The way we interact with the internet has fundamentally changed. We are no longer tethered to keyboards or small screens to find answers. We are speaking to the air and expecting the air to answer back with precision. This is the reality of Voice Search 2.0. It is a shift from simple command-based queries to complex, multi-turn conversations with intelligent agents.
Table of Contents
For business leaders and marketers in the USA, this transition represents both a massive threat and an unprecedented opportunity. The era of scrolling through ten blue links is ending for a significant portion of search volume. In the world of AI voice search optimization, there is often only one result. We call this “Position Zero.” If your brand is not the single answer recited by Siri, Alexa, or Google Gemini, you are effectively invisible.

This guide is not a superficial overview. It is a deep tactical breakdown of how to engineer your digital presence for the age of Answer Engine Optimization (AEO). We will explore how to restructure your data, optimize your content infrastructure, and align your brand with the neural networks that now power the world’s information retrieval systems.
Understanding the Mechanics of AI Voice Search Optimization and Neural Algorithms
To rank for the next generation of search, you must first understand how the engine works. Traditional SEO was about matching keywords. If a user typed “best running shoes,” the search engine looked for pages containing that phrase. Voice Search 2.0, powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI, operates on entirely different principles. It does not just look for matches. It looks for meaning.
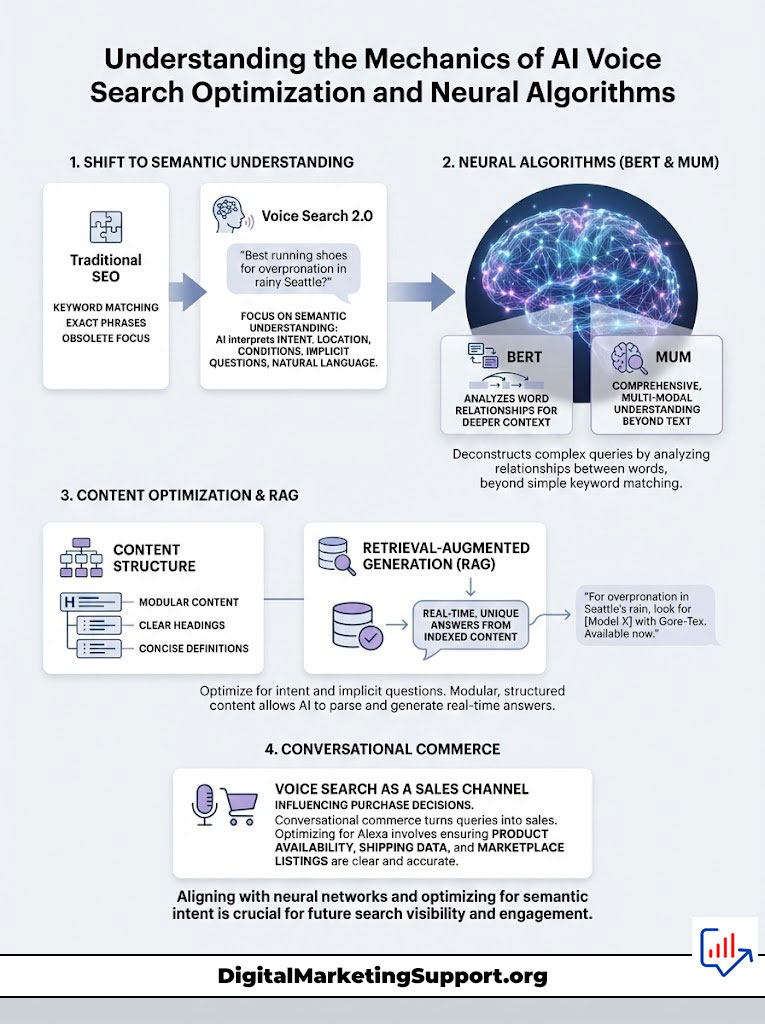
Moving Beyond Lexical Search to Semantic Search Intent
The core engine of Voice Search 2.0 is semantic understanding. When a user asks a question via voice, they use natural language. They do not say “weather Chicago.” They ask, “Do I need an umbrella if I go downtown this afternoon?”
The AI must deconstruct this query. It identifies the intent (weather forecast), the location (Chicago downtown), and the specific condition (rain probability). This is processed through neural search algorithms like Google’s BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) and MUM (Multitask Unified Model). These algorithms understand the relationship between words rather than just the words themselves.
For content creators, this means keyword stuffing is dead. You must optimize for semantic search intent. Your content needs to answer the implicit questions within a query. If you are targeting “best coffee,” you must also contextually cover “bean origin,” “roast levels,” and “atmosphere,” because the AI understands these concepts are semantically linked to the user’s core need for a quality café experience.
Leveraging Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for Dynamic Answers
The most advanced shift in Voice Search 2.0 is the adoption of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). In the past, voice assistants often recited pre-programmed snippets. Today, assistants like Google Gemini and Microsoft Copilot use RAG to generate fresh answers in real-time.
Here is how RAG impacts your SEO strategy. When a user asks a complex question, the AI retrieves relevant documents from its index (your website) and then “reads” them to generate a new, unique answer. If your content is buried in unstructured text, the AI cannot parse it. It will skip your site. To be visible, your content must be modular. You need clear headings, concise definitions, and logical data structures that allow the AI to easily “grab” the facts it needs to construct its response.
The Rise of Conversational Commerce and Transactional Voice Queries
Voice search is no longer just for checking facts. It is a sales channel. In the USA, millions of consumers utilize smart speakers to replenish household goods, order food, and research high-ticket items. This phenomenon is known as conversational commerce.
Alexa voice ranking factors are heavily weighted toward this transactional intent. When a user says, “Alexa, buy me some toothpaste,” the algorithm does not just search the web. It checks purchase history first. If there is no history, it looks for “Amazon’s Choice” or highly-rated products with fast shipping. For brands, this means optimization extends beyond the website. It involves optimizing product availability, shipping speed data, and third-party marketplace listings to ensure you are the path of least resistance for the AI to recommend.
Technical SEO Frameworks for Maximizing Conversational AI Search Visibility
You cannot charm a robot with clever metaphors. You must speak its native language. Technical SEO is the foundation of AI visibility. Without a robust technical infrastructure, your high-quality content will remain inaccessible to the bots that power Siri and Alexa.
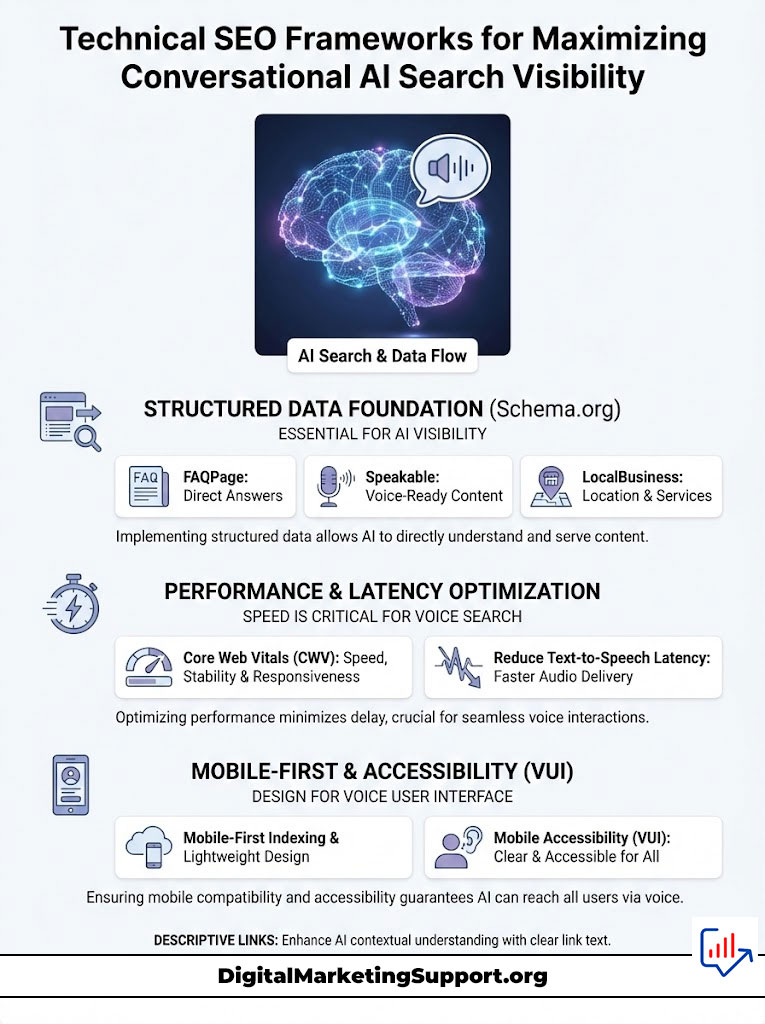
Implementing Structured Data for Voice to Define Context
The most powerful weapon in your arsenal is Schema.org markup. Structured data acts as a translator. It tells the AI exactly what your content is, differentiating a product price from a phone number. For AI voice search optimization, three specific schema types are non-negotiable.
First is FAQPage Schema. This is the direct pipeline to Position Zero. By wrapping your questions and answers in this markup, you explicitly provide the AI with a Q&A format it can easily recite. Data shows that pages with valid FAQ Schema are significantly more likely to trigger a voice response on Google Assistant.
Second is Speakable Schema. Originally designed for news publishers, this property uses XPath to designate specific sections of an article that are suitable for audio playback. By marking up your summary or key takeaways with “Speakable,” you are inviting Google Assistant to read that specific section to the user.
Third is LocalBusiness Schema. For Siri SEO tactics, this is vital. You must strictly define your geo-coordinates, opening hours, and price range. When a user asks, “Is there a pharmacy open right now?”, the AI does not crawl your text. It looks at the openingHours property in your structured data. If that tag is missing or broken, you do not exist in that moment.
Optimizing Core Web Vitals and Reducing Text-to-Speech Latency
Speed is a critical ranking factor for voice. When a user speaks to an assistant, they expect an immediate reply. The tolerance for latency is near zero. If your server takes two seconds to respond, the AI assistant will likely time out and choose a faster competitor to ensure a fluid user experience.
You must optimize your Time to First Byte (TTFB). Voice search results typically load 52% faster than the average desktop page. This means you need a high-performance hosting environment, aggressive caching, and a Content Delivery Network (CDN) that serves data from the edge.
Furthermore, mobile-first indexing is the standard. Most voice searches happen on mobile devices or smart speakers connected to Wi-Fi. Your site must be lightweight. Heavy JavaScript execution can delay the AI’s ability to parse your content. Server-side rendering (SSR) or static site generation (SSG) are preferred architectures for content that needs to be “AI-readable” instantly.
Ensuring Mobile Accessibility and Voice User Interface (VUI) Compatibility
Your website must be designed for a Voice User Interface (VUI). This goes beyond responsive design. It means your content is accessible without a screen. Navigation should be logical, and anchor text should be descriptive.
Avoid using generic links like “click here.” Instead, use “view our full menu” or “read the pricing guide.” When an AI parses your page, descriptive links help it understand the relationship between pages. Additionally, ensure that no critical content is hidden behind “click-to-expand” buttons or complex user interactions. AI bots often struggle to execute JavaScript events to reveal text. All answers should be visible in the DOM (Document Object Model) on initial load.
Strategic Content Writing Techniques for Answer Engine Optimization (AEO)
Once the technical foundation is laid, you must revolutionize your writing style. Writing for Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) is different from writing for human readers who scan visual pages. You are writing for listeners.
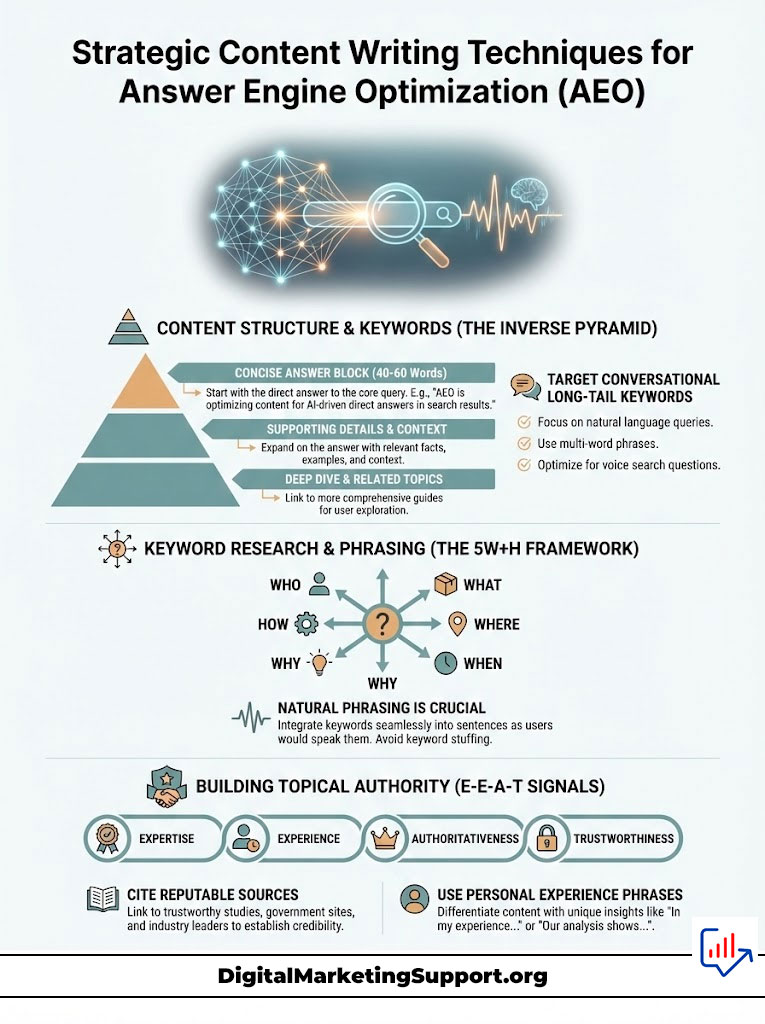
The Inverse Pyramid Method for Capturing Featured Snippets
To win the Featured Snippet optimization game, you must structure your content using the Inverse Pyramid method. Traditional storytelling builds up to a conclusion. AEO demands the conclusion first.
Start every major section with a direct, concise answer. This “answer block” should be between 40 and 60 words. It must be factual, objective, and self-contained. For example, if the header is “How long does it take to rank for voice search?”, the immediate paragraph should be: “It typically takes 3 to 6 months to see significant results in voice search rankings. The timeline depends on your domain authority, the implementation of valid schema markup, and the competitiveness of your target keywords.”
Once you have provided this direct answer (which the AI will scrape), you can then expand with nuance, examples, and data in the subsequent paragraphs. This structure satisfies both the bot (who wants a snippet) and the human (who wants detail).
Targeting Conversational Long-Tail Keywords and Natural Phrasing
Keyword research for Voice Search 2.0 requires a shift to conversational phrasing. Users do not speak in keywords; they speak in sentences. Your strategy must focus on conversational long-tail keywords.
Focus on the “Who, What, Where, When, Why, and How” framework. These interrogative words trigger the vast majority of voice queries. Use tools like AnswerThePublic or analyzing “People Also Ask” boxes to find the exact questions your audience is asking.
Do not force these keywords. The phrasing must sound natural. If you stuff the phrase “best SEO agency USA cheap” into a sentence, it will sound robotic when read aloud by Siri. Instead, write “If you are looking for an affordable SEO agency in the USA, consider…” This natural syntax helps the NLP algorithms match your content to the user’s spoken conversational pattern.
Building Topical Authority with High E-E-A-T Signals
Google’s E-E-A-T signals (Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) are the gatekeepers of voice search. AI assistants are programmed to be risk-averse. They avoid citing unverified sources to prevent spreading misinformation, especially in medical, financial, or legal topics.
To build authority, you must cite sources. Link to reputable studies, government data, or industry whitepapers. This creates a “trust web” that tells the AI your data is grounded in reality. Additionally, ensure your content is authored by credible experts. Author bios with links to LinkedIn profiles or other publications help Google verify the expertise of the writer.
Experience is also key. Use phrases like “In our testing…” or “We found that…” to demonstrate first-hand experience. This distinguishes your content from generic AI-generated fluff and signals to the ranking algorithms that you possess unique, verifiable knowledge.
Analyzing Platform-Specific Algorithms for Siri, Alexa, and Google Gemini
A “one-size-fits-all” strategy does not work in Voice Search 2.0. Each major assistant draws data from different sources and prioritizes different metrics. To maximize AI assistant visibility, you need to tailor your approach for each ecosystem.
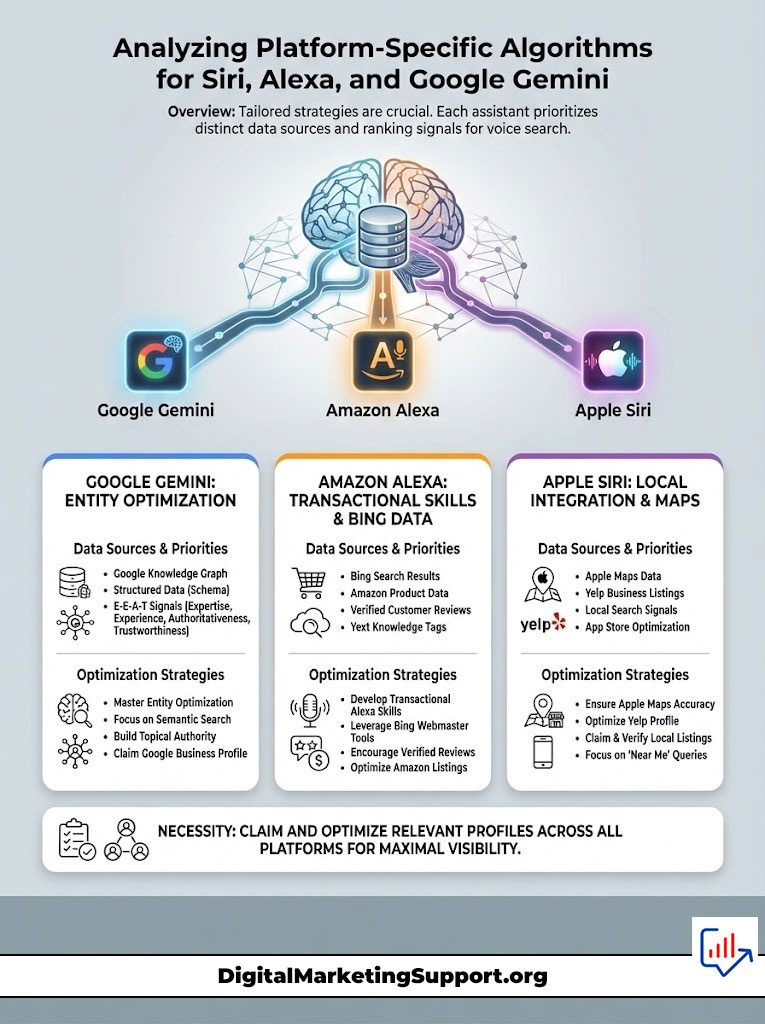
Comparison of Optimization Priorities for Major AI Assistants
| Feature | Google Gemini / Assistant | Amazon Alexa | Apple Siri |
| Primary Data Source | Google Search Index & Knowledge Graph | Bing Index, Amazon Retail Data, Yext | Apple Maps, Yelp, TripAdvisor, WolfamAlpha |
| Ranking Priority | Featured Snippet Optimization, Page Speed, E-E-A-T | Amazon Sales History, Bing Places Accuracy | Geo-Proximity, Yelp Reviews, Apple Maps Data |
| Best Content Type | In-depth Blog Posts, Videos, How-To Guides | E-commerce Listings, Skills, FAQs | Local Listings, “Near Me” Data, Navigation |
| Schema Focus | FAQ, Article, HowTo, Speakable | Product, Offer, Merchant | LocalBusiness, GeoCoordinates |
| Strategic Goal | Win Position Zero | Be the “Amazon Choice” | Be the Top Local Recommendation |
| Key Algorithm | BERT, MUM, Gemini (Multimodal) | Alexa Rank, Sales Velocity | Siri Suggestions, Proximity Logic |
Mastering Google Gemini and Knowledge Graph Entities
Google Gemini represents the bleeding edge of search. It is multimodal, meaning it can understand text, images, and video simultaneously. To rank here, you must focus on Entity Optimization. Google needs to understand who you are.
Ensure your “About Us” page and “Contact” page are robust. Claim your Google Knowledge Panel. Use Organization Schema to link your social profiles and Wikipedia entry (if applicable). The more Google understands your brand as a verified entity, the more likely it is to cite you as a trusted source. For content, focus on comprehensive guides that cover a topic from every angle, using the topic cluster model to signal deep expertise.
dominating Amazon Alexa with Transactional Skills and Bing Data
Alexa voice ranking factors are unique because Alexa is primarily a shopping assistant. While it uses Bing for general information, its core function is commerce. If you sell products, your Amazon SEO is your Voice SEO.
Optimize your Amazon product titles to be spoken. Instead of keyword-stuffed titles, use clear, descriptive names. Focus on getting verified reviews, as Alexa often reads “the top-rated product” first. For non-retail businesses, ensure your business is listed on Bing Places. Alexa pulls local business data heavily from Microsoft’s ecosystem, so a missing Bing profile means silence on millions of Echo devices.
Optimizing for Siri with Apple Maps and Yelp Integration
Siri SEO tactics are intensely local. Siri relies heavily on Apple Maps and third-party data providers like Yelp and TripAdvisor. It does not crawl the open web as aggressively as Google for local queries.
Your primary task is to claim and optimize your Apple Maps Connect profile. Ensure your categories are correct. Upload high-quality photos. Crucially, encourage customers to leave reviews on Yelp. Siri frequently qualifies its recommendations by saying, “I found a place with good reviews on Yelp.” If you neglect Yelp, you neglect the iPhone user base.
Local Voice Search SEO Strategies for “Near Me” Dominance
For brick-and-mortar businesses, local voice search SEO is the holy grail. Queries containing “near me” have exploded in volume. Users are driving, walking, or multitasking, and they need immediate, actionable location data.

Deploying Hyper-Local Geo-Fencing Content
To win “near me” searches, you need to go beyond just your city name. You must optimize for hyper-local geo-fencing. This means creating content that references specific neighborhoods, landmarks, and cross-streets.
If you are a plumber in Austin, do not just say “Plumber in Austin.” Write content that mentions “Plumbing services near Rainey Street” or “Emergency repairs in Hyde Park.” AI assistants use GPS data to determine proximity. By explicitly mentioning these micro-locations in your text and schema, you align your content with the user’s precise coordinates, increasing the likelihood of being the chosen result.
Managing Directory Consistency and NAP Data Integrity
Data consistency is a trust signal. If your phone number is different on Facebook than it is on your website, the AI gets confused. It lowers your trust score. You must ensure your NAP (Name, Address, Phone) data is identical across the entire ecosystem.
This includes major aggregators like Data Axle, Foursquare, and Neustar. These data hubs feed the smaller directories and apps. A single discrepancy can propagate and cause Siri to send a user to the wrong location. Regular audits of your listings are essential for maintaining AI assistant visibility.
Leveraging Reputation Management for Verbal Ranking
In Voice Search 2.0, star ratings are more than social proof; they are a ranking filter. Users often filter their voice queries: “Find me a 4-star Italian restaurant.” If you are sitting at 3.9 stars, you are filtered out before the search even happens.
You must implement an active reputation management strategy. Solicit reviews via SMS or email immediately after a transaction. Respond to every review. The keywords within reviews matter too. If a customer writes, “They have the best vegan burger,” that review text can help you rank for the voice query “Who has the best vegan burger near me?”
Future-Proofing for Multimodal Search and Agentic AI
The horizon of search is expanding. We are moving toward a world where voice interacts with vision and where search engines act as agents.
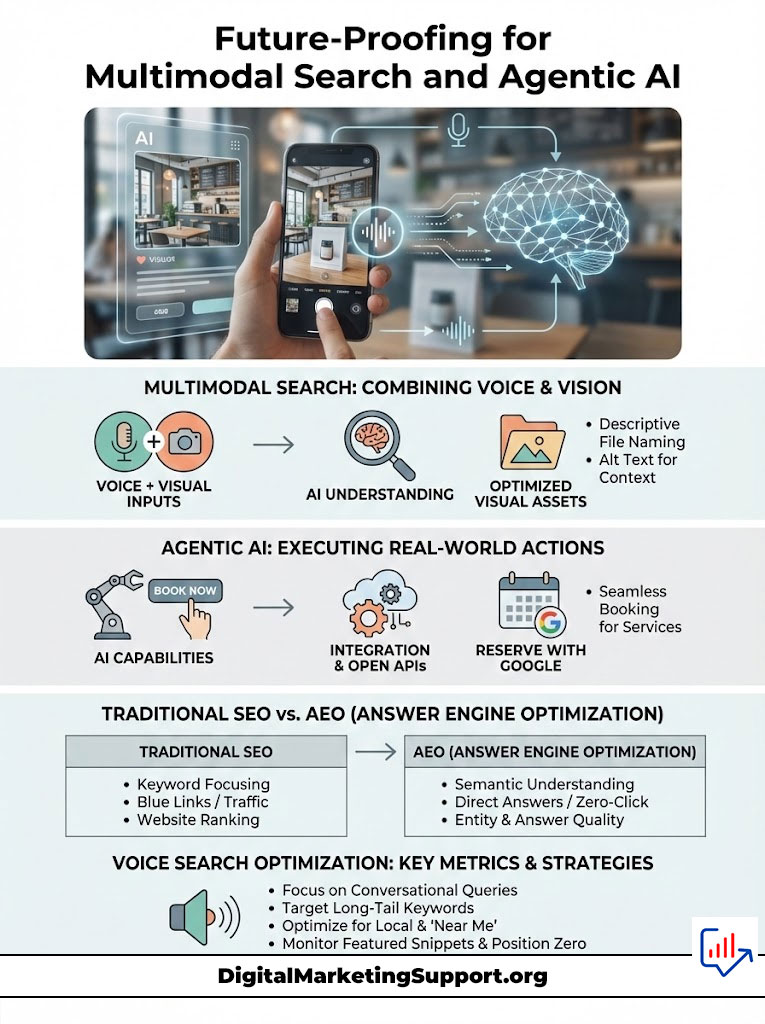
Integrating Visual Search with Voice Commands
Multimodal search allows users to query with images and voice simultaneously. A user might point Google Lens at a broken part on their car and ask, “How do I replace this?”
To capture this traffic, you must optimize your visual assets. Use descriptive file names. Write Alt Text that is conversational and descriptive. Instead of “img123.jpg” with alt text “car part,” use “2024-sedan-alternator-replacement-guide.jpg” with alt text “Step by step guide on how to replace an alternator in a 2024 sedan.” This helps the AI connect the visual input with the spoken intent.
Preparing for Agentic AI and Action-Based Queries
The future of Voice Search 2.0 is “Agentic AI.” This refers to AI that can perform actions. Users will soon say, “Book me a table at a romantic restaurant for Friday at 7 PM.” The AI will not just give a list; it will execute the booking.
To prepare for this, your business needs to be technically integrated. Use booking platforms that have APIs open to Google and Apple (like OpenTable or Resy). If you are a service business, ensure your “Reserve with Google” integration is active. The brands that make it easiest for the AI to complete a transaction will win the majority of the market share in this agent-driven future.
Comparative Analysis of Traditional SEO vs Answer Engine Optimization (AEO)
| Metric | Traditional SEO | Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) |
| Primary Goal | Rank on Page 1 (Blue Links) | Rank as the Single Answer (Position Zero) |
| User Interaction | Scrolling, Reading, Clicking | Listening, Conversing, Acting |
| Content Structure | Long paragraphs, keyword density | Concise answers, bullet points, conversational |
| Target Keywords | Short-tail (e.g., “SEO Tips”) | Long-tail keywords / Questions (e.g., “How do I optimize for Siri?”) |
| Success Metric | Click-Through Rate (CTR) | Brand Mention / Zero-Click Attribution |
| Technical Focus | Meta Tags, Backlinks | Structured data for voice, API Integration |
| Device Context | Desktop / Laptop focus | Mobile / Smart Speaker / Car Play |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What distinguishes Voice Search 2.0 from previous voice technologies?
Voice Search 2.0 represents a leap from simple keyword recognition to advanced semantic understanding powered by Generative AI and Large Language Models. Unlike older systems that required rigid commands, new assistants understand context, nuance, and multi-turn conversations.
How can I test if my website is optimized for Siri and Alexa?
You can test optimization by asking specific questions related to your brand or industry on the actual devices. Additionally, use Google’s Rich Results Test tool to verify that your structured data for voice is correctly implemented and eligible for rich snippets.
Why is Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) vital for modern businesses?
Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) is vital because search behavior is shifting toward “zero-click” interactions. If your content is not optimized to be the direct answer, you lose visibility entirely in screenless environments like smart speakers and connected cars.
Does using Schema markup guarantee I will rank in voice search?
No, using Schema markup does not guarantee a ranking, but it is a necessary prerequisite. It ensures the AI can understand your content. To actually rank, you must also demonstrate high E-E-A-T signals and fast page performance.
How do smart assistants determine results for “near me” voice search queries?
Assistants prioritize three factors: your current GPS location, the consistency of business listings across maps (Google/Apple/Bing), and the sentiment of customer reviews. They combine these to offer the most convenient and trusted option.
What is the most effective way to target conversational long-tail keywords?
The most effective strategy is to build content around the “Who, What, Where, When, Why” framework. Research the specific questions your audience asks and answer them directly in your headings and opening paragraphs using natural, spoken language.
Is it possible to track voice search traffic in Google Analytics?
Direct tracking is not currently possible as Google does not tag voice queries separately. However, you can infer success by tracking the performance of pages that own Featured Snippets and monitoring keywords that are phrased as questions.
How does the Google Gemini update impact SEO strategies?
Google Gemini forces marketers to think multimodally. It integrates text, image, and video understanding. Strategies must now include optimizing visual assets and video transcripts to ensure they are accessible to this advanced AI model.
How significantly does page speed affect AI assistant rankings?
Page speed is crucial. Voice search results typically load 52% faster than standard mobile pages. AI assistants have a strict timeout threshold; if your site is slow, the assistant will bypass it to avoid a long pause in the conversation.
What is the ‘Speakable’ Schema property and who should use it?
Speakable Schema is a structured data type that identifies sections of a web page best suited for audio playback. It is primarily recommended for news organizations and publishers to help their articles get read aloud by Google Assistant.
How do I establish E-E-A-T for better voice search visibility?
Establish E-E-A-T signals by ensuring all content is fact-checked, citing authoritative sources, maintaining up-to-date author bios with credentials, and actively managing your brand’s reputation on third-party review platforms.
Will voice search eventually replace screen-based search?
It will not replace it entirely, but it will dominate specific contexts. “On-the-go” queries and quick facts will move to voice, while deep research and visual shopping will likely remain on screens. Marketers must optimize for both behaviors.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes. Search engine algorithms and AI technologies are proprietary and subject to rapid evolution. The strategies outlined here reflect the best practices for the current digital landscape.
References:
- Google Search Central: Introduction to Structured Data.
- Schema.org: Documentation for FAQPage and Speakable.
- Bing Webmaster Tools: Guidelines for Voice Search Optimization.
- Amazon Developer Docs: Alexa Skills Kit and SEO.
- Apple Maps Connect: Business Listing Verification Standards.









