AI marketing runs on a simple, powerful principle: the more data it has, the smarter it gets. This data is the fuel that powers incredible personalization, shockingly accurate predictive insights, and automated campaigns that can optimize themselves in real time. But this high-octane fuel is also highly flammable. The vast, centralized pools of customer data that make AI so effective also create a treasure trove for cybercriminals, making AI marketing data security one of the most critical challenges for modern businesses.
Table of Contents
For companies across the USA, this creates a difficult paradox. The very data that unlocks competitive advantage also presents a massive liability. A single data breach is no longer just an IT headache; it’s a catastrophic business event. According to a 2023 report from IBM, the average cost of a data breach in the United States has soared to a staggering $9.44 million, a figure that can easily bankrupt a small or medium-sized business.

This article is a comprehensive guide to navigating the complex world of AI marketing data security. We will dissect the primary AI marketing risks, provide a clear framework for evaluating the security of AI vendors, and offer actionable best practices for how to secure customer data while still harnessing the immense power of AI. This isn’t just a conversation for your IT department; it’s a core strategic concern for every marketer, manager, and business owner.

How AI Marketing Tools Use and Handle Your Customer Data
Before we can secure the data, we need to understand what it is and how it flows through an AI system. The conversation around data privacy in AI marketing begins with understanding the complete data lifecycle.
What Data Are We Talking About?
When we discuss data in the context of AI marketing, we’re talking about a wide spectrum of information that these tools collect and analyze. This often includes:
- Contact & Demographic Data: Names, email addresses, locations, age, and gender.
- Behavioral Data: Website pages visited, links clicked, time spent on site, and videos watched.
- Transactional Data: Past purchase history, average order value, products viewed, and abandoned shopping carts.
- Social Media & Public Data: Publicly available information like interests, likes, and comments.
Crucially, this mix often includes personally identifiable information (PII), which is the most sensitive and highly regulated category of customer data.
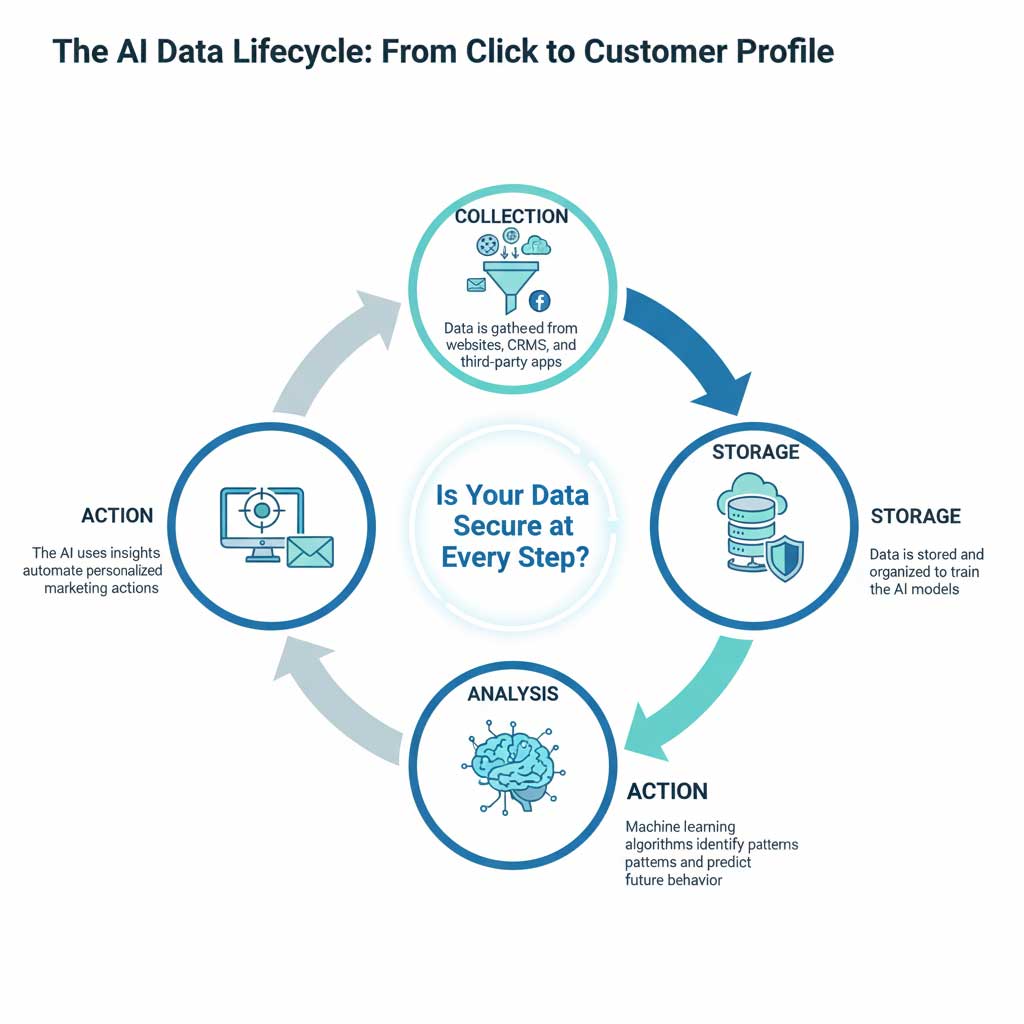
The Data Lifecycle in an AI System
The journey of your customer data through an AI marketing tool can be broken down into a simple lifecycle. The core security question we must ask is: “How is each stage of this process protected?”
- Collection: Data is first collected from various sources, such as tracking pixels on your website, integrations with your CRM platform, or APIs connected to social media channels.
- Storage: This collected data is then stored, most often in a cloud-based environment, where it is used to train the AI’s machine learning models.
- Analysis: The AI’s algorithms process the stored data, looking for patterns, making predictions, and generating insights.
- Action: Finally, the AI uses these insights to take an automated action, such as launching a targeted ad, sending a personalized email, or recommending a product.
Understanding this flow is the first step in developing a robust AI marketing data security strategy.
The Top 5 Data Security Risks in AI-Powered Marketing
The potential rewards of AI marketing are immense, but so are the risks. A successful strategy requires a clear-eyed understanding of the threat landscape. These are the most significant AI marketing risks that businesses face today.
Understanding the Threat Landscape
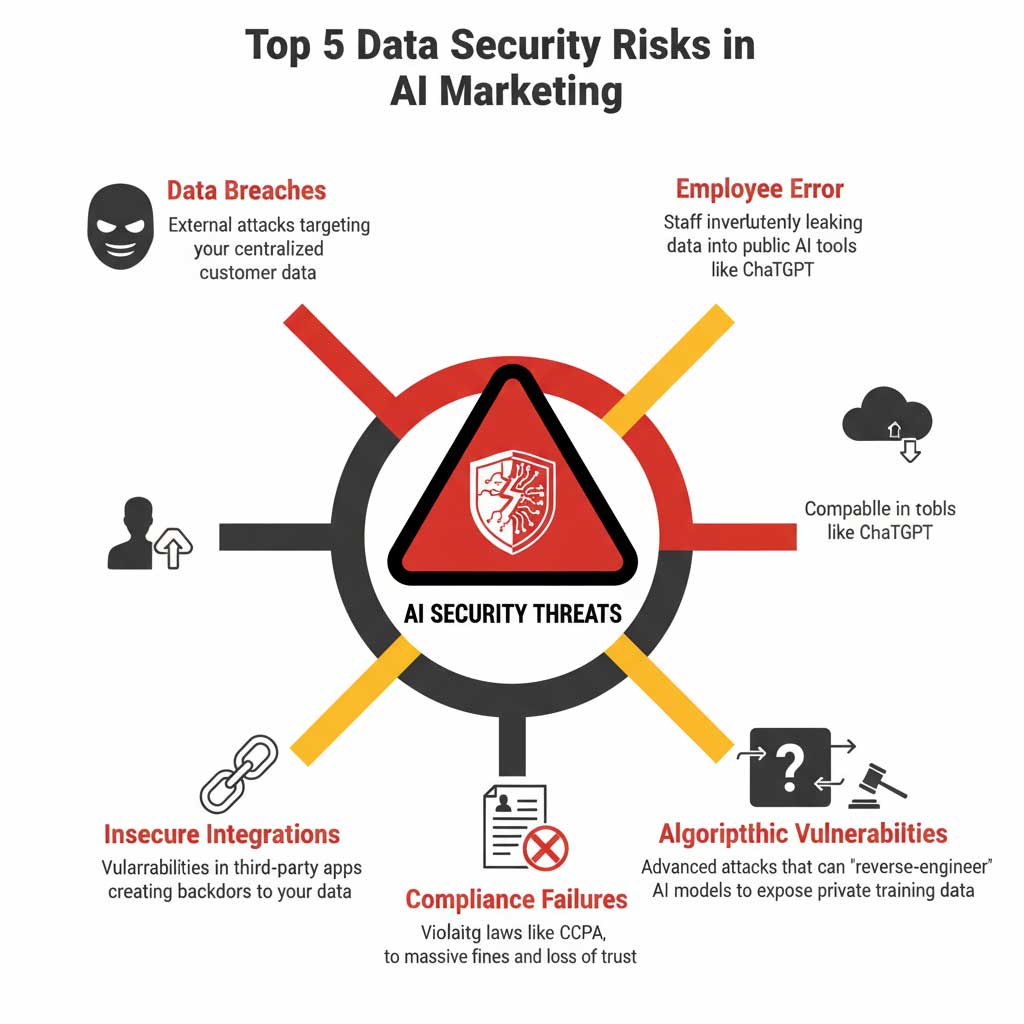
Risk #1: Sophisticated Data Breaches
AI systems, by their nature, require large, centralized datasets to function. This makes them an incredibly high-value target for cybercriminals. A single successful attack on your AI vendor’s servers could expose the personal data of your entire customer base.
Risk #2: Insider Threats & Employee Error
One of the most significant and often overlooked AI marketing risks comes from within your own company. This includes both malicious insiders who intentionally steal data and, far more commonly, well-intentioned employees who make simple mistakes.
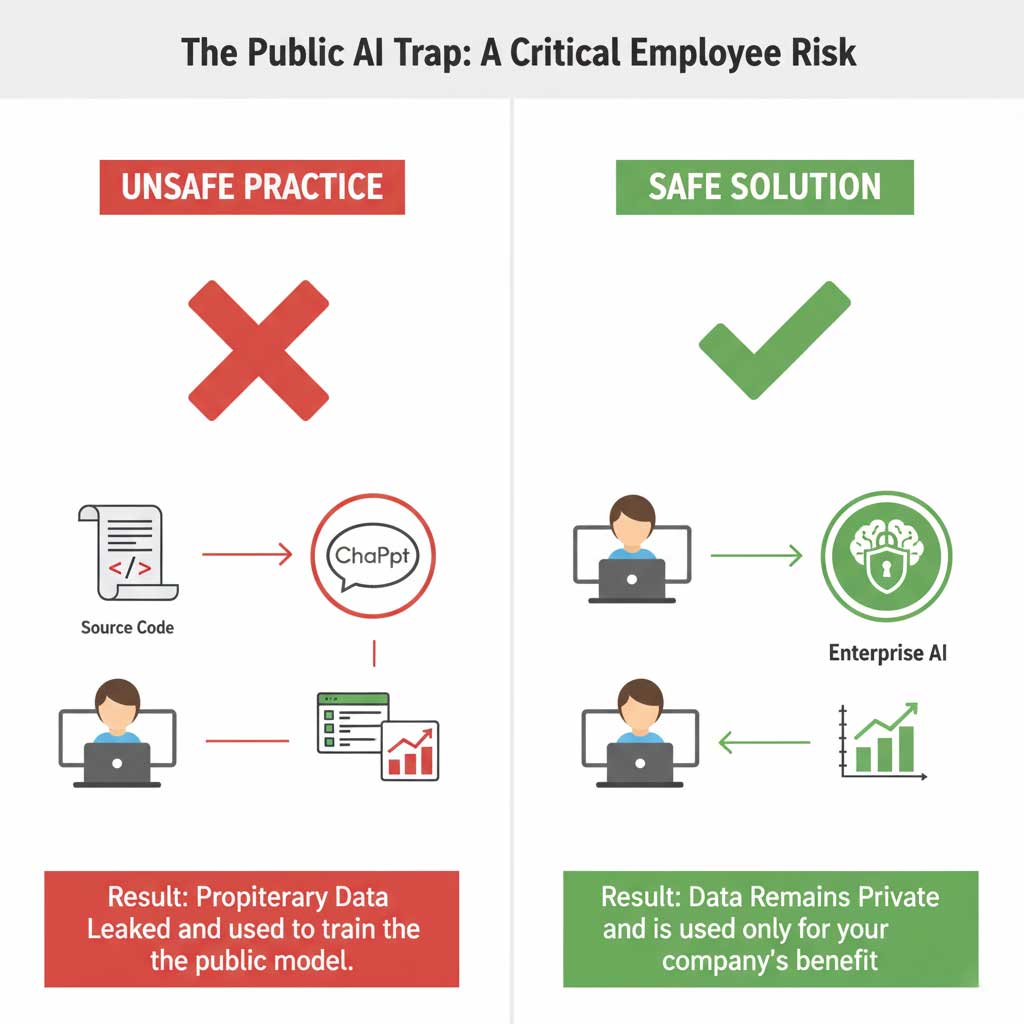
Instance: The Dangers of ChatGPT for Business
The rise of generative AI data privacy concerns provides a perfect example. In a widely publicized incident, employees at Samsung were found to have pasted confidential, proprietary source code into the public version of ChatGPT to ask for help with their work. This sensitive data was then absorbed by the model, effectively leaking company secrets. This highlights the critical need for clear policies and training regarding the dangers of ChatGPT for business and other public AI tools.
Risk #3: Insecure Third-Party Integrations
Your core AI marketing platform might be a fortress, but what about the five other marketing apps it’s connected to? Every third-party tool you integrate into your AI system represents a potential new doorway for attackers. A vulnerability in a small, seemingly insignificant app can be used as a backdoor to compromise your entire marketing data ecosystem.
Risk #4: Algorithmic Vulnerabilities
This is a more advanced threat, but it’s a growing concern in the world of AI marketing data security. Researchers have demonstrated that it’s possible for attackers to “reverse-engineer” an AI model. Through sophisticated techniques like “model inversion” attacks, a bad actor can probe an AI with specific queries to try and deduce the private, sensitive data it was trained on.
Risk #5: Compliance Failures and Legal Penalties
The risk isn’t just the technical breach itself; it’s the massive financial and reputational fallout from failing to comply with data privacy laws. For US businesses, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a major factor. An intentional violation of the CCPA can result in fines of up to $7,500 per individual violation. For a breach affecting thousands of customers, these penalties can easily climb into the millions, not to mention the loss of customer trust that can cripple a brand.
The Mark of a Secure AI Tool: Your Vendor Vetting Checklist
The foundation of good AI marketing data security is choosing the right partners. Not all secure AI marketing tools are created equal, and performing thorough due diligence before you sign a contract is non-negotiable. An AI vendor security evaluation should be a standard part of your procurement process.
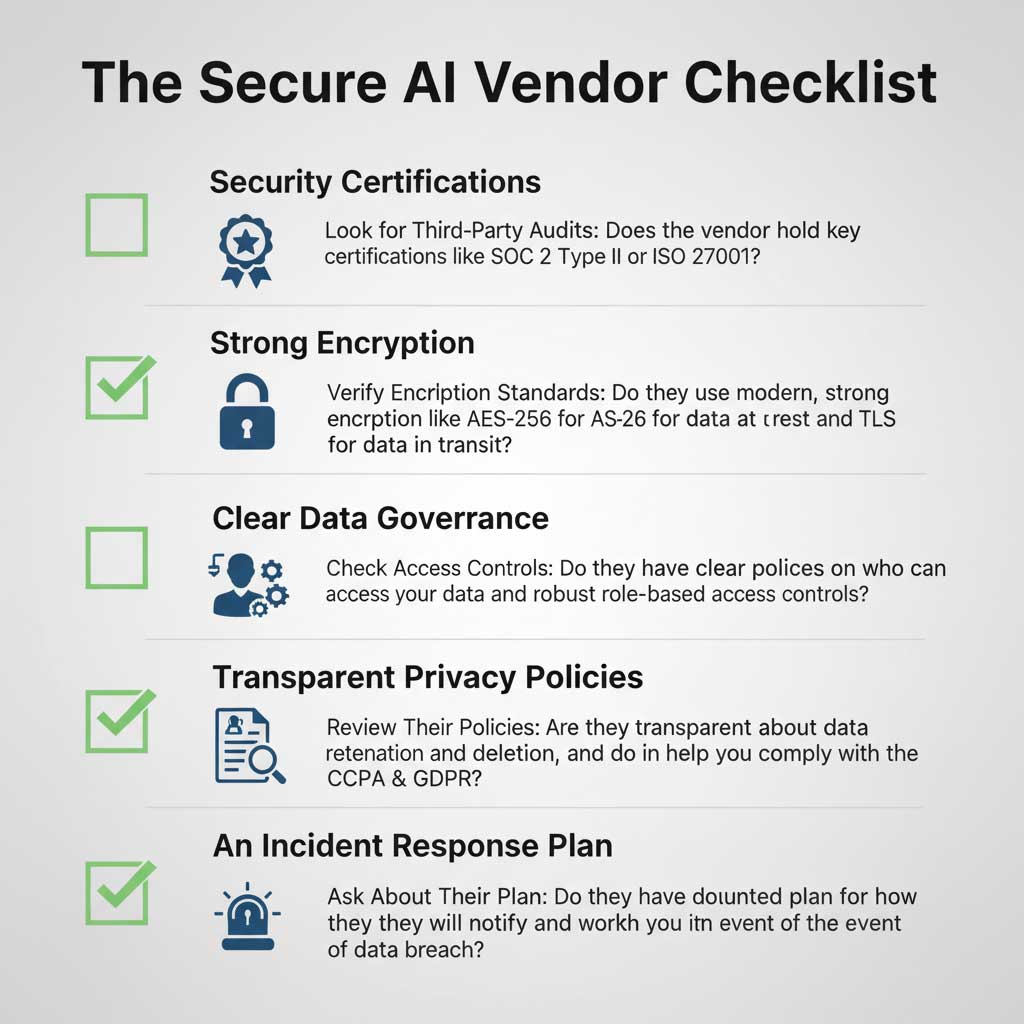
How to Conduct an AI Vendor Security Evaluation
You don’t need to be a cybersecurity expert to ask the right questions. A vendor’s willingness and ability to provide clear, confident answers to the following is a strong indicator of their commitment to protecting your data.
Key Questions to Ask Your AI Marketing Vendor
| Security Domain | The Core Question to Ask | The “Red Flag” If They Can’t Answer Clearly |
| Certifications | “What security certifications do you hold, like SOC 2 or ISO 27001?” | No third-party audited certifications to verify their claims. |
| Legal Compliance | “How does your platform help us maintain CCPA and GDPR compliance?” | They are unclear on how their features support regulatory needs. |
| Data Encryption | “Do you use current, end-to-end encryption standards like AES-256?” | Vague answers or use of outdated, vulnerable standards. |
| Data Governance | “What are your specific policies on who can access our data and when?” | Lack of clear, strict role-based access control policies. |
| Data Storage | “Where is our customer data physically stored?” | They cannot provide clear information on data residency. |
| Data Retention | “What is your policy for data retention and complete data deletion?” | Vague or indefinite retention policies that increase risk. |
| Incident Response | “Can you provide your documented data breach incident response plan?” | They have no formal, documented plan for how to handle a crisis. |
| Vendor Security | “What is your process for vetting the security of your own third-party tools?” | They have no clear process for securing their own supply chain. |
After the table, a crucial takeaway is that a vendor’s transparency is just as important as their technical specifications. If a vendor is evasive or dismissive of your security questions, that is a major red flag. True partners in AI marketing data security will welcome these discussions.
Your Company’s Responsibility: Best Practices for How to Secure Customer Data
Choosing a secure tool is only half the battle. The security of your data ultimately depends on the policies, processes, and culture you build within your own organization. AI marketing data security follows a shared responsibility model: the vendor is responsible for the security of the cloud, but you are responsible for security in the cloud.
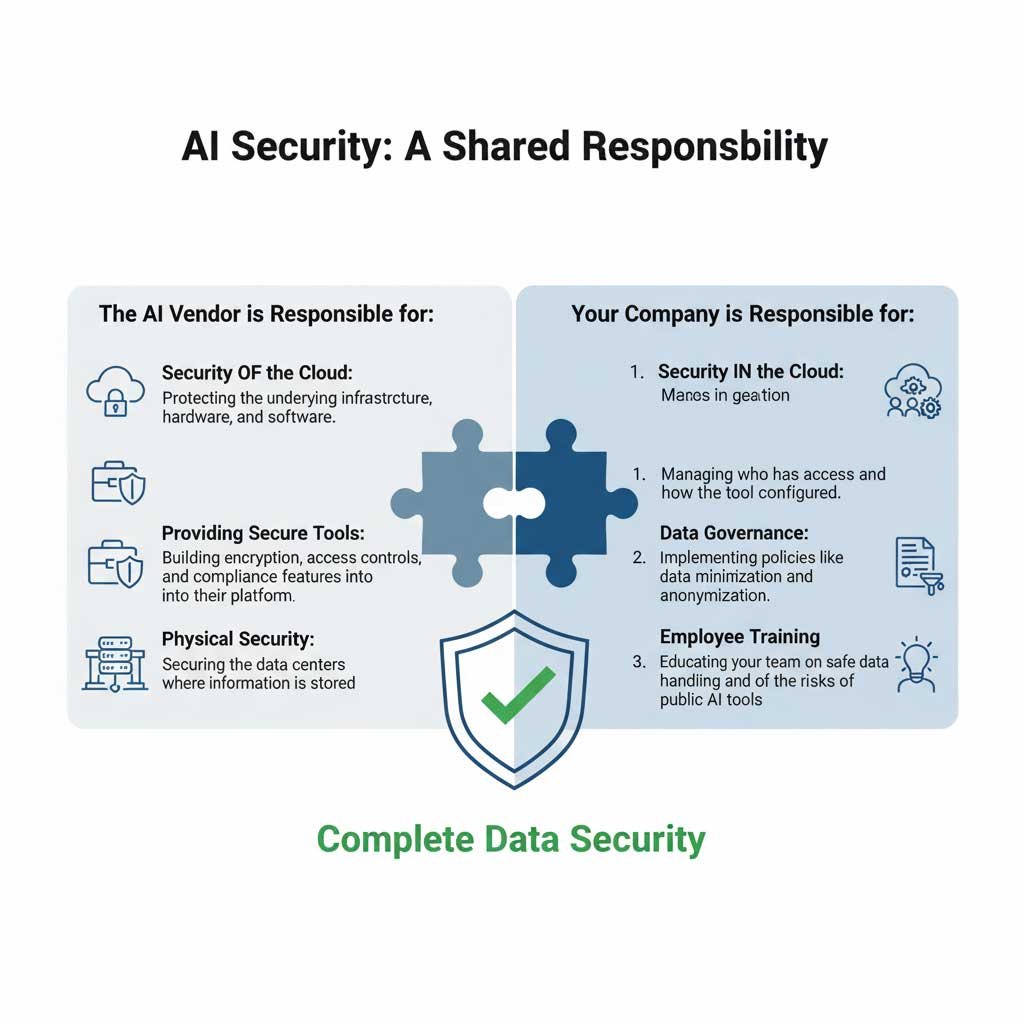
Security is a Partnership: Your Role in the Shared Responsibility Model
Here are the essential best practices for how to secure customer data when using AI tools.
Practice #1: Implement Data Minimization
This is one of the most effective yet simple data minimization best practices. The principle is straightforward: only collect, store, and process the data that is absolutely necessary to achieve your specific, defined marketing objective. The less data you hold, the lower your risk profile if a breach does occur.
Practice #2: Embrace Data Anonymization Techniques
Whenever possible, you should remove personally identifiable information (PII) from your datasets before feeding them into an AI for analysis. Data anonymization techniques like tokenization or aggregation allow your AI to identify broad market trends and customer patterns without exposing the identities and private information of individual customers.
Practice #3: Enforce Strict Access Controls
Not everyone on your marketing team needs access to every piece of customer data. Implement the “principle of least privilege,” which means each employee should only have access to the specific data and tools they need to do their job. This dramatically reduces the risk of both accidental and malicious data exposure from insiders.
Practice #4: Mandate Rigorous Employee Training
Your employees are your first line of defense. Regular, mandatory training is essential. This training must cover your company’s data governance policies, how to spot and avoid phishing attacks, and, critically, a strict and explicit prohibition on entering any sensitive company or customer data into public, non-vetted AI tools. This is your most important defense against generative AI data privacy risks.
Practice #5: Choose Your Architecture: Cloud AI Security vs. On-Premise
A common question is whether to use a cloud-based AI tool or an on-premise one. While on-premise solutions offer maximum control, they are incredibly expensive to purchase and require a dedicated, expert-level security team to maintain. For the vast majority of businesses, a reputable cloud provider (like Amazon Web Services or Google Cloud) offers far superior security. The investment these companies make in cloud AI security is something no single business could hope to match.
Ethics, Privacy, and Building Trust in the AI Era
Beyond the technical aspects of security, there is a deeper conversation to be had about the responsible use of customer data. The long-term success of AI marketing depends on maintaining customer trust, which requires a commitment to ethical practices and transparency.
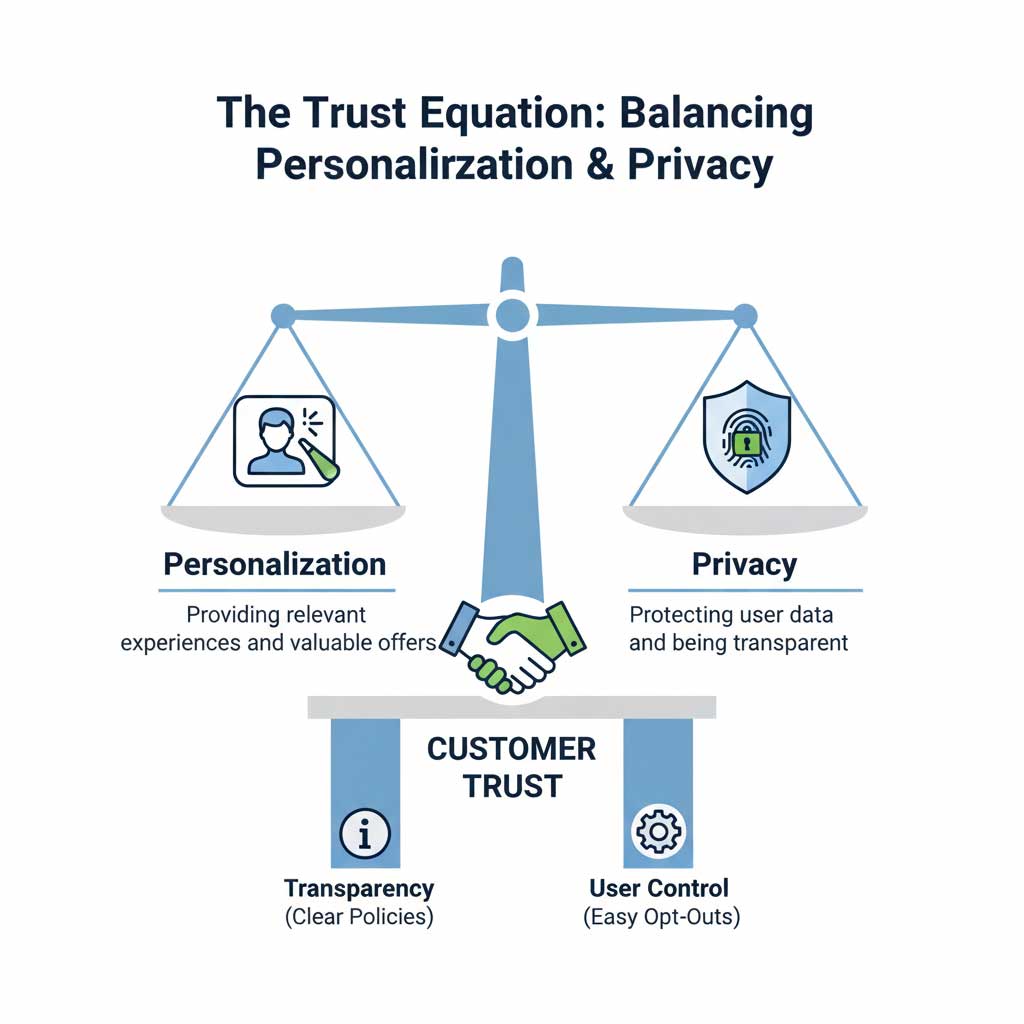
The Critical Conversation around Ethics in AI Marketing
The core tension of data privacy in AI marketing is the “privacy paradox”: consumers report being highly concerned about their data privacy, yet they also demand and reward the highly personalized experiences that this data enables.
The solution to this paradox is radical transparency. Companies that are open and honest about what data they are collecting and how they are using it to provide a better service are the ones that will win customer trust.
Balancing Personalization and Privacy
Balancing personalization and privacy is not about choosing one over the other; it’s about finding a respectful equilibrium. This can be achieved by:
- Giving Consumers Control: Provide customers with a clear, easy-to-use privacy dashboard where they can control what data is collected and how it is used.
- Focusing on a Value Exchange: Frame data collection as a clear trade. Be explicit: “By allowing us to use your browsing data, you will receive more relevant product recommendations and exclusive offers.” This turns the interaction from surveillance into a mutually beneficial relationship and is the cornerstone of building trust around data privacy in AI marketing.
Conclusion: Making AI Marketing Secure by Design
The question of how secure is data when using AI marketing tools does not have a simple yes or no answer. The reality is that AI marketing data security is not an automatic feature; it is a deliberate and ongoing strategy. It relies on a robust partnership—a shared responsibility model—between the AI vendor who builds the secure infrastructure and the business that uses it wisely.
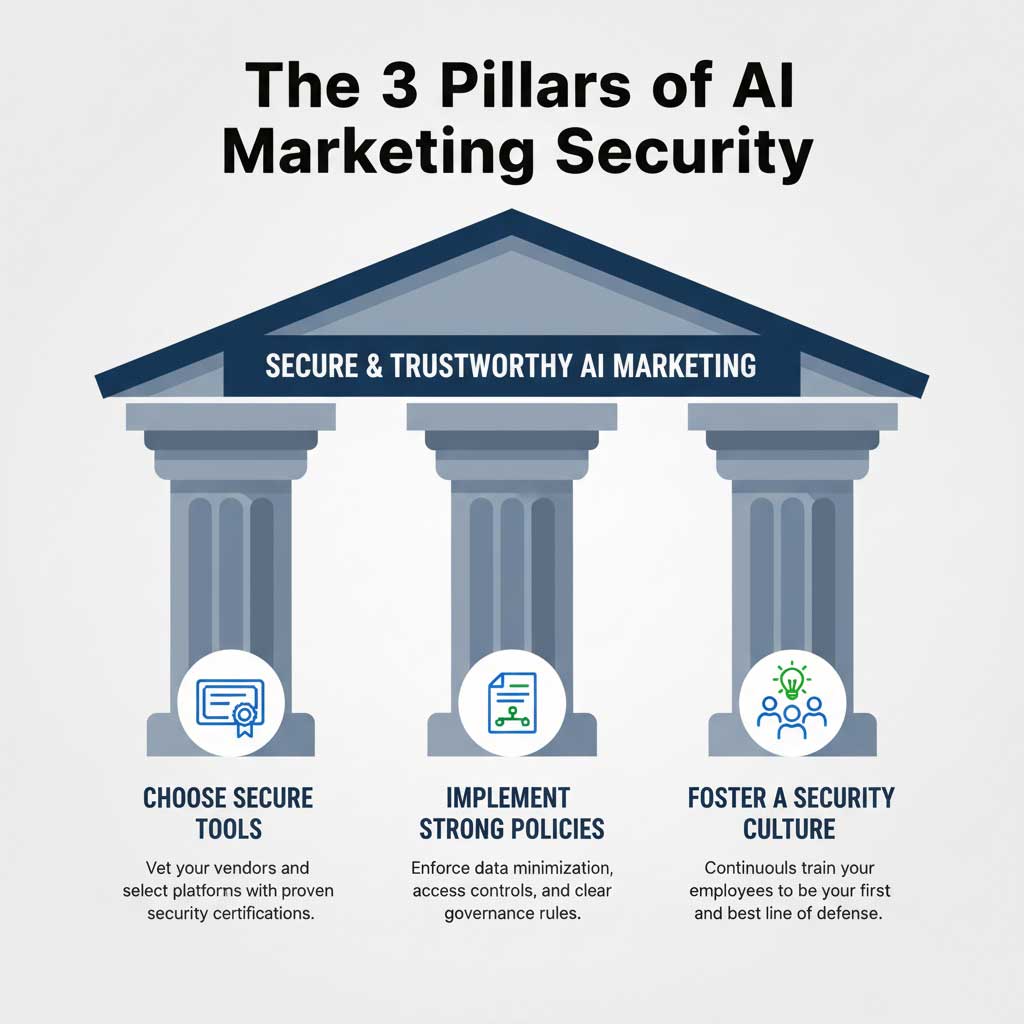
True security is built on a three-pronged approach:
- Choosing Secure Tools: Diligently vetting your vendors and selecting platforms with proven, certified security measures.
- Implementing Strong Policies: Creating and enforcing strict internal rules for data governance, access, and use.
- Fostering a Security Culture: Continuously training your team to be the first and best line of defense.
By following this framework, you can move forward with confidence. Security should not be viewed as a barrier to innovation, but as the essential foundation upon which trustworthy, ethical, and highly effective AI marketing is built.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is a cloud-based AI tool less secure than one I host myself?
For most businesses, a reputable cloud-based tool is actually more secure. Major cloud providers like AWS and Google invest billions in security, a level of protection that is nearly impossible for an individual company to replicate with an on-premise system.
2. What is SOC 2 compliance, and why does it matter for an AI vendor?
SOC 2 is an auditing procedure that ensures a service provider securely manages your data to protect the interests of your organization and the privacy of its clients. A vendor with SOC 2 compliance AI has had its security policies and controls independently verified, providing a high level of assurance.
3. My employees use the free version of ChatGPT for work. Is that a real risk?
Yes, it is a massive risk. Any data entered into the public version of ChatGPT can be used to train OpenAI’s models, meaning you are effectively leaking that data. This is why it is critical to have a strict policy against using public generative AI tools for any work involving confidential company or customer information.
4. What’s the difference between data anonymization and data encryption?
Data encryption scrambles data so it’s unreadable without a key, but the identity of the individual is still tied to the data. Data anonymization permanently removes personally identifiable information from a dataset, so that it’s impossible to link the data back to a specific individual.
5. How do I know if my company is compliant with CCPA for our AI marketing?
CCPA and AI marketing compliance requires, at a minimum, that you provide a clear privacy policy, inform customers what data you collect, and offer them an easy and accessible way to opt out of the “sale” or “sharing” of their personal information for targeted advertising.
6. Can AI itself be used to improve data security?
Yes. Cybersecurity is one of the fastest-growing applications for AI. AI-powered security tools can analyze network traffic to detect threats in real time, identify anomalies that might signal a breach, and automate responses to attacks far faster than a human team could.
7. What should be our first step if our AI marketing vendor has a data breach?
Your first step should be to activate your company’s predetermined incident response plan. This involves immediately contacting the vendor to understand the scope, identifying what customer data was affected, and preparing to notify affected individuals and regulatory bodies as required by law.
8. Are smaller businesses bigger targets for AI-related cyberattacks?
Smaller businesses are often seen as “softer” targets. They have valuable data but typically have fewer resources dedicated to cybersecurity than large corporations, making them more vulnerable to attacks.
9. What is a “data clean room” and how does it help with privacy?
A data clean room is a secure, neutral environment where two or more companies can bring their customer datasets together for joint analysis without either party having to share its raw, personally identifiable information with the other. It allows for collaborative insights while preserving privacy.
10. Does using AI for marketing automatically mean I’m violating my customers’ privacy?
No. Using AI is not inherently a privacy violation. A violation occurs when data is collected without proper consent, used for purposes the customer is unaware of, or is not adequately protected. Responsible, transparent, and secure use of AI can enhance the customer experience without violating privacy.










