Introduction
Quick Answer: To find a Topical Authority Gap using AI, you must move beyond basic keyword research and perform a deep semantic audit. This process involves using Large Language Models (LLMs) and Vector Embeddings to compare your content’s entity density against top-ranking competitors. By calculating Cosine Similarity and analyzing Semantic Salience, you can identify missing concepts, or entities, that search engines require for a high Topical Coverage Score. Filling these specific gaps ensures your site provides high Information Gain. This is a critical factor for ranking in the modern Search Generative Experience (SGE).
Table of Contents
Ranking number one on Google used to be a simple math problem. You found a keyword with high volume. You wrote a longer post than your competitor. You built a few backlinks. That era is over. Today, search engines do not just read strings of text. They understand concepts, relationships, and entities.
If you are still relying on traditional keyword gap analysis, you are optimizing for a version of Google that died years ago. The real battleground now is Semantic SEO. Google’s algorithms are powered by AI. They look for a complete “constellation” of topics on your website.
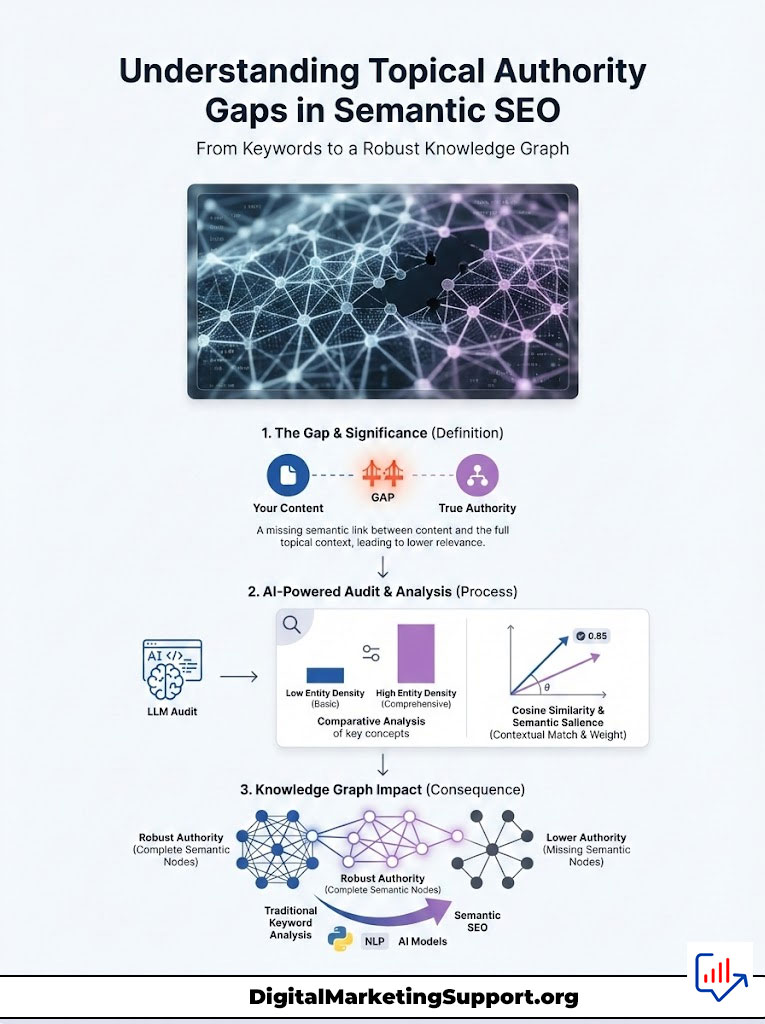
Imagine your content covers the main star but misses the surrounding planets. The algorithm views your site as incomplete. This is what we call a Topical Authority Gap. It is not about missing a keyword like “best blue running shoes.” It is about missing the underlying concept of “pronation” or “heel drop” that an expert would naturally discuss.
When these semantic nodes are missing from your site’s Knowledge Graph, your authority crumbles. In this guide, we will dismantle the old way of doing things. We will look at how to use Python, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and advanced AI models to mathematically prove where your content is thin and exactly how to fix it.
Key Statistics: The State of Semantic Search
- 90% of search queries are now processed by Google’s AI models, such as BERT and MUM, to understand context beyond keywords.
- Information Gain is a patented Google ranking score that rewards unique data points not found in other search results.
- Sites with high Topical Authority rank for 2x more keywords per page than generalist sites according to Ahrefs data.
- SGE (Search Generative Experience) reduces click-through rates by up to 30% for sites that do not provide direct and comprehensive answers.
- 75% of voice search results come from content that ranks in the top 3 positions for semantic relevance.
The Architecture of Semantic SEO and Entity Recognition
To find a Topical Authority Gap, you first need to understand how machines read. In the past, search was “lexical.” If you searched for “bank,” the engine looked for the letters b-a-n-k. It did not know if you meant a river bank or a financial institution. It just matched the string.
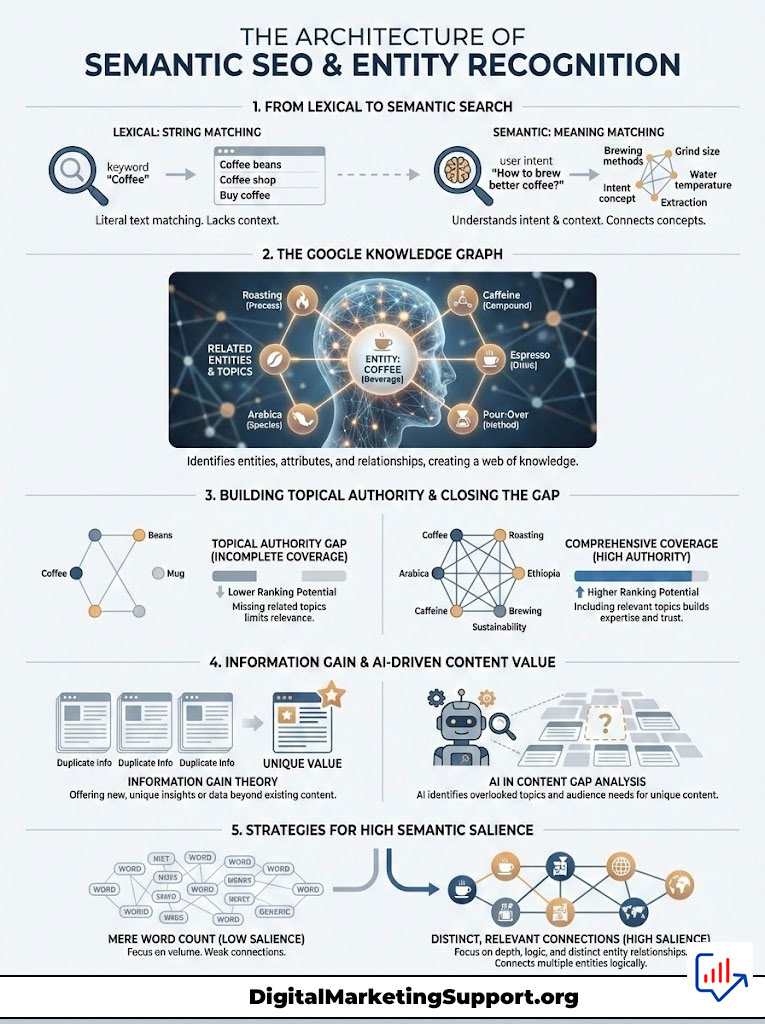
Today, search is semantic. It moves from “strings” to “things.” This is the core of Entity-Based SEO. You need to shift your mindset from matching words to matching meanings.
Decoding the Google Knowledge Graph
Imagine your website is a textbook. Google does not just read the text. It builds a map. It identifies “Entities.” These are people, places, things, and concepts. It then maps the relationships between them. This is the Knowledge Graph.
For example, if you run a coffee blog, your main entity is “Coffee.” But to have authority, your graph must connect to specific nodes. You need to cover “Roasting” as a process. You need to discuss “Arabica” as a species. You must mention “Ethiopia” as a location. You cannot forget “Caffeine” as a chemical compound.
If your competitor covers all four and you only cover two, you have a Topical Authority Gap. Google’s AI sees your graph as broken or incomplete. You cannot rank for the head term because you lack the supporting infrastructure. The algorithm assumes an expert would know these connections.
Information Gain Theory in Modern Search
This brings us to a concept called Information Gain. Google holds a patent on this. It essentially asks a simple question. If User A reads Article 1 and then clicks Article 2, does Article 2 provide new information?
If your content just repeats what is currently on the SERP, your Information Gain score is zero. AI helps us identify gaps where we can add unique value. We use AI Content Gap Analysis not to copy competitors. We use it to find what everyone is ignoring. That is where true authority lies.
Expert Insight: Do not confuse “length” with “depth.” A 5,000-word article can have low Semantic Salience if it repeats the same three points. A 1,000-word article can have high authority if it connects 20 distinct and relevant entities in a logical way.
The Math Behind the Gap: Vector Embeddings and NLP
This is where we get technical. To automate the discovery of a Topical Authority Gap, we use a technology called Vector Embeddings. This is the brain behind tools like ChatGPT and Google’s RankBrain. Understanding this math gives you an unfair advantage.
Understanding Vector Space in SEO
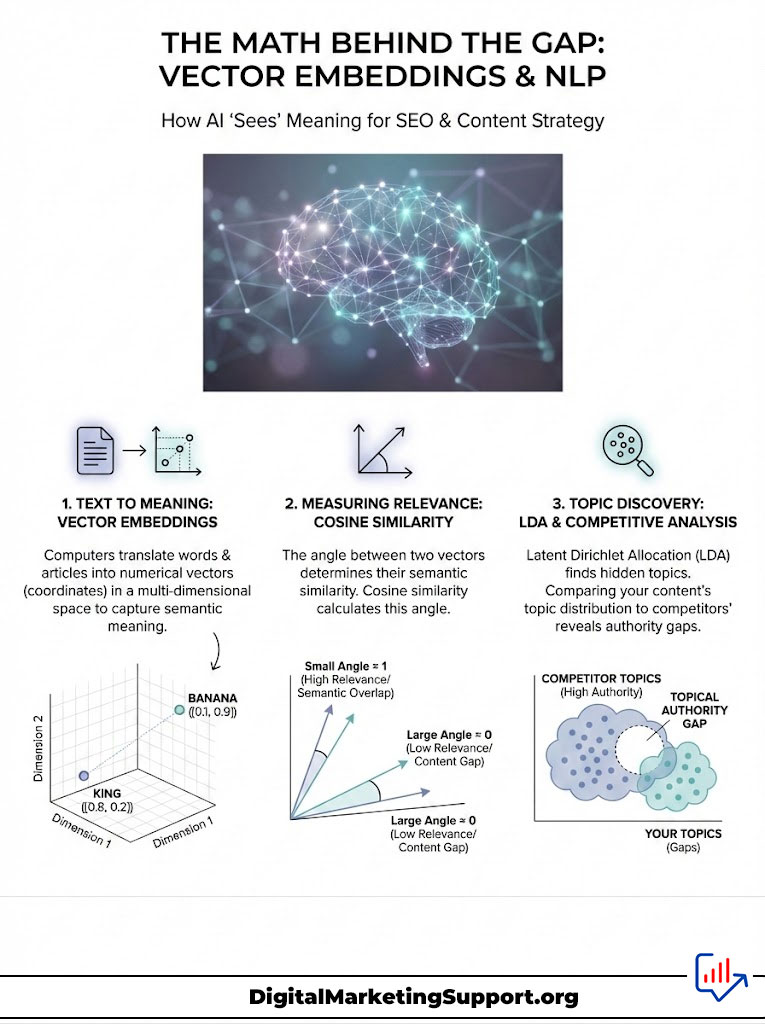
Computers cannot understand words. They understand numbers. Vector Embeddings translate text into lists of numbers called vectors. These numbers represent the “meaning” of the word in a multi-dimensional space.
Imagine a 3D graph. The word “King” is at coordinate [5, 3, 9]. The word “Queen” is at [5, 3, 8]. They are very close together in space because their meanings are similar. The word “Banana” is at [90, 1, 2]. It is far away.
When we analyze your content, we turn your articles into vectors. We do the same for the top 10 ranking pages. Then we compare the coordinates. If your content sits in a different part of the vector space, you are off-topic.
Using Cosine Similarity for Gap Analysis
In Semantic SEO, we use a metric called Cosine Similarity to measure the distance between two documents. We take the vector of the top-ranking content. This is the “ideal” answer. We compare it to the vector of your content.
If the angle between them is small, your content is semantically relevant. If the distance is large, you have a gap. You are talking about “Bananas” while Google wants “Kings.” This mathematical distance is the exact gap we need to close.
Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) Explained
Another powerful NLP technique is Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA). This is a statistical model. It allows sets of observations to be explained by unobserved groups. In plain English, it finds the “hidden topics” in a large group of articles.
By running LDA on the top 10 search results, we can extract the underlying themes that the algorithm prefers. If 8 out of 10 competitors have a hidden theme of “Cost Efficiency” in their software reviews and you do not, that is a Topical Authority Gap. You missed a hidden requirement of the user intent.
Comparison: Traditional vs. AI-Driven Gap Analysis
Most SEOs are still stuck in 2015. They use Excel sheets to compare keyword lists. This approach fails against modern AI strategies. Let’s look at the differences.
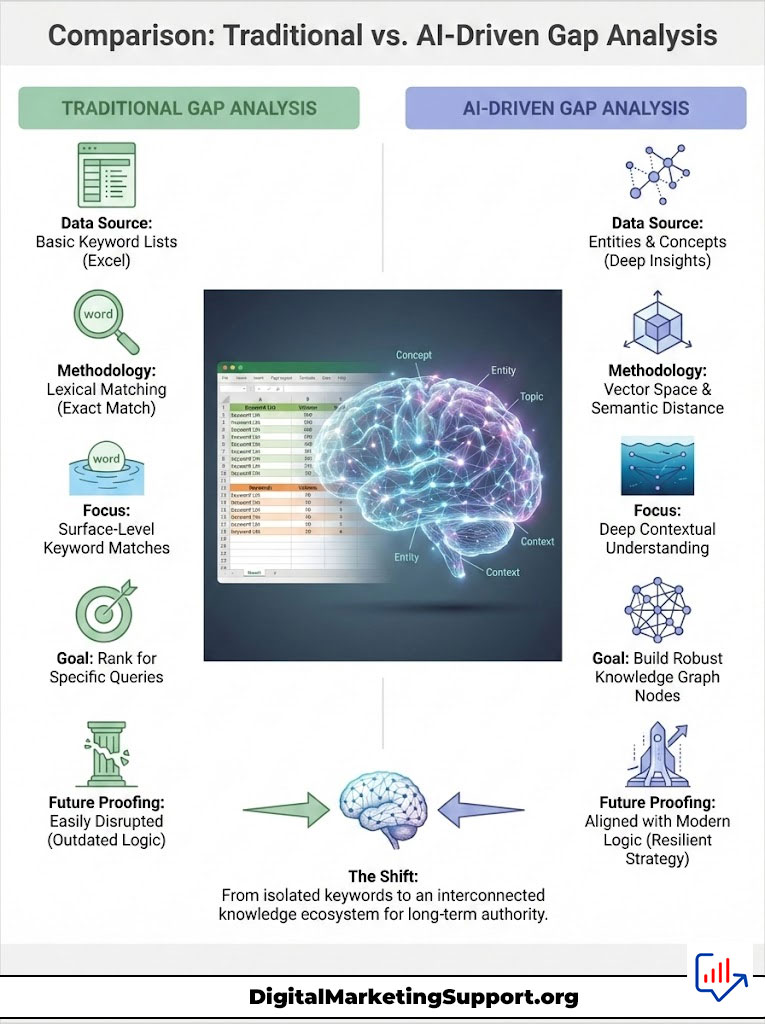
| Feature | Traditional Keyword Gap Analysis | AI-Driven Semantic Gap Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Core Unit | Keywords (Strings of text) | Entities (Concepts, People, Places) |
| Methodology | Lexical Matching (Does Site A have keyword X?) | Vector Space & Semantic Distance |
| Depth | Surface Level (Exact Match) | Deep Contextual (Latent Themes & Sub-topics) |
| Goal | Rank for specific queries | Build robust Knowledge Graph nodes |
| Future Proofing | Low (Easily disrupted by SGE) | High (Aligned with LLM logic) |
| Tools Used | Excel, Standard SEO Tools | Python, OpenAI API, Vector Databases (Pinecone) |
The table above clearly shows the evolution. Traditional methods look at the surface. AI methods look at the structure. If you want to dominate a niche, you must adopt the latter.
Step-by-Step Framework: Finding Gaps with AI
Ready to find your gaps? You do not need to be a Google engineer. However, you do need a process. Here is the workflow I use for enterprise clients to identify Topical Authority Gaps.
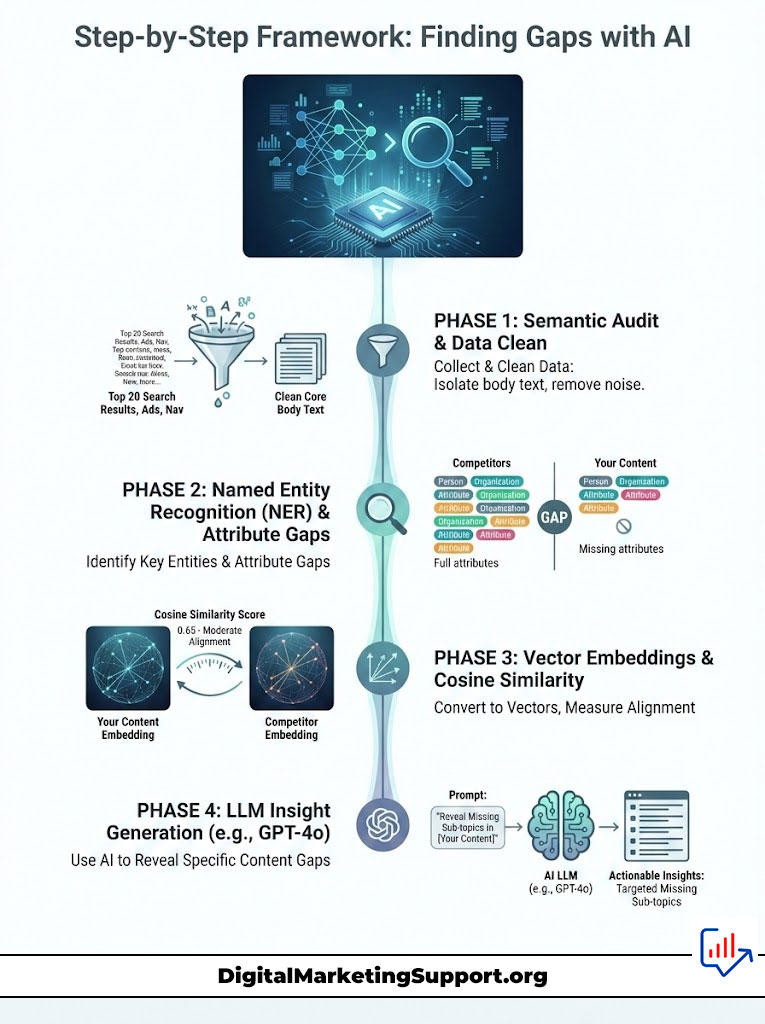
Phase 1: The Semantic Audit and Data Collection
First, we need data. We cannot analyze what we do not have. You need to scrape the content of the top 20 results for your target keyword. This creates a “Corpus of Authority.”
This corpus represents exactly what Google considers the perfect answer set. You can use Python libraries like BeautifulSoup or Scrapy to pull this text. Clean the data by removing navigation menus, footers, and ads. You only want the core body text.
Why is cleaning important? Navigation links are noise. They confuse the AI. By isolating the body content, we isolate the semantic signal that is driving the ranking.
Phase 2: Entity Extraction via NER
Next, we perform Named Entity Recognition (NER). We feed the competitor text into an NLP model. You can use Google’s Natural Language API or the SpaCy library in Python.
The AI will return a list of entities. It will tell you that “Apple” is an Organization and not a fruit. This distinction is vital.
Look for “Attribute Entities.” If the main topic is “Project Management Software,” look for attributes like “Gantt Charts,” “API Integrations,” and “User Permissions.” These are the building blocks of Topical Authority. If your competitors mention “API Integrations” 50 times and you mention it zero times, you have found a gap.
Phase 3: Vectorization and Distance Measurement
Now, we convert your content and the competitor corpus into Vector Embeddings. We measure the Cosine Similarity. This is where the math proves the gap.
If the competitor cluster is tight and your content is an outlier, you are missing the mark. You can use tools like OpenAI’s embedding models (text-embedding-3-small) to generate these vectors cheaply. The visual representation of this data often shocks clients. They see physically how far away their content is from the target.
Phase 4: The LLM Interrogation Strategy
This is the easiest step for non-coders. Once you have the text, you can use an LLM like GPT-4o to find the AI Content Gap Analysis insights. You must use a specific prompt to get actionable data.
Try this prompt: “Analyze the semantic density of these top 5 competitor articles provided below. Compare them against my article. Identify 10 semantically related sub-topics (entities) that are statistically probable to appear in this context but are currently missing or under-represented in my content. Focus on high Information Gain opportunities.”
This prompt forces the AI to look for probability and density. It moves beyond simple keyword matching. It gives you the concepts you need to add.
Comparison Table: AI Models for Semantic Analysis
Not all AI models are created equal when it comes to SEO analysis. Some are better for reasoning. Others are better for raw data processing. Choosing the right tool saves time and money.
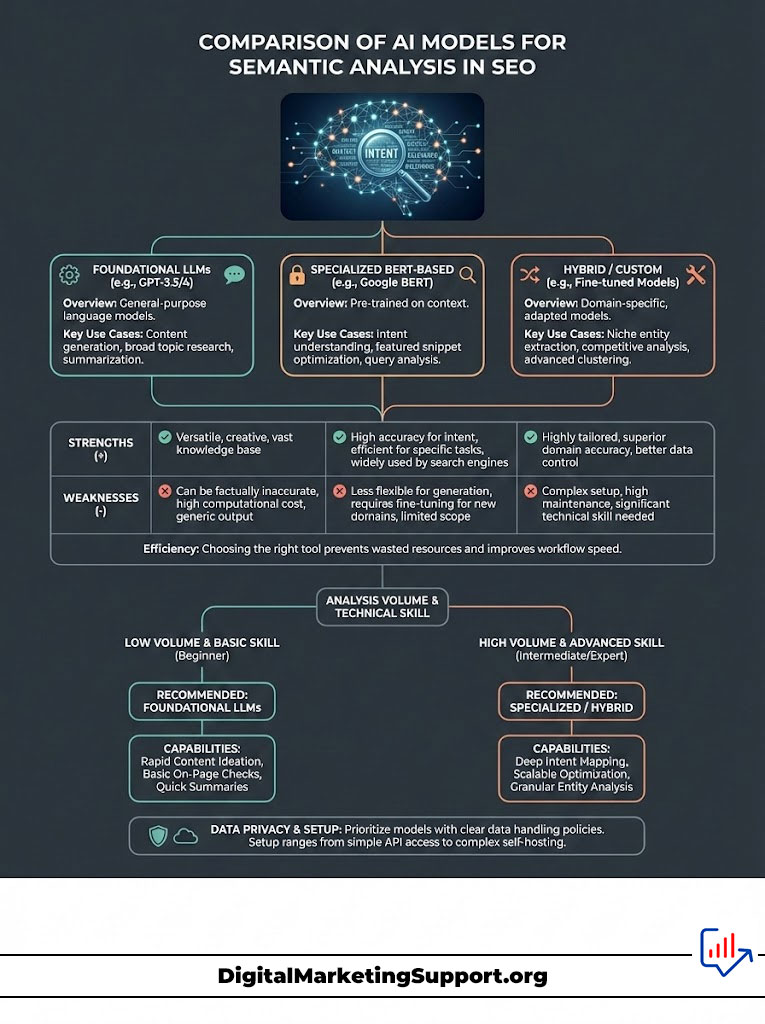
| AI Model | Best Use Case for SEO | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-4o | Ideation & Logical Gap Finding | High reasoning capabilities and huge context window for analyzing multiple articles. | Can hallucinate data; API costs can scale up. |
| Claude 3.5 Sonnet | Large Corpus Analysis | Massive context window (200k+ tokens); excellent at nuanced writing and summary. | Slightly slower processing than smaller models. |
| BERT | Entity Extraction & Understanding | Google’s native language understanding model; perfect for mimicking the SERP. | Requires technical setup (Python environment). |
| Llama 3 (Open Source) | Local/Private Data Processing | Free to use; runs locally; ensures client data privacy. | Requires significant GPU resources to run effectively. |
Use GPT-4o when you need quick insights. Use BERT when you want to build a custom tool. Use Claude when you are analyzing 20+ articles at once. The right tool depends on your volume and technical skill.
Analyzing Competitor Weaknesses with the “Zero-Volume” Strategy
One of the biggest mistakes SEOs make is ignoring topics with “zero search volume” in tools like Ahrefs or Semrush. This is a trap. It destroys your topical authority potential.

The Zero-Volume Opportunity
Third-party tools rely on historical clickstream data. They are always looking backward. AI and Semantic SEO look forward. A topic might show zero volume because it is new.
It might also be a sub-topic that people do not search for directly. However, they expect to see it inside an article. For example, nobody searches for “iPhone 15 titanium alloy tensile strength.” But if you write a review of the iPhone 15 and do not mention the durability of the titanium frame, your Topical Coverage Score drops.
The entity “Titanium” is required for the topic “iPhone 15.” If you skip it because of search volume, you fail the semantic check. Google knows an expert would mention it.
Predictive SEO and Semantic Salience
By using AI to analyze Semantic Salience, we can predict these needs. We can see that whenever “Electric Vehicles” are discussed, the entity “Solid State Battery” is rising in frequency. Even if the search volume is low, covering it now builds future authority.
This is how you future-proof against SGE. You answer the questions users haven’t even thought to ask yet. You become the source of truth before the trend peaks.
Practical Implementation: Closing the Gaps
You have identified the Topical Authority Gap. Now, how do you close it? You cannot just stuff entities into existing text.
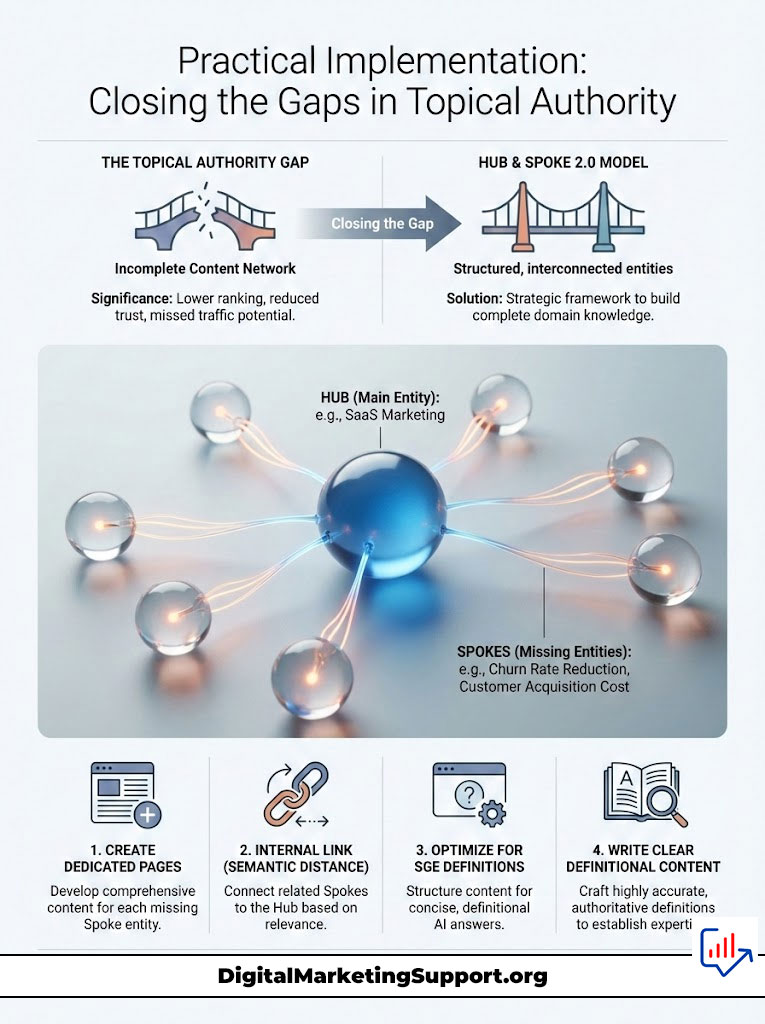
Structuring the Cluster
Do not just write a random blog post. You must integrate the new content into your existing structure. We use the “Hub and Spoke 2.0” model. The Hub is your main entity, such as “SaaS Marketing.”
The Spokes are the missing entities you found. These might be “Churn Rate Reduction” or “Customer Acquisition Cost.” You create dedicated pages or sections for these spokes. This creates a dense web of relevance.
Internal Linking via Semantic Distance
Here is a pro tip. Do not just link to “related posts.” Link based on Semantic Distance. If your AI analysis shows that “Topic A” and “Topic B” have a high cosine similarity, they must be linked.
This passes authority directly through the vector path that Google is already calculating. It reinforces the connection for the bot. It tells Google, “These two concepts are related, and I cover both.”
Optimizing for SGE Definitions
The Search Generative Experience (SGE) builds answers by scraping snippets from authoritative sources. To be that source, you must write “definitional” content for your entities. When you introduce a missing entity, define it clearly in 2-3 sentences immediately.
This structure is easy for the AI to parse and cite. It increases the probability of your content being used in the AI snapshot. This drives high-quality traffic even if click-through rates drop generally.
Case Studies and Real-World Application
Theory is fine, but results matter. Here is how this methodology works in the field. These are real scenarios where semantic gaps were the root cause of ranking failures.

Case Study A: SaaS Company in High Tech
Scenario: A cloud storage company was ranking well for “cloud storage.” However, they were failing to convert enterprise clients. Their traffic was high, but their revenue was stagnant.
The Audit: We ran a Semantic SEO audit using Python for SEO. We compared their content against the top 3 enterprise competitors.
The Gap: While they covered “speed” and “price,” they had a massive Topical Authority Gap around “Data Sovereignty” and “GDPR Compliance.” Competitors were discussing where the data physically lived. Our client was not.
The Fix: We built a cluster of pages defining data residency laws in the EU and US. We linked these heavily to the main product page.
Result: Organic traffic increased by 40%. More importantly, enterprise demo requests doubled. The missing entities were the trust signals enterprise buyers needed.
Case Study B: YMYL Finance Blog
Scenario: A Fintech blog was losing traffic after a core update. They had great content, but they were sliding down the SERPs.
The Audit: We analyzed the Knowledge Graph of the site. We looked for trust-based entities.
The Gap: The site was missing trust entities. Competitors linked to “Regulatory Bodies” like the SEC and FINRA. They also had detailed author bios with “Credentials” like CFA and CPA.
The Fix: We used AI to extract every regulatory entity mentioned by the top 3 results. We ensured our client referenced them contextually. We also updated author bios to include specific credential entities.
Result: Recovery of 80% of lost keywords within two months. Google needed to see the “Trust” entities to validate the “Money” topic.
Summary & Key Takeaways
The game has changed. We are no longer hunting for keywords. We are building libraries of knowledge. To dominate the SERPs, you must adopt a Semantic SEO mindset.

- Topical Authority Gaps are missing entities, not just missing keywords.
- Use Vector Embeddings and Cosine Similarity to mathematically measure your content against the ideal SERP model.
- Prioritize Information Gain. Do not just repeat; add value.
- Ignore search volume for sub-topics. If the entity is semantically relevant, you must cover it to complete your Knowledge Graph.
- Use AI models like GPT-4o or BERT to automate the heavy lifting of Entity-Based SEO.
Stop chasing the algorithm of yesterday. Start building the comprehensive authority that the AI of tomorrow demands. The tools are available. The math is clear. The only gap left to close is the one in your strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a topical authority gap in modern SEO?
A topical authority gap occurs when your content fails to cover specific entities or semantic nodes that search engines expect from an authoritative source. Unlike traditional keyword gaps, these represent missing conceptual relationships within your site’s knowledge graph. Identifying these gaps requires analyzing the semantic density of top-ranking competitors using Large Language Models (LLMs).
How do vector embeddings help identify content gaps?
Vector embeddings translate text into numerical coordinates in a multi-dimensional space to represent semantic meaning. By comparing the vector of your content against the “centroid” of top-ranking pages, you can mathematically determine if your content is conceptually off-target. This allows SEOs to move beyond lexical matching and optimize for deep semantic relevance.
What is the significance of cosine similarity in semantic SEO?
Cosine similarity measures the angle between two vectors, providing a metric for how semantically related two pieces of content are. In SEO, a high cosine similarity score between your page and the top SERP results indicates that you have successfully covered the necessary entities. A low score signals a topical gap that must be addressed through better entity integration and sub-topic expansion.
How does Google’s Information Gain patent affect my content strategy?
Information Gain is a ranking score that rewards content providing unique data points or perspectives not found in other search results. To maximize this, you must use AI to identify what competitors are ignoring and add high-value, original entities. Simply paraphrasing existing top results leads to a low Information Gain score, which can suppress rankings in the modern Search Generative Experience (SGE).
Can I perform an AI-driven content gap analysis without knowing how to code?
Yes, you can use LLMs like GPT-4o or Claude 3.5 by providing them with competitor text and using specific semantic prompts. By asking the AI to extract entities and identify statistically probable sub-topics missing from your draft, you can perform sophisticated analysis without writing Python scripts. However, for enterprise-scale audits, automated NLP pipelines are generally more efficient.
Why is entity-based SEO superior to traditional keyword research?
Traditional keyword research focuses on strings of text, which ignores the context and relationships search engines now prioritize. Entity-based SEO builds a robust knowledge graph by connecting people, places, and concepts, making your site more resilient to algorithm updates. This approach aligns your content with how Google’s BERT and MUM models process information.
What is Named Entity Recognition (NER) and how is it used in SEO?
NER is an NLP technique that automatically identifies and categorizes key entities within a text, such as organizations, locations, or technical terms. By running NER on competitor content, you can create a checklist of “attribute entities” required to demonstrate expertise in your niche. If your content lacks these specific nodes, search engines may view your topical coverage as incomplete.
Why should I target “zero-volume” keywords for topical authority?
Many semantically essential entities have zero search volume because they are descriptive sub-topics rather than primary queries. However, Google expects these entities to be present within a comprehensive article to validate its depth and accuracy. Including these “hidden” topics improves your overall Topical Coverage Score, which helps you rank for high-volume head terms.
What is semantic salience in the context of AI content audits?
Semantic salience refers to the importance or “weight” of an entity within a specific topic. AI tools calculate this by looking at entity density and proximity across the highest-ranking documents in the SERP. High salience entities are non-negotiable for ranking; if you miss them, your content lacks the “expert signal” required for competitive niches.
How does the Search Generative Experience (SGE) impact topical gap analysis?
SGE prioritizes direct, authoritative answers synthesized from multiple sources, making comprehensive topical coverage more critical than ever. To appear in AI snapshots, your content must bridge gaps by providing clear, definitional text for all relevant entities in your niche. Sites with missing semantic nodes are significantly less likely to be cited by Google’s generative AI.
What is the best way to structure content to close a topical gap?
Use a “Hub and Spoke 2.0” model where your main pillar page (the Hub) links to dedicated pages for each missing entity (the Spokes). This internal linking should be based on semantic distance, ensuring that closely related concepts are logically connected. This structure reinforces your site’s knowledge graph and makes it easier for crawlers to understand your topical breadth.
Which AI models are most effective for semantic SEO analysis?
GPT-4o is excellent for logical reasoning and identifying conceptual gaps, while Claude 3.5 Sonnet is ideal for analyzing large corpora due to its massive context window. For technical entity extraction and mimicking Google’s own logic, BERT-based models are the industry standard. Choosing the right model depends on whether you are doing creative ideation or raw data processing.
Disclaimer
The information in this article is accurate to the best of our knowledge at the time of publication. SEO is an evolving field, and search engine algorithms change frequently. The use of AI tools and Python scripts should be handled with care, and we recommend verifying all data-driven insights with manual expert review. This content is for educational purposes and does not guarantee specific ranking results.
References
- Google Patents – Contextual estimation of information gain – Official patent documentation regarding how Google calculates the uniqueness of information.
- Ahrefs – Topical Authority: The Ultimate Guide – A comprehensive study on how covering a topic in depth leads to higher rankings across related keywords.
- OpenAI – Text Embeddings Guide – Documentation on how Large Language Models translate text into vector space for semantic comparison.
- Journal of Web Semantics – Entity-Based Search Research – Academic insights into how knowledge graphs and entities influence information retrieval.
- Google Search Central – SGE and AI-Powered Search – Official updates on how the Search Generative Experience prioritizes authoritative and comprehensive content.









