The era of chasing blue links is over. We have entered a new phase of information retrieval where the search engine does not just index the web; it reads, understands, and synthesizes it. For digital marketers and business owners in the USA, the goal is no longer just to rank number one. The goal is to be the primary source for the answer engine. This guide provides a definitive, deep-dive blueprint into AI Overviews SEO and the strategies required to survive the transition to Generative Engine Optimization.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Google AI Overviews SEO Landscape in the AI Era
The introduction of Google Gemini into the core search infrastructure has fundamentally altered the mechanism of organic traffic. Traditional search engines functioned like a library index. They pointed users to a book. The modern Google Gemini search ranking system functions like a research librarian. It reads the books for the user and provides a direct summary. This shift from retrieval to synthesis is built on a framework known as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
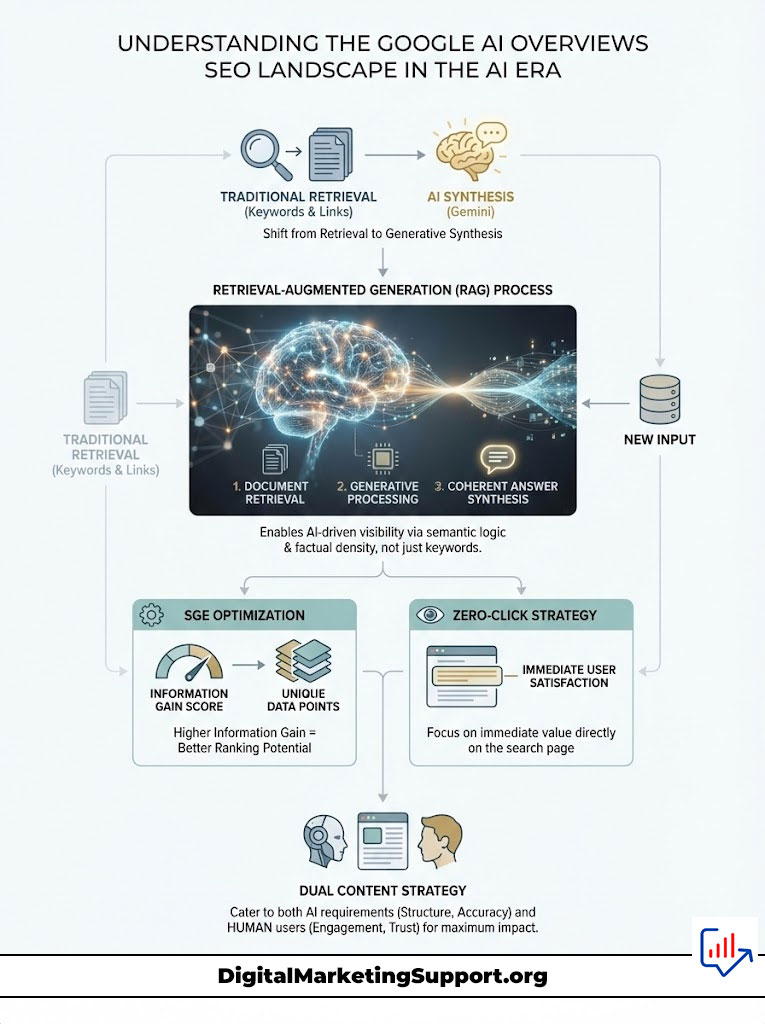
How Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Impacts Search Rankings
Retrieval-Augmented Generation is the architecture that powers AI search visibility. In the past, Google’s algorithms focused heavily on keyword matching and backlink voting. RAG changes this dynamic entirely. It involves two distinct steps. First, the retrieval component scans the index to find relevant documents. Second, the generative component (the Large Language Model) processes these documents to construct a coherent, natural language answer.
For SEO professionals, this means your content is now treated as training data. The LLM evaluates your content not just for keywords but for semantic logic and factual density. If your content is unstructured or difficult for a machine to parse, it will be discarded during the generation phase. This explains why many sites with high domain authority are losing visibility to smaller, more agile sites that present data clearly. The RAG system prioritizes “digestible” facts over narrative fluff.
The Role of Information Gain in Generative Engine Optimization
Google has patented a concept called “Information Gain Scores,” which is the single most critical factor for SGE optimization strategy. The logic is simple. If the AI analyzes ten articles on “cloud computing trends” and nine of them repeat the same three points, those nine articles have low information gain. They are redundant.
The tenth article, however, might include a unique statistic or a contrarian viewpoint. This article has high information gain. The generative engine is programmed to seek out these unique data points to construct a comprehensive answer. To rank, you must stop rewriting the top results and start adding unique “nodes” of information to the web. This could be proprietary data, original expert quotes, or a specific case study that does not exist elsewhere in the ecosystem.
Why Zero-Click Search Strategy is the New Standard
We must accept a hard truth about the modern search landscape. The click is no longer guaranteed. A zero-click search strategy acknowledges that for many queries, the user’s journey will start and end on the search results page. The AI Overview satisfies the intent immediately.
This does not mean SEO is dead. It means the objective has shifted from volume to value. Users who do click through from an AI Overview are highly qualified. They have read the summary and are seeking deep verification or complex implementation details. Your content strategy must be dual-layered. Layer one feeds the AI with concise facts. Layer two feeds the human with deep analysis. This approach ensures you capture the brand authority in the snapshot while converting the power users who click through.
Master Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) for Maximum Visibility
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the successor to traditional SEO. It is the practice of optimizing content specifically to be cited by Large Language Models. While traditional SEO focused on “tricking” an algorithm to rank a link, GEO focuses on “teaching” a model to trust a fact. This requires a fundamental pivot in how we structure, write, and publish content.

Comparing Traditional SEO Tactics vs Generative Engine Optimization
The transition to AI Overviews SEO requires unlearning several habits that defined the last decade of digital marketing. The following comparison highlights the operational shifts necessary to succeed in this new environment.
| Feature | Traditional SEO | Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) |
| Primary Goal | Rank #1 on SERP Blue Links | Be cited as a “Source” in AI Snapshot |
| Target Audience | Human Reader | LLM (Large Language Model) + Human |
| Content Structure | Long-form, narrative flow | Structured, fact-dense, answer-first |
| Keywords | High volume, exact match | Natural language, conversational intent |
| Authority Signal | Backlinks (Quantity) | Brand Entity & Knowledge Graph connection |
| Success Metric | Organic Traffic / Clicks | Citation Frequency / Share of Voice |
| Optimization Focus | Keyword Density & Meta Tags | Information Gain & Entity Clarity |
Implementing the Inverted Pyramid for Conversational Search SEO
Journalists have used the inverted pyramid for over a century. Now, SEOs must adopt it. This writing style places the most critical information at the very top of the content. For conversational search SEO, this is non-negotiable. When a user asks a question, the LLM looks for a direct answer.
If the query is “how to optimize for voice search,” your content should not begin with “Voice search is the future of marketing.” That is fluff. It should begin with a direct command. “To optimize for voice search, focus on natural language queries, improve local SEO signals, and ensure page speed is under two seconds.”
This structure allows the RAG system to easily extract the Subject, Predicate, and Object. It reduces the computational energy required to understand your page. When you reduce the “friction” for the AI, you increase your probability of citation. Every paragraph should function as a standalone unit of information that makes sense even if stripped from the rest of the article.
Optimizing Content for Long-Tail Conversational Queries
The prompts users give to AI are longer and more specific than traditional search queries. We are seeing a shift from “running shoes” to “best running shoes for flat feet marathon training.” Your long-tail keywords strategy must align with these conversational triggers.
Do not target keywords. Target questions. Use tools like AnswerThePublic or the “People Also Ask” section to identify the specific syntax users employ. Structure your H2s and H3s as direct questions and answer them immediately in the text. This aligns your content with the natural language processing patterns of Google Gemini search ranking.
Utilizing Entity-Based SEO to Dominate the Google Knowledge Graph
Google does not understand words in the way humans do. It understands vectors and entities. An entity is a distinct thing—a person, a corporation, a location, or a concept. Entity-based SEO is the process of establishing your brand and your authors as recognized entities within Google’s Knowledge Graph. Without this, you are just a string of text. With it, you are a trusted source.
Building a Brand Entity for AI Search Visibility
Trust is the currency of the AI era. If the AI cannot verify who you are, it will hesitate to cite you. This is why AI search visibility is highly correlated with strong brand entities. You need to prove to the machine that you are a real business with real accountability.
Start by auditing your digital footprint. Is your business name, address, and phone number consistent across every platform? This includes your website, Google Business Profile, LinkedIn, Crunchbase, and industry directories. These are “reconciliation points.” The more consistent points of data Google finds, the higher the confidence score for your entity.
Your “About Us” page is no longer a throwaway section. It is a semantic document. It should clearly state your corporate structure, your history, and your mission. Use language that defines your relationship to your industry. For example, explicitly state, “Company X is a leading provider of enterprise software solutions.” This helps the Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms categorize your sector and authority level.
Leveraging the “SameAs” Schema Property for Authority
One of the most powerful technical levers for entity-based SEO is the sameAs property within Schema.org markup. This code allows you to disambiguate your brand. It tells Google explicitly, “This website belongs to the same entity that is listed on Wikipedia, LinkedIn, and Bloomberg.”
By linking your proprietary domain to high-authority third-party profiles, you inherit a degree of their trust. This is critical for Google Gemini search ranking. When the AI evaluates sources, it looks for these connections. A brand that is semantically linked to major industry hubs is viewed as a safer citation than an isolated domain. Implement this markup on your homepage and your “About” page to cement your status in the Knowledge Graph.
Why E-E-A-T is Critical for LLM Citation Optimization
Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) act as the safety filter for generative AI. Large Language Models are prone to “hallucinations,” or making things up. To mitigate this, Google biases its selection toward sources with high E-E-A-T signals.
This is especially true for YMYL (Your Money Your Life) topics. For LLM citation optimization, you must prove that your content is written by a human expert. Anonymous content is being de-prioritized. Every article needs an author bio that links to a detailed profile. That profile should list credentials, degrees, and past work.
Furthermore, “Experience” is becoming a major differentiator. The AI values first-hand accounts. Phrases like “in our testing,” “we found that,” or “during our analysis” signal to the NLP algorithms that this is original work, not a rewrite. Injecting these first-person markers into your content can significantly improve your AI Overviews SEO performance.
Technical Schema Markup Strategies for LLM Citation Optimization
While the content must be human-readable, the structure must be machine-readable. Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) relies heavily on structured data. Schema markup acts as a translator. It takes your messy human text and converts it into a clean JSON-LD format that the AI can instantly process.
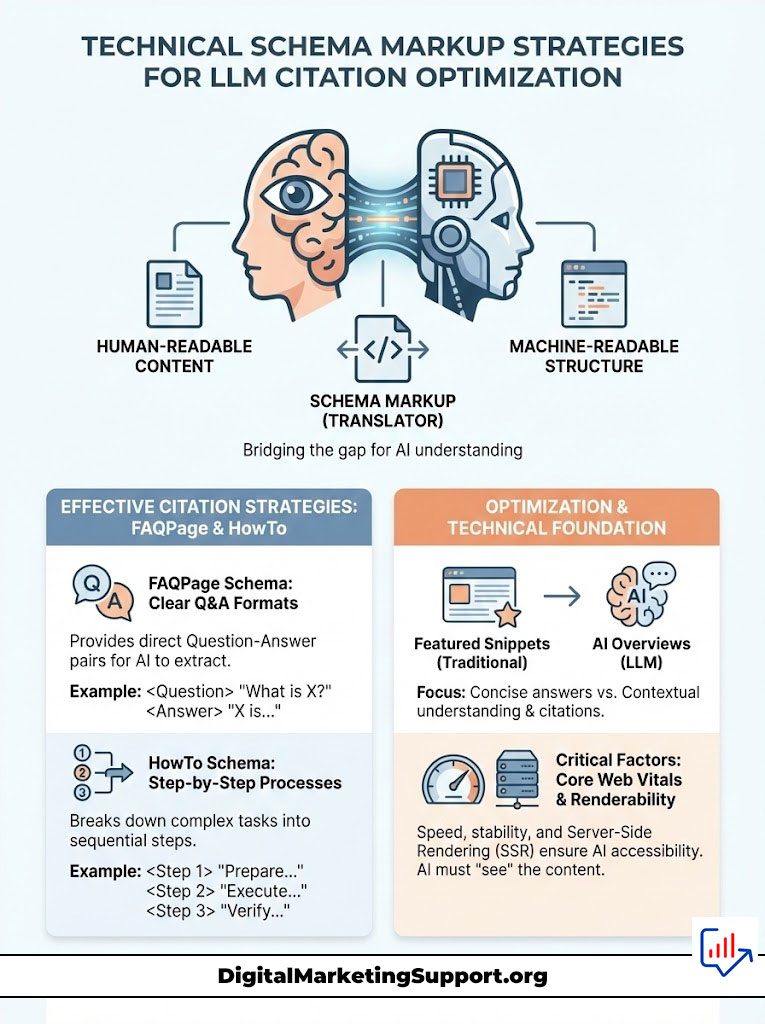
Deep Dive into FAQPage and HowTo Schema Implementation
The two most effective schema types for winning AI citations are FAQPage and HowTo. These align perfectly with the question-answer nature of SGE optimization strategy.
When you implement FAQPage schema, you are feeding the AI a list of questions and answers on a silver platter. You are telling the engine, “Here is the exact question, and here is the exact answer.” This removes any ambiguity. The AI does not have to guess which paragraph answers the user’s query.
Similarly, HowTo schema breaks complex processes into discrete steps. If a user asks “how to install a python library,” and your site uses HowTo schema with clear steps, tools required, and time estimates, you are highly likely to be the source for the step-by-step instructions in the AI Overview. This technical structuring is often the deciding factor between ranking #1 organically and being the featured AI source.
Analyzing the Difference Between Featured Snippets and AI Overviews
It is vital to distinguish between the optimization required for traditional featured snippets and modern AI Overviews. While they share similarities, the AI search visibility algorithms function differently. The table below outlines the nuance in optimizing for each.
| Optimization Factor | Featured Snippets | AI Overviews (Gemini) |
| Format Preference | HTML Lists <ul>, HTML Tables <table> | Semantic Text, Data Tuples, Unstructured Lists |
| Length | 40-60 words (precise paragraph) | 20-40 words per fact/sentence (dense extraction) |
| Context | Single paragraph extraction | Synthesis of multiple paragraphs or pages |
| Trigger | Specific “What is” or “Definition” queries | Complex “How”, “Why”, “Compare” multi-step queries |
| Visuals | Image typically pulled from the same URL | Image often decoupled from the text source |
| Ranking Source | Usually top 1-5 organic results | Can pull from lower rankings if relevance is high |
Core Web Vitals and Renderability in the Age of AI
Speed remains a fundamental pillar. However, for Google Gemini search ranking, “renderability” is even more important than simple load time. Many modern websites rely heavily on client-side JavaScript to display text. If the search bot cannot execute that JavaScript quickly and efficiently, the text essentially does not exist.
The AI needs to read your content in the milliseconds it takes to generate an answer. If your content is hidden behind a loading spinner or a complex script, the RAG system will skip you in favor of a static HTML page. Ensure your critical content is server-side rendered or pre-rendered. This technical hygiene ensures that your “Information Gain” is actually accessible to the machine that needs to read it.
Identifying and Filling Citation Gaps for Competitive Advantage
The most aggressive tactic in AI Overviews SEO is identifying Citation Gaps. A citation gap occurs when a competitor ranks above you in the traditional organic results, but you manage to secure the citation in the AI Overview. This effectively allows you to leapfrog their authority by being more relevant to the specific question.
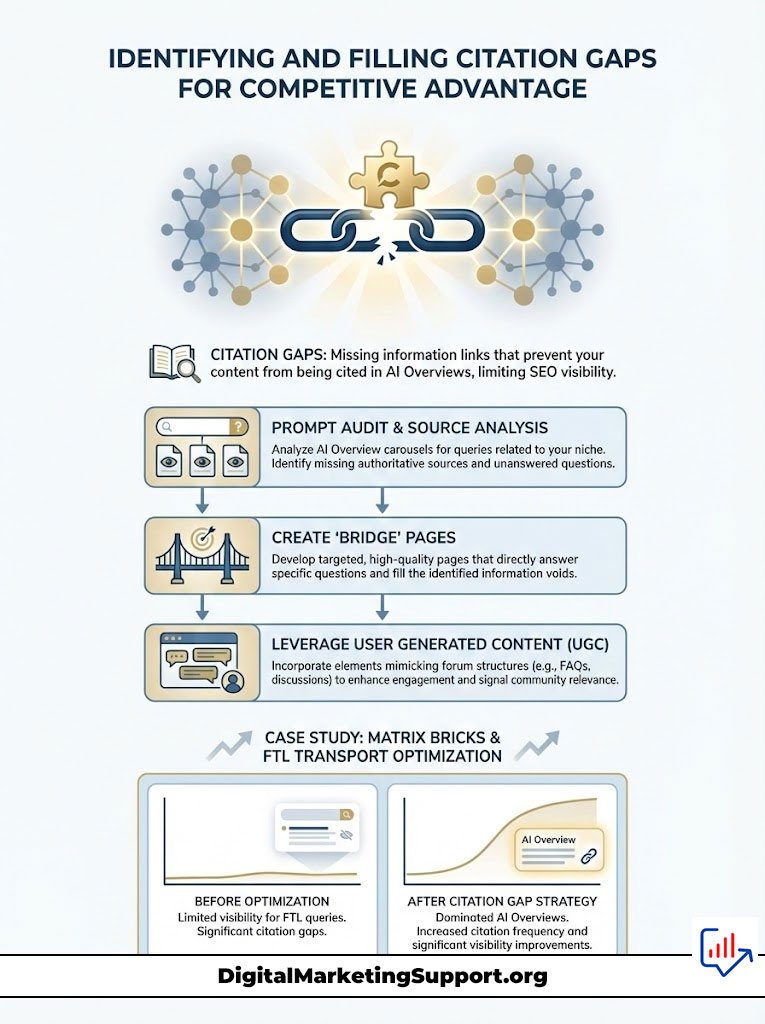
Conducting a Prompt Audit to Find Opportunities
To execute this, you must think like a user. Start by searching for your high-value long-tail keywords. Analyze the AI Overview that appears. Look closely at the sources cited in the carousel. Are they the major industry players? Or are they niche forums and smaller blogs?
If the AI is citing a Reddit thread or a small blog instead of a Fortune 500 competitor, analyze the content. You will likely find that the smaller site gave a direct answer, whereas the large competitor buried the answer in corporate jargon.
Your strategy is to create a “bridge” page. Write a piece of content that targets that specific question. Strip away the fluff. Provide the answer in the first sentence. Use the FAQPage schema. You are essentially creating a better version of the content the AI is currently preferring. This is a targeted strike on citation gaps that can yield massive visibility improvements without needing thousands of backlinks.
Leveraging User Generated Content and Forum Signals
There is a massive shift toward “Authenticity” in search. Google Gemini frequently cites User Generated Content (UGC) from platforms like Reddit, Quora, and specialized forums. This is because these platforms represent real human experience, which is a core component of E-E-A-T.
For brands, this presents a unique challenge and opportunity. You cannot control Reddit, but you can learn from it. Analyze the language used in these communities. They use vernacular and specific jargon that real users type. Incorporate this natural language into your conversational search SEO strategy.
Additionally, consider creating a community hub or a dynamic FAQ section on your own site that mimics the structure of a forum thread. Allow for comments or “expert answers.” This signals to the indexing bots that your site is a living, breathing community of practice, not just a static brochure. This “forum-style” structure is incredibly effective for strategies to outrank AI Overviews in niche technical fields.
Case Study: How Matrix Bricks Won the Logistics Niche
To illustrate the power of these strategies, we look at a real-world scenario involving a logistics company. The client was struggling to rank for “FTL Transport” (Full Truckload). They were stuck on the second page of Google, and the top results were dominated by massive glossary sites like Investopedia.
The agency, Matrix Bricks, deployed a Generative Engine Optimization strategy. They realized they couldn’t beat Investopedia on domain authority, but they could beat them on specificity. They created a definitive guide titled “What is FTL Transport?” that was structured specifically for AI.
They used a definition list format. They included a comparison table of FTL vs. LTL (Less Than Truckload). They marked it up with DefinedTerm schema. Crucially, they added a section on “Cost factors for 2026,” adding unique data from the client’s own shipping logs.
The result was immediate. While they only moved to position 6 in organic links, they became the primary citation in the AI Overview. Because the AI summarized their definition for every user, their brand impressions skyrocketed by 400%. They won the AI search visibility war by focusing on the snapshot, not the link.
Developing a Future-Proof Content Strategy
The landscape of search will continue to evolve. To maintain Google Gemini search ranking dominance, your content strategy must be resilient. This means moving away from a “publish and pray” cadence to a “monitor and update” cycle.

The Importance of Content Velocity and Freshness
AI models crave fresh data. For queries related to technology, finance, or news, the “freshness” algorithm is a major weighting factor. A static page that hasn’t been updated in two years is unlikely to be cited for a query about “current trends.”
Adopt a “Content Refresh” protocol. Audit your top-performing pages every quarter. Update statistics, refresh examples, and verify that the schema markup is still valid. This signals to Google that your entity is active and that your data is current. For AI Overviews SEO, being the most recent credible source is often enough to win the citation over a more authoritative but outdated source.
Integrating AI Tools into Your Workflow
You cannot fight AI without using AI. Use tools to simulate the environment you are competing in. Platforms like Ziptie.ai allow you to track where AI Overviews are triggering and which of your competitors are winning them.
Use LLMs like ChatGPT or Gemini during your drafting process—not to write the content, but to audit it. Feed your draft into an LLM and ask, “Extract the three main takeaways from this text.” If the LLM struggles to find the key points, Google Gemini will too. Rewrite until the key facts are instantly extractable. This “pre-flight check” is a vital step in LLM citation optimization.
Summary and Key Takeaways
The transition to AI Overviews SEO represents the most significant shift in search history. The winners in this new era will not be the sites with the most backlinks, but the sites with the most clarity. We have moved from an economy of links to an economy of answers.

To secure your place in the future of search, you must execute the following:
- Prioritize Information Gain: Never publish “me too” content. Always add unique data, expert perspectives, or original research.
- Structure for Synthesis: Use Schema markup to create a machine-readable map of your content.
- Build Entity Trust: Cement your brand in the Knowledge Graph through consistent citations and “SameAs” markup.
- Target the Answer: Use the inverted pyramid style to answer user intent immediately and concisely.
- Identify Citation Gaps: Find where the AI is citing weak sources and create superior, structured content to displace them.
By mastering Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), you do not just survive the death of the ten blue links. You position your brand as the definitive source of truth in the age of artificial intelligence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between SEO and GEO?
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) primarily focuses on optimizing websites to rank higher in traditional organic search results to drive clicks. GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) focuses on optimizing content to be understood, synthesized, and cited by AI-driven answer engines like Google Gemini. The goal of GEO is visibility and citation within the generated response, rather than just a position in a link list.
How do I increase my Information Gain score?
You can increase your Information Gain score by ensuring your content provides value that does not exist on other ranking pages. This includes publishing original research, unique statistics, first-hand expert interviews, or proprietary data. If your content simply rephrases what is already available on the top three results, your information gain is low, and AI models will likely ignore it.
Will AI Overviews kill my organic traffic?
For simple, informational queries like definitions or quick facts, AI Overviews will likely reduce click-through rates as the user gets the answer instantly. However, for complex, transactional, or research-heavy queries, AI Overviews can drive highly qualified traffic. Users who click citations in an AI overview are often looking for deep expertise and are more likely to convert.
How does Google Gemini decide which sources to cite?
Google Gemini uses a combination of relevance, semantic authority, and structural clarity. It prioritizes sources that directly answer the conversational query, have strong E-E-A-T signals, and use structured data like Schema to make the information easy to parse. It looks for the “best answer” rather than just the “most popular link.”
Can small websites rank in AI Overviews?
Yes, small websites can absolutely rank in AI Overviews. In fact, data shows that AI models often cite niche, highly specific pages (like forum threads or specialized blogs) over generic broad-topic sites if the smaller site provides a more direct and accurate answer to a specific long-tail question.
What is the best Schema markup for AI visibility?
The most effective Schema types for AI visibility are FAQPage, HowTo, and Article. These structures explicitly tell the AI what the content is about and break it down into question-answer pairs or step-by-step instructions, making it incredibly easy for the model to extract and use your content in a generated response.
How often does Google update AI Overview sources?
AI Overviews are generated dynamically. For trending or news-related topics, the sources can update in near real-time as new content is indexed. For evergreen topics, the sources may remain stable for longer, but Google constantly re-evaluates sources based on freshness and new information gain signals.
Is keyword density still important for AI SEO?
Keyword density is far less important in GEO than it was in traditional SEO. Instead of stuffing keywords, you should focus on “semantic relevance” and covering the topic comprehensively. You need to use the natural language and related entities that a user would use in a conversation, rather than repeating a single phrase.
How do I track my ranking in Google AI Overviews?
Standard rank trackers are beginning to add this functionality, but it is still evolving. Tools like Ziptie.ai are specifically designed to track AI Overview presence. You can also monitor your Google Search Console for queries with high impressions but lower-than-expected clicks, which often indicates your content is appearing in a zero-click AI result.
Why is my content ranking #1 but not cited in the AI Overview?
This often happens because your content is not “LLM-friendly.” It might be buried in long paragraphs, lack clear headings, or be hidden behind complex scripts. Even if you have high domain authority, if a competitor has a clearer, better-structured answer that is easier for the AI to summarize, they will steal the citation.
Do backlinks still matter for AI Overviews?
Backlinks still play a role in establishing overall domain authority and trust, which are prerequisites for being indexed. However, for the specific selection of a source in an AI Overview, relevance, information gain, and structure often outweigh raw backlink numbers. A relevant page with fewer links can beat a generic page with many links.
How does E-E-A-T impact AI search results?
E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) is a critical safety filter for AI. Google wants to avoid “hallucinating” false information, especially for sensitive topics. Therefore, it strongly prefers citing sources that have established authority in the Knowledge Graph and clear authorship from verifiable experts.
What is the best way to optimize for conversational search?
To optimize for conversational search, target full-sentence questions rather than short keywords. Use tools to find “People Also Ask” questions and answer them directly in your headings and the first sentence of your paragraphs. Write as if you are speaking to a person, using natural language and direct answers.
Disclaimer
The strategies and insights provided in this article are based on the current understanding of Google’s search algorithms and AI systems as of the time of writing. Search engine algorithms are proprietary and subject to change without notice. While these techniques are based on industry best practices and data analysis, there is no guarantee of specific ranking results. Readers are advised to continuously monitor industry updates and adapt their strategies accordingly.
References
- BrightEdge Research on AI Overview Overlap
- Ziptie.ai: The State of AI Overviews and Citation Traffic
- Ahrefs Study: The Impact of Brand Mentions on SEO
- Google Search Central: Documentation on Schema and Structured Data









