Google deletes apps from Play Store repositories primarily to protect the Android ecosystem from dangerous malware infections like the Anatsa banking trojan, enforce strict “Minimum Functionality” policies, and purge dormant developer accounts. If an app disappears from your device, you can often restore deleted Android apps via your library history. For software that has been permanently banned, the safest solutions involve sideloading verified APKs from APKMirror or utilizing privacy-focused alternatives like Aurora Store and F-Droid.
Table of Contents
Why Google Deletes Apps From Play Store
You unlock your smartphone to open a PDF scanner or a trusted banking tool you have used for years only to find it missing from your home screen. You search the store but the results come up empty. It is not a glitch. It is a calculated purge.

Every year Google deletes apps from Play Store databases by the millions. In a single recent sweep over 2.3 million applications were removed or blocked from entering the ecosystem entirely. For the average American user this sudden removal feels like a violation of digital ownership. You paid for it or you downloaded it so why is it gone?
The reality is that the Google Play Store is a “walled garden” governed by an automated sheriff known as Google Play Protect. While its primary goal is to stop dangerous code like the Anatsa banking trojan Android users fear the net is often cast so wide that legitimate tools abandonware and indie projects get caught in the crossfire.
This guide provides a forensic analysis of why apps removed from Google Play Store vanish and serves as a technical manual for getting them back. We will move beyond basic troubleshooting and delve into advanced recovery tactics using APKMirror and Aurora Store.
The Scale of the Google Play Store Purge and Automated Defense
To understand how to recover your software you must first understand the mechanism of deletion. Google operates the largest app repository on earth scanning over 125 billion installed apps every single day. When Google deletes apps from Play Store listings it is rarely a human decision. It is an algorithmic one.
The ecosystem is designed to be open but the Play Store is a private business under immense pressure from regulatory bodies and cybersecurity firms to maintain hygiene. Reports from security giants like Zscaler and Malwarebytes often trigger massive ban waves. When these firms identify a cluster of apps containing malware Google does not just delist them. In severe cases Google Play Protect blocked apps are forcibly uninstalled from your device remotely to prevent data theft. This automated defense system is necessary but it is also aggressive often deleting apps that were safe yesterday but flagged today due to a policy change.
Understanding the Minimum Functionality Policy and App Abandonment
Not every deleted app is a virus. Thousands of apps removed from Google Play Store every month are victims of the “Minimum Functionality” policy. Google requires that an app provide a stable and engaging user experience to remain listed.
If an app crashes frequently offers no utility or simply loads a website inside a frame these are known as “web wrapper” or “webview” apps it is flagged for removal. This is why many simple flashlight apps or basic “tips and tricks” guides disappear overnight. They are viewed as spam that clogs the search algorithms. Furthermore apps that do not function as promised or lack basic interactivity are purged to ensure that the store remains a repository of quality software rather than a dumping ground for low-effort code.
How Dormant Developer Accounts Trigger Mass Removals
Recently Google introduced strict requirements for developer identity verification. To combat spam networks Google now deletes developer accounts that have been inactive for over one year. If a developer fails to verify their identity with legal documentation or does not update their apps to target the latest Android API levels such as Android 14 or 15 the entire account is terminated.
Consequently every app associated with that account is wiped from the store leaving users with broken links and missing tools. This is particularly devastating for “abandonware” classic games or utilities that still work perfectly but whose creators have moved on. These apps are not dangerous but they are casualties of Google’s push for modernization.
Security Threats That Cause Apps Removed From Google Play Store
The most urgent reason Google deletes apps from Play Store is the presence of active threats. Understanding these specific entities helps you decide if you should even try to restore deleted Android apps or if you dodged a digital bullet.

The Anatsa Banking Trojan Android Infection Risks
The Anatsa banking trojan Android ecosystem has faced is one of the most sophisticated malware strains in recent history. Security researchers at Zscaler identified Anatsa hiding in seemingly innocent PDF readers and QR code scanners.
Once installed Anatsa does not attack immediately. It waits. Later it downloads a malicious payload and requests “Accessibility Services” permissions. If granted it can overlay fake login screens on top of legitimate banking apps like JPMorgan Wells Fargo or Schwab to steal credentials. Google aggressively deletes these apps but they often rack up thousands of downloads before detection. If your app was removed due to Anatsa you must check your bank statements immediately.
Identifying Joker Malware Apps and Fleeceware Subscriptions
Another frequent offender is Joker malware apps. Unlike Anatsa which steals credentials Joker is “fleeceware.” It quietly subscribes users to premium SMS services or WAP billing subscriptions in the background. You might not notice the app is malicious until you see unauthorized charges on your phone bill.
Google’s machine learning algorithms are constantly hunting Joker variants leading to the sudden disappearance of calculators photo editors and translators. These apps often employ “clooting” or masking techniques where they function normally for weeks before activating the malicious billing code making them difficult for automated scanners to catch during the initial review process.
The Harly Trojan and Dropper Techniques in Utility Apps
The Harly trojan operates similarly to Joker but uses a technique called “dropping.” The app you download from the store is clean. However upon first launch it decrypts and drops a malicious file hidden within its own resources. Because the initial download is clean it often bypasses initial Google Play Protect scans. When Google catches up the ban is immediate and permanent. These trojans are often found in video downloaders and custom keyboard apps.
Comparison of Google Play Violation Types
| Violation Type | Description | Consequence | Recovery Recommended? |
| Malware (High Risk) | Contains Anatsa, Joker, or Harly code. Steals money/data. | Immediate ban; remote deletion from user devices. | NO. Do not restore. |
| Policy Violation | Ad fraud, misleading metadata, or copyright issues. | Removal from Store; account strike. | Yes (If verified safe). |
| Dormancy | Developer inactive for 1+ years; outdated API level. | Hidden from search; “Not Compatible” error. | Yes (Safe via sideloading). |
| Minimum Functionality | App crashes or offers zero utility (Spam). | Removal from Store. | Yes (If you found it useful). |
How to Restore Deleted Android Apps Using Verified Methods
If you have determined that your missing app was likely removed for policy or dormancy reasons rather than malware you can proceed with recovery. Here are the most effective methods to restore deleted Android apps.

Recover Deleted Apps via the Official Google Play Library History
Many users do not realize that apps removed from Google Play Store search results often remain in their personal history. Google distinguishes between “Unpublished” which are hidden from new users and “Suspended” which are banned completely. If an app is merely unpublished you can often reinstall it directly.
- Open the Google Play Store on your device.
- Tap your Profile Icon in the top right corner.
- Select Manage Apps & Device.
- Tap the Manage tab.
- Change the filter button usually labeled “Installed” to “Not Installed”.
- Sort by “Name” or “Recently Added” to find the missing app.
- If the cloud icon is present tap it to reinstall.
This method is the safest first step because it relies on Google’s own servers. If the app appears here it means Google has deemed it safe enough for existing users to keep even if they do not want new users downloading it.
Sideload Android Apps Safely Using the APKMirror Repository
When an app is fully banned it vanishes from your library entirely. The solution is “sideloading” which means installing the app manually using an APK file. However downloading APKs from random websites is dangerous and exposes you to the very malware Google is trying to stop. You must use a verified repository.
APKMirror is the industry standard for safety. Unlike other sites APKMirror verifies the cryptographic signature of every file uploaded. They ensure the signature matches the original key from the developer. If the keys do not match indicating tampering they reject the file.
Step-by-Step Recovery:
- Navigate to APKMirror.com using your mobile browser.
- Search for the name of your deleted app.
- Look for the “Verified Safe” shield badge next to the download.
- Scroll to “All versions” and download the latest available APK.
- Open the file. Android will warn you that the browser is not allowed to install apps.
- Tap “Settings” on the prompt and toggle “Allow from this source.”
- Proceed with the installation.
This method allows you to bypass the Play Store entirely while maintaining a chain of trust regarding the software’s integrity.
Fix “This App Is No Longer Compatible With Your Device” Errors
Sometimes an app is not deleted but is hidden because your phone is “too new.” Google hides apps that do not target the latest Android API levels. To fix this you need a store client that bypasses these checks such as the Aurora Store. By using Aurora Store you can often force the installation of older apps that the official Play Store claims are incompatible with your device.
Using the Wayback Machine to Locate Missing Package Names
If you cannot remember the exact name of the app or if it was a niche tool use the Internet Archive. Search Google for “site:play.google.com” followed by a description of the app. Find the broken Play Store link in the search results. Copy the URL and paste it into the Wayback Machine. Retrieve the “Package Name” the ID in the URL usually looking like com.developer.appname. Search that specific package name on APKMirror or other archives to find the file. This digital forensics approach is often the only way to recover obscure utilities.
Safe Play Store Alternatives for Unrestricted Access
Relying solely on the Play Store means you are at the mercy of Google’s algorithms. To prevent future data loss you should diversify your sources. There are several safe Play Store alternatives that offer better privacy and stability.

Aurora Store vs Play Store: Anonymous Downloading Explained
Aurora Store is an open-source client that connects directly to Google’s servers. It allows you to download legitimate Play Store apps without signing into a Google account.
- Privacy: It strips away the tracking associated with your Google ID.
- Utility: It allows you to spoof your device info and location. This is excellent for accessing region-locked apps or apps that Google deletes apps from Play Store in specific countries due to local censorship.
- Spoofing: You can trick Google into thinking you are using a different device allowing you to download apps marked as “incompatible.”
F-Droid Safe Repositories for Open Source Utilities
If Google deletes apps from Play Store due to ad fraud or tracking violations the best replacement is often found on F-Droid.
F-Droid is a repository exclusively for Free and Open Source Software (FOSS). Every app on F-Droid is compiled from source code by the maintainers ensuring there are no hidden trackers no Joker malware apps and no proprietary analytics. It is the safest place to find utilities like calculators file managers and QR scanners. Unlike the Play Store F-Droid prioritizes user freedom and privacy over commercial interests.
How to Install Progressive Web Apps (PWA) on Android
For services like Twitter (X) Uber or Starbucks you do not actually need the store app. You can install a Progressive Web App (PWA).
- Open the website in Chrome or Firefox.
- Tap the three-dot menu.
- Select “Add to Home Screen” or “Install App.”
- This creates an icon that functions exactly like an app but bypasses the store entirely.
Google cannot delete a website from your phone. This method is completely resilient to app store bans and ensures you always have access to the service regardless of store policies.
Comparison of App Store Ecosystems
| Store Name | Best Use Case | Security Model | Privacy Score | Account Required? |
| Aurora Store | Anonymous access to Play Store library. | Google Server Data + Spoofing. | High | No |
| F-Droid | Replacing utilities with safe FOSS tools. | Source Code Audit. | Very High | No |
| APKMirror | Restoring older/deleted versions. | Signature Verification. | Medium | No |
| Samsung Store | Galaxy-exclusive apps and fonts. | Samsung Verification. | Low | Yes |
Preventing Data Loss When Google Play Protect Blocked Apps
Once you step outside the Play Store you must take responsibility for your own security. Sideload android apps safely by following these protocols.
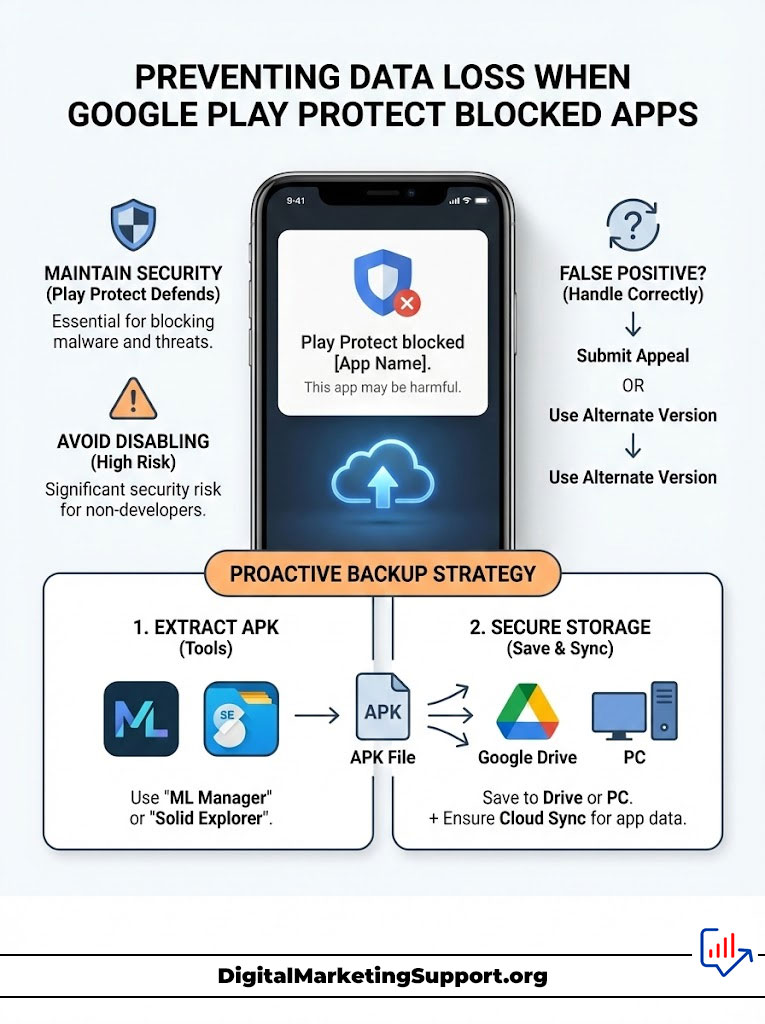
Configuring Play Protect Settings Without Compromising Security
Even if you use third-party stores Google Play Protect continues to run on your device. It scans every app you install regardless of where it came from.
Do Not Disable It: Unless you are a developer testing specific code keep Play Protect enabled. It acts as a final line of defense against Anatsa banking trojan Android infections.
The False Positive Problem: Occasionally Google Play Protect blocked apps are legitimate. If Play Protect keeps deleting a safe app you sideloaded you can submit an appeal to Google but the faster fix is often to use a different version of the app from APKMirror.
Backing Up APK Files Before They Vanish
Do not wait for a purge to save your data. Proactive users create their own archives.
APK Extraction: Use a tool like “ML Manager” or “Solid Explorer” to extract the APK files of your favorite installed apps. Save these files to Google Drive or a PC. If Google deletes apps from Play Store you have your own backup ready to reinstall.
Data Backup: For non-rooted users app data settings and game saves is hard to backup if the app is removed. However ensuring you are logged into the app’s own cloud sync if available is critical.
The Impact of Developer Identity Verification on App Availability
It is important to note that not all apps removed from Google Play Store are malicious. The developer identity verification process has caused chaos for indie developers.

Google now requires personal home addresses and phone numbers from developers. Many privacy-conscious coders refuse to provide this leading to their apps being purged. Additionally the “Association Ban” is a dreaded event where Google bans a developer simply because they are associated with another banned account e.g. sharing the same laptop or Wi-Fi network.
Understanding this helps users realize that a deleted app is not always dangerous sometimes it is just a casualty of corporate bureaucracy. These developers often migrate to F-Droid or host their APKs on GitHub making it essential for users to learn how to sideload to follow their favorite creators.
Summary & Key Takeaways
The disappearance of your software is not a random event it is a calculated action by Google to manage its massive ecosystem. While the removal of Anatsa banking trojan Android threats and Joker malware apps is necessary for safety the collateral damage often includes useful legitimate tools.

To navigate this landscape in 2026 you must adopt a “Plan B” mindset:
- Check the Library: Always look in “Manage Apps > Not Installed” first.
- Verify Then Sideload: If the app is gone use APKMirror to sideload android apps safely. Never use unverified APK sites.
- Embrace Alternatives: Use Aurora Store for anonymous access and F-Droid for tracker-free utilities.
- Stay Alert: If an app is removed search online to see if it was flagged for malware like Anatsa. If it was do not try to restore it.
By diversifying how you access applications you ensure that no single corporate decision can wipe out your digital toolkit.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Frequently Asked Questions
Why did Google delete my paid app from Play Store?
Google removes paid apps for the same reasons as free ones policy violations malware or developer bans. Unfortunately removal does not automatically trigger a refund. You must request a refund manually via your account’s “Budget & history” section though Google typically denies requests for apps purchased more than 48 hours ago.
Is it safe to keep using an app that Google removed?
It depends entirely on the reason for removal. If Google Play Protect blocked apps due to malware like Anatsa or Joker you must uninstall it immediately. However if the app was removed for business policy reasons like Fortnite or developer dormancy it is generally safe to keep using it though it will stop receiving security updates.
How do I install apps blocked by Google Play Protect?
If you are certain a file is safe a false positive you can bypass the block by opening the Play Store tapping your Profile Icon selecting Play Protect tapping the Settings gear and toggling off “Scan apps with Play Protect.” Warning This leaves you vulnerable to real malware re-enable it immediately after installation.
Can I get a refund for an app removed from the Play Store?
If the app ceases to work because it was removed you have grounds for a refund. If the automated refund system denies you contact Google Support directly and cite “item defective or doesn’t work as advertised” as the reason.
Is APKMirror safe to use for banking apps?
While APKMirror is technically safe because it verifies signatures it is highly discouraged to sideload banking apps. Financial institutions often check the installation source. If they detect the app was not installed via the Play Store the banking app may refuse to run for security reasons.
What is the difference between disabling an app and deleting it?
Disabling is for pre-installed system apps bloatware that cannot be removed. Deleting removes the app data and code entirely. When Google deletes apps from Play Store it does not delete them from your phone unless they are dangerous malware.
How do I find the name of a deleted app I forgot?
Go to Google Takeout and export your “Google Play Store” data. This will provide a list of every app you have ever installed including the package names of deleted apps which you can then search for on APKMirror.
Does factory resetting restore deleted Play Store apps?
No. A factory reset returns the phone to its out-of-the-box state. It will only restore the bloatware and system apps that came with the phone. Apps that Google deletes apps from Play Store servers will not reappear.
Why is Aurora Store better than the Play Store?
Aurora Store offers privacy. It allows you to download the same apps from the same Google servers but without linking your activity to your personal Google identity. It also helps bypass regional restrictions.
What is the Anatsa banking trojan?
Anatsa also known as TeaBot is a malware strain that targets Android banking apps. It overlays fake login screens to steal passwords and intercepts SMS codes to bypass Two-Factor Authentication.
How to fix “This app is no longer compatible with your device”?
This error usually means the developer has not updated the app for your Android version. You can bypass this by downloading the APK from APKMirror and installing it manually as the operating system is often backward compatible even if the Store restricts it.
Will my app data be lost if Google removes the app?
If the app remains on your phone your data is safe. If Google remotely uninstalls the app rare only for severe malware the data is deleted. If you uninstall the app yourself to reinstall it via sideloading you will lose your data unless you have backed it up externally.
Disclaimer
This guide is for educational purposes only. Sideloading applications carries inherent risks. The author and publisher are not responsible for any data loss malware infections or financial damages resulting from the installation of apps outside the Google Play Store. Always verify sources and proceed with caution.
References
- Zscaler ThreatLabz. Technical Analysis of Anatsa Banking Trojan Campaigns.
- Malwarebytes Labs. State of Mobile Malware: The Rise of Fleeceware.
- Google Play Policy Center. Enforcement Process and Developer Requirements.









