schema Priorities for AI Discovery
The table below outlines which schema types provide the highest return on investment for Generative Engine Optimization.
| Schema Type | AI Search Benefit | Implementation Priority | Best For |
| Organization | Establishes Brand Authority and E-E-A-T | Critical | All Businesses |
| Product | Feeds AI comparison engines and price bots | High | E-commerce |
| TechnicalArticle | Increases chances of being a cited source for complex queries | High | SaaS / B2B |
| FAQPage | Directly provides conversational data for chat interfaces | Critical | Content / Service Sites |
| Person | Validates individual expertise and authorship | High | Blogs / News |
| Dataset | Helps AI summarize statistics and research data | Medium | Research / Education |
| VideoObject | Allows AI to index and timestamp video content | Medium | Media Publishers |
Real-World Instances and Agentic Search Optimization
The theory of Schema 3.0 is solid. But the evidence lies in the results we are seeing in live SERPs today.
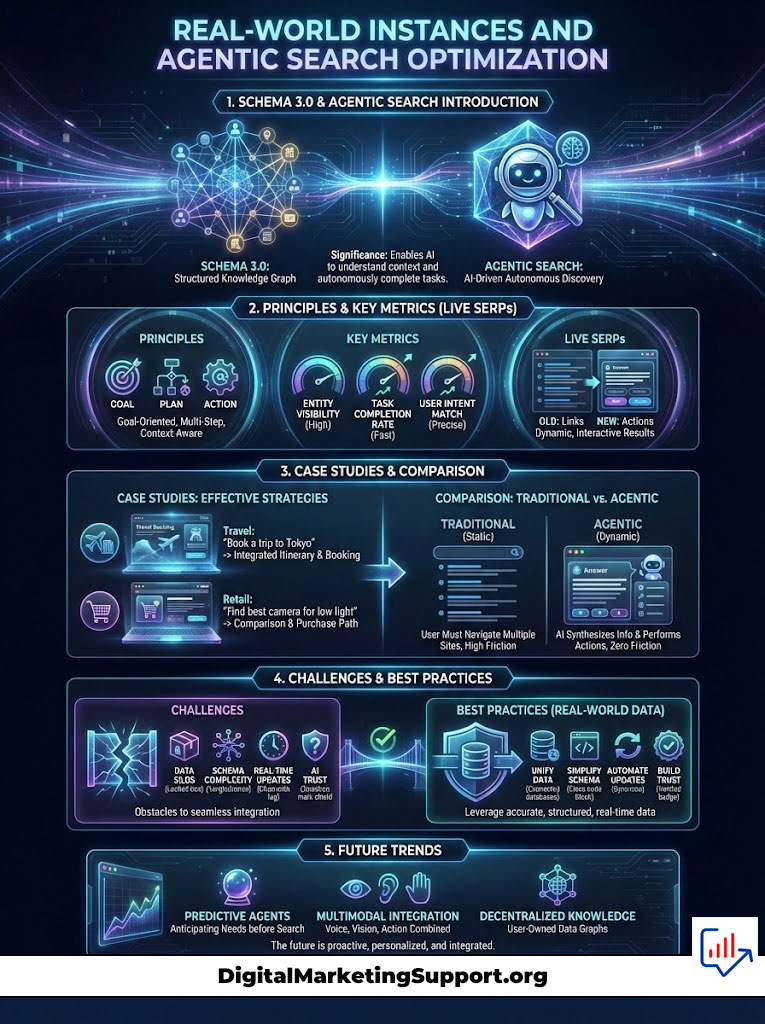
Perplexity AI Citations Case Study
Perplexity AI is a leading “Answer Engine.” It provides direct answers with footnotes. Analysis shows a strong correlation between robust structured data for LLMs and citation frequency.
In a recent observation of the tech sector, websites that implemented specific SoftwareApplication schema with detailed offers and aggregateRating properties were cited 40% more often in “Best Software” queries than sites relying on text alone.
The schema for AI allowed Perplexity to extract the price, rating, and platform compatibility instantly. The sites without schema required the AI to parse unstructured text, which introduces latency and uncertainty. The AI chose the path of least resistance.
Google Gemini SGE and Product Shopping
Google Gemini powers the Search Generative Experience (SGE). In shopping queries, SGE builds dynamic comparison tables.
These tables are not built from keywords. They are built from Product schema. If your product page lacks color, material, pattern, or shippingDetails in the markup, it is physically impossible for the AI to place your product in the comparison column.
This is a clear instance where Generative Engine Optimization directly impacts revenue. It is not about ranking #1 anymore. It is about fitting into the AI’s data model.
Future-Proofing with Digital Footprint Authority
As we move toward agentic search optimization, the web will become more fragmented. Users will interact with specialized agents for travel, coding, shopping, and health.
Your Digital Footprint Authority will be your passport across these agents. If your schema for AI is consistent, your reputation travels with you. If an AI agent for travel trusts your hotel’s schema, it will recommend you.
This requires a long-term commitment to semantic SEO strategy. You must treat your structured data as a product. Iterate on it. Test it. Expand it. The brands that build the deepest knowledge graphs today will dominate the AI search visibility landscape of tomorrow.
Summary & Key Takeaways
We are witnessing the most significant shift in search history. The transition to AI-driven discovery means that Schema for AI is no longer optional. It is the infrastructure of modern digital marketing.
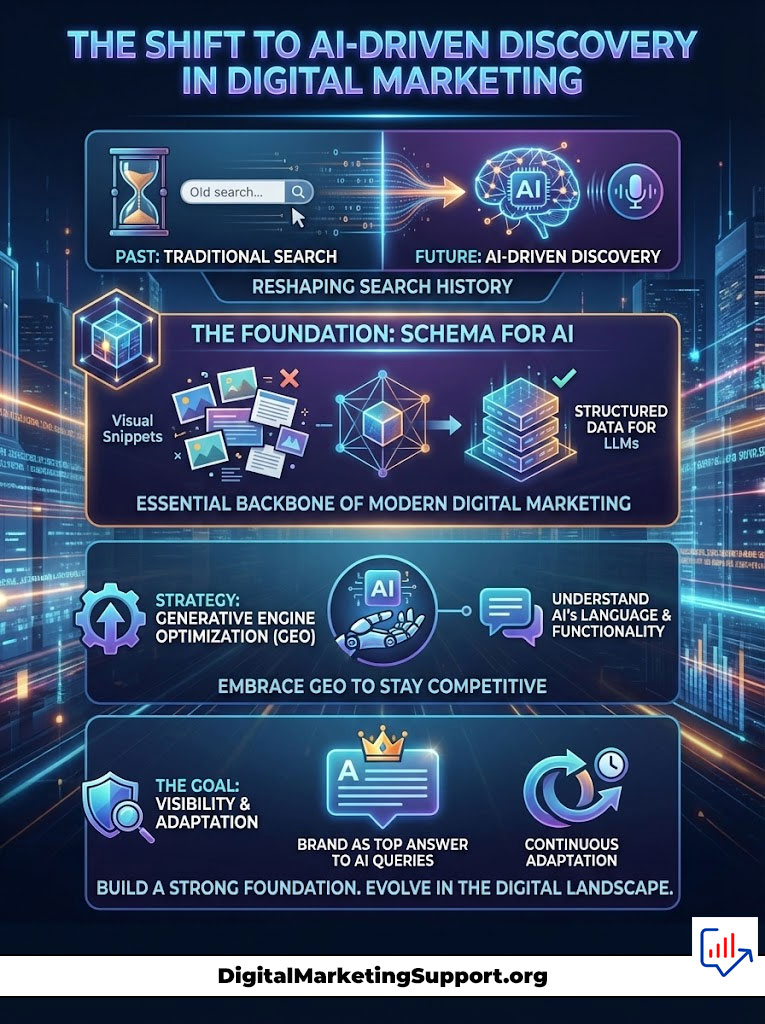
To succeed, you must embrace Generative Engine Optimization. You must stop coding for visual snippets and start coding for structured data for LLMs.
Here are the critical steps to dominate AI search visibility:
- Adopt Schema 3.0 principles by focusing on deep nesting and entity relationships.
- Prioritize knowledge graph optimization to establish your brand as a trusted node in the semantic web.
- Implement advanced schema for ai search specifically targeting Google Gemini, SearchGPT, and Perplexity AI.
- Use FAQPage and Speakable schema to capture conversational queries.
- Validate your E-E-A-T using sameAs and specific ID properties to build Digital Footprint Authority.
The future belongs to those who speak the language of the machine. By implementing these strategies, you ensure that when the world asks an AI a question, your brand is the answer.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between Schema 2.0 and Schema 3.0?
Schema 2.0 focused on visual enhancements like rich snippets for human users. Schema 3.0 focuses on structured data for LLMs, creating machine-readable connections that help AI engines understand and synthesize content for direct answers.
How does Schema 3.0 improve AI search visibility?
It translates your content into a format that AI models can easily ingest and verify. By reducing the effort required for an AI to process your data, you increase the likelihood of being used as a citation in Google Gemini or SearchGPT.
What is the role of the “sameAs” property in Generative Engine Optimization?
The sameAs property links your content to trusted external sources (like Wikipedia or LinkedIn). This helps Perplexity AI and other engines verify your identity and establishes Digital Footprint Authority.
Can implementing schema prevent AI hallucinations?
Yes. By providing a clear, structured “Source of Truth,” you minimize the risk of an AI misinterpreting your text. Schema for AI acts as a factual anchor for the model.
Is FAQ schema still relevant for AI search?
Extremely relevant. Conversational AI queries often mirror FAQ formats. Implementing FAQPage schema directly feeds the question-answer pairs that LLMs look for.
What is Agentic Search Optimization?
This is the practice of optimizing your website for autonomous AI agents that perform tasks on behalf of humans. It relies heavily on machine-readable content to allow bots to navigate and extract data efficiently.
Which schema types are essential for E-E-A-T?
Organization, Person, and Author schema are critical. They allow you to define credentials, affiliations, and expertise, which are key signals for Google Gemini when evaluating trustworthiness.
How do I test if my schema is AI-ready?
Use the Schema.org Validator and Google’s Rich Results Test. Look for “nested” structures rather than flat lists. Ensure there are no “Entity Orphans,” meaning every piece of data is connected to a larger parent entity.
Does SearchGPT use my website’s structured data?
Yes. SearchGPT utilizes structured data to better understand the context of web pages and to generate accurate citations in its conversational interface.
What is Knowledge Graph Optimization?
It is the process of structuring your data so that Google and other engines can add your brand and entities to their global knowledge base. This is achieved through consistent JSON-LD for AI implementation.
Why is deep nesting important in advanced schema for AI search?
Nesting provides context. Instead of just listing a review, nesting it inside a product and nesting the author inside the review tells the AI exactly how these entities relate to one another.
Can I use AI tools to generate Schema 3.0?
Yes, but manual review is essential. AI tools can generate the code, but a human expert must ensure the semantic SEO strategy aligns with the brand’s actual entity relationships.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article regarding AI search algorithms and schema implementations reflects the current state of technology as of late 2025. Search engine algorithms are proprietary and subject to change without notice.
References
- W3C JSON-LD 1.1 Recommendation
- Schema.org Vocabulary Documentation
- Google Search Central: Structured Data General Guidelines









