Every time a marketer uses ChatGPT for copy, an analyst runs a query on a large language model, or a designer generates an image with DALL-E, they are accessing a global network of immense computational power. That network is now undergoing a monumental expansion in the American Midwest. The announcement of the OpenAI data center Michigan is not just a regional economic story; it’s a critical signal about the future scale, cost, and capabilities of the artificial intelligence tools that are reshaping digital industries. This development is a cornerstone of a much larger, globally significant strategy.
Table of Contents
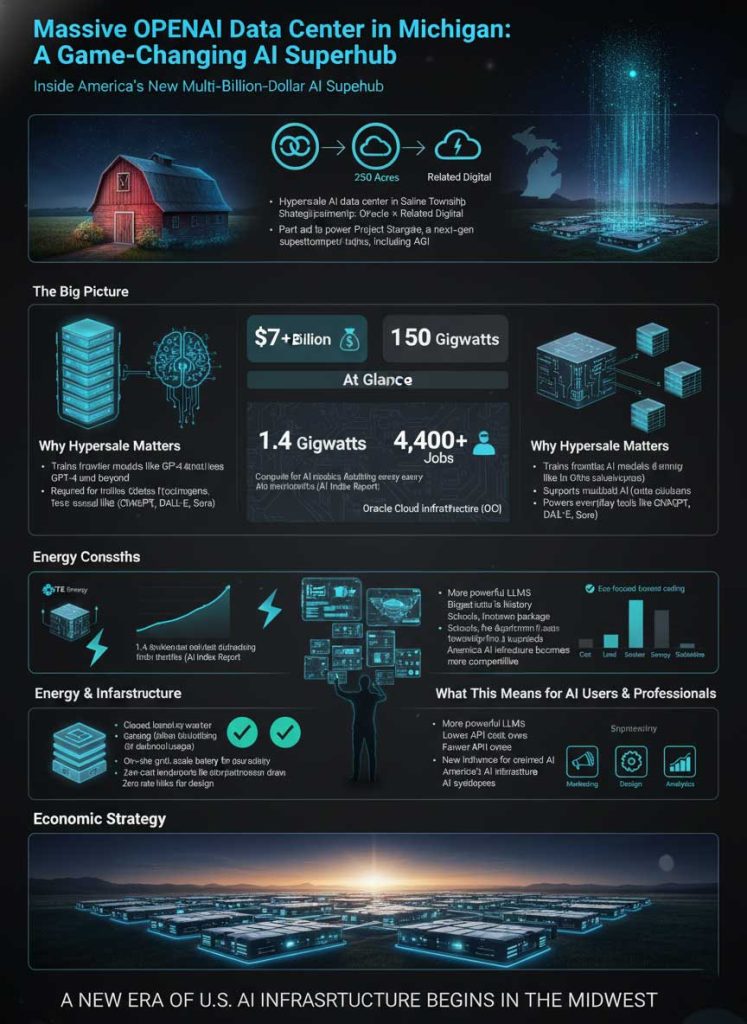
This article will provide a comprehensive analysis of the OpenAI, Oracle, and Related Digital hyperscale data center in Saline Township, moving beyond the headlines to explore its profound implications for AI infrastructure, energy consumption, economic strategy, and what it means for every professional whose work is becoming increasingly intertwined with AI. We will deconstruct this massive project to understand its foundational role in the next era of digital transformation, establishing the region as a pivotal Michigan AI development hub.
Project Stargate Michigan: Deconstructing the Multi-Billion Dollar AI Superhub
At the core of the digital revolution lies a physical reality: the data center. The new Ann Arbor hyperscale data center represents the next evolution of this reality, an infrastructure project of unprecedented scale and ambition designed specifically to fuel the future of artificial intelligence. Understanding its components is key to grasping its significance.
What is a Hyperscale Data Center and Why is it Essential for AI?
A standard data center might host websites or corporate data, but a hyperscale facility operates on an entirely different plane. These are colossal structures, often spanning hundreds of thousands of square feet, engineered for massive, scalable computing. They are the engine rooms of Big Tech, powering global cloud services and, most importantly, the voracious computational needs of AI.

Training large language models (LLMs) like those that power ChatGPT requires processing trillions of data points, a task that would be impossible without the concentrated power of a hyperscale environment. This is where Project Stargate Michigan comes in. It is the public name for OpenAI’s ambitious, multi-billion dollar initiative to build a series of supercomputers capable of developing the next frontier of AI, potentially leading to artificial general intelligence (AGI).
This venture is not a solo effort. It’s a strategic alliance between three key players:
- OpenAI: The world-renowned AI research and product laboratory, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with models like GPT-4 and Sora.
- Oracle: The enterprise technology giant providing the high-performance cloud infrastructure through its Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
- Related Digital: The specialized developer responsible for building the physical campus for the Related Digital data center Saline.
This new OpenAI data center Michigan is more than just another server farm; it’s a purpose-built supercomputing hub designed to solve the world’s most complex AI challenges.
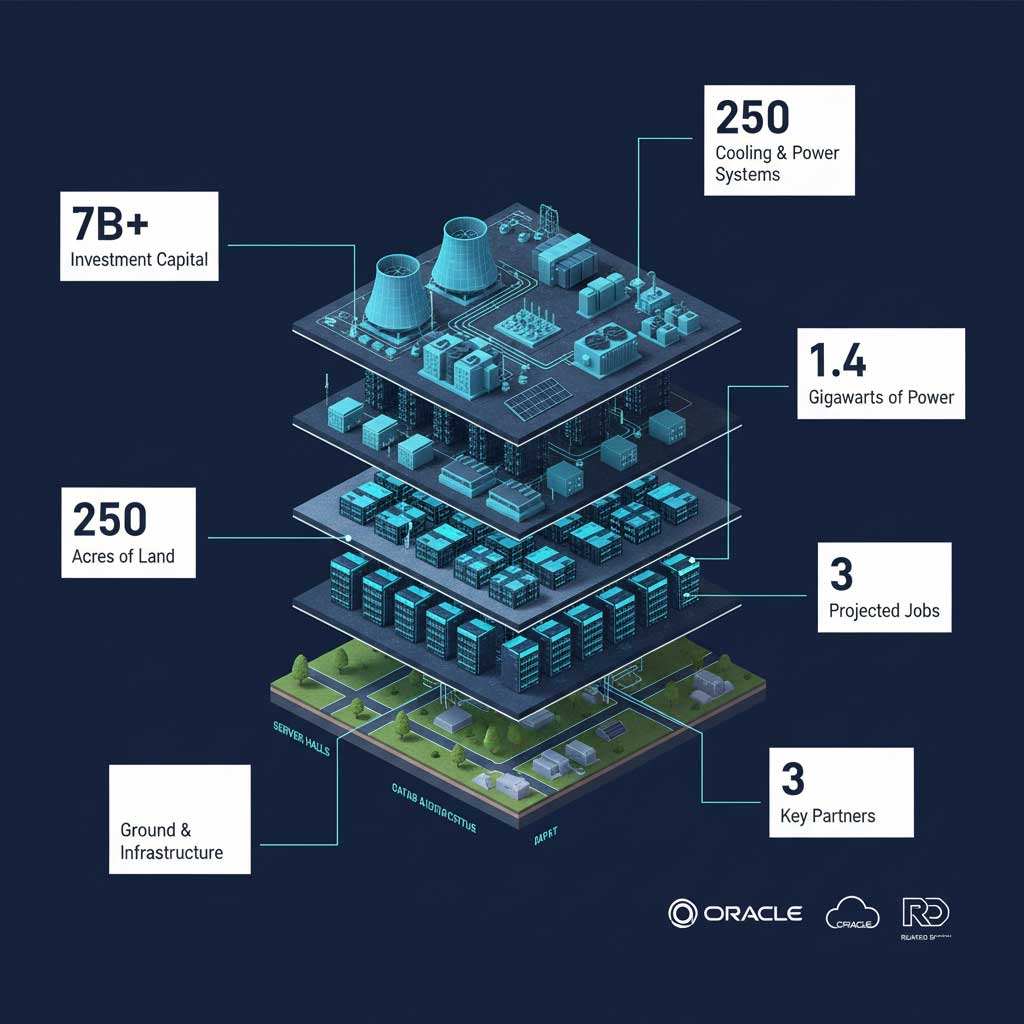
| Anatomy of the Michigan Stargate Project | Key Statistic |
| Total Estimated Investment | Over $7 Billion |
| Total Campus Size | 250 Acres |
| Projected Power Requirement | 1.4 Gigawatts |
| Total Jobs Created (Direct & Indirect) | Over 4,400 |
| Primary Cloud Partner | Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) |
The Technical & Economic Blueprint: Power, Politics, and Performance
Building an AI superhub involves navigating a complex web of technical challenges, economic incentives, and local politics. The Saline Township project serves as a masterclass in how these elements converge to create one of the most significant AI infrastructure projects USA has ever seen. The details reveal a carefully orchestrated plan for long-term growth and performance.
The 1.4 Gigawatt Question: Fueling the Insatiable Compute Demands of Generative AI
The headline figure that has drawn the most attention is the facility’s staggering 1.4-gigawatt power requirement. To put this in perspective, that’s enough energy to power over a million homes and represents a 25% increase in DTE Energy’s entire customer load. This massive figure directly addresses the issue of hyperscale data center energy consumption.
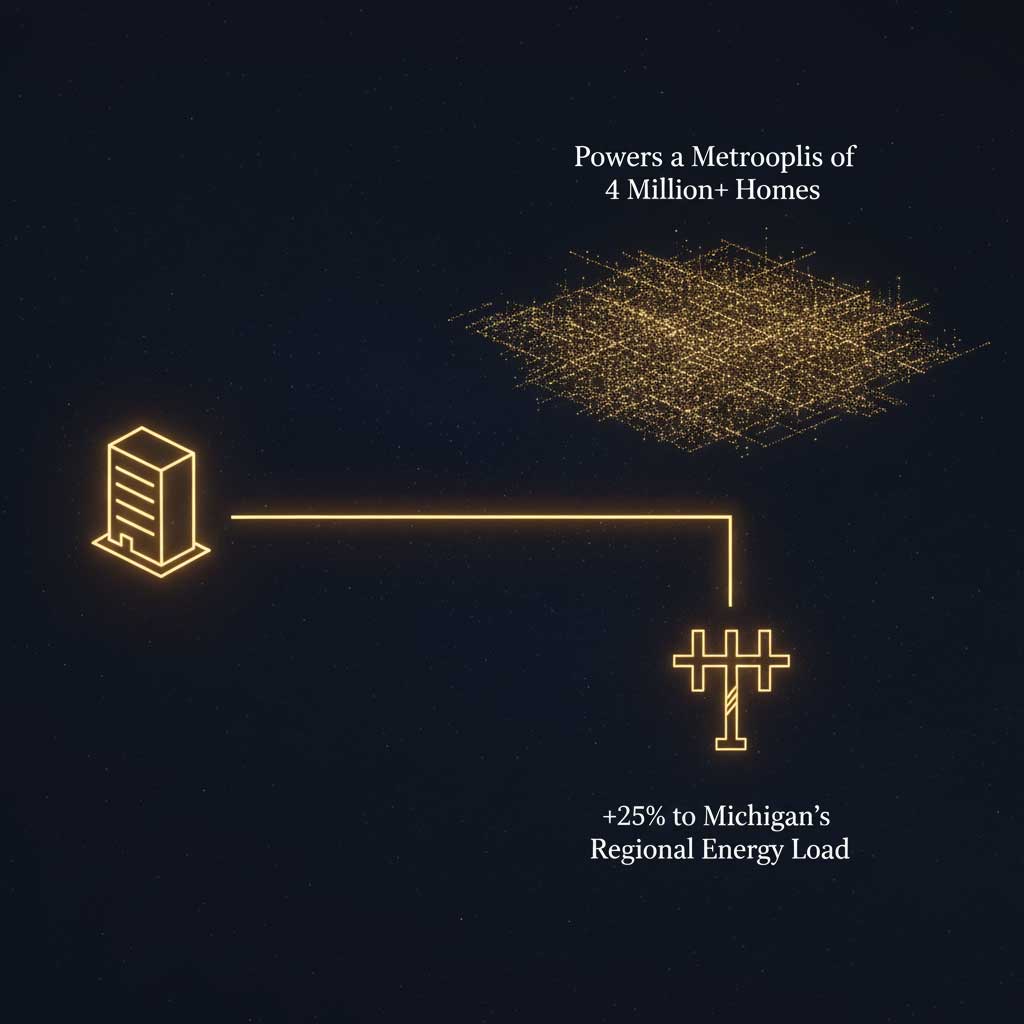
This immense need is driven by the exponential growth in computational power required to train frontier AI models. The leap from GPT-3 to GPT-4 saw training costs and energy demands skyrocket, a trend that continues with each new generation. According to the Stanford University AI Index Report, the compute used for training the largest AI models has been doubling every six months, a rate that far outpaces Moore’s Law. This hyperscale data center energy consumption is divided into two primary categories:
- AI Training: The intensely power-hungry process of building a model from scratch, which can take months and consume terawatt-hours of electricity.
- AI Inference: The ongoing energy cost of running queries on a trained model—every time a user prompts ChatGPT, it requires a small but significant amount of power.
The Ann Arbor hyperscale data center is being built to handle both at a scale that will define the next decade of AI development. The massive power draw is a direct reflection of the project’s ambition.
A New Model for Grid-Scale Energy Partnerships: The DTE Collaboration
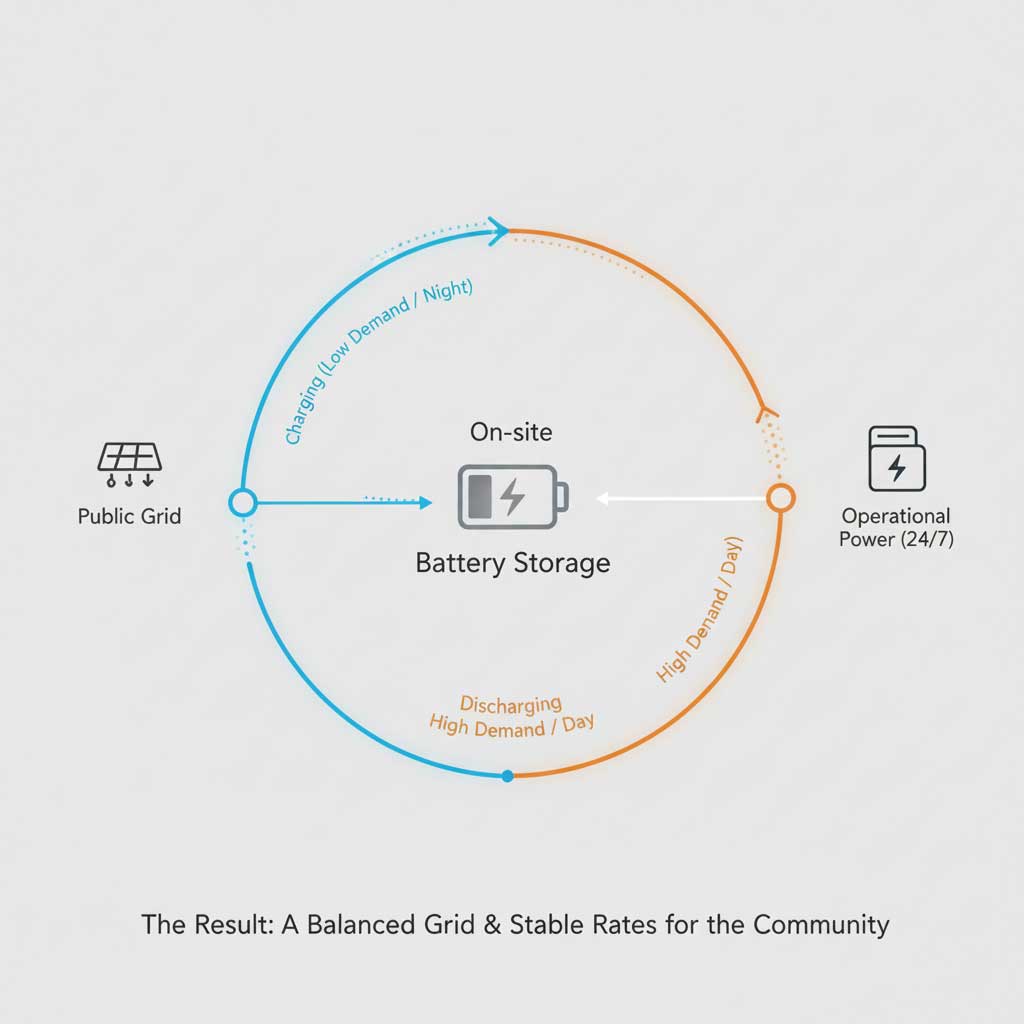
Such a colossal energy demand raises a critical question: How will the Ann Arbor data center impact DTE energy rates? The answer lies in the innovative DTE Energy data center partnership. In a move designed to mitigate public concern, DTE and the developers have structured a deal where the data center funds its own energy infrastructure upgrades.
This includes the construction of a massive, cutting-edge battery storage system on-site. This system will draw power from the grid during off-peak hours and discharge it during peak times, effectively acting as a shock absorber for the local energy grid. This ensures grid stability and prevents the project’s cost from being passed on to residential and commercial customers. This forward-thinking approach is a blueprint for how future AI infrastructure projects USA can be integrated into existing utility networks without disrupting service or raising costs for the public. The DTE Energy data center partnership is a landmark agreement in sustainable industrial development.
From Rust Belt to AI Belt: Why Michigan’s Economic Strategy is Paying Off
The decision to establish this Michigan AI development hub was no accident. It is the result of a deliberate and aggressive economic strategy by the state to attract high-tech investment. The economic impact of data centers is transformative, and Michigan has positioned itself to reap the rewards.
Several factors made the state an ideal choice:
- Strategic Incentives: In early 2025, Michigan extended its sales and use tax exemptions for data center equipment, a powerful financial incentive for a project of this magnitude.
- Geographic Advantages: The Midwest offers more affordable land, a cooler climate that naturally reduces cooling costs, and a lower risk of natural disasters compared to coastal tech hubs.
- Local Buy-In: Despite initial local opposition, a $14 million community benefits agreement was reached, allocating funds to local schools, fire departments, and farmland preservation. This demonstrated a commitment to being a long-term community partner.
This massive Michigan technology investment is a testament to the state’s successful pivot from traditional manufacturing to a future-focused, high-tech economy. The economic impact of data centers extends beyond direct jobs, creating a ripple effect that boosts local businesses, real estate, and skilled trades.
Strategic Implications for AI Professionals and Digital Marketing Leaders
While the headlines focus on construction and kilowatts, the true impact of the OpenAI data center Michigan will be felt in the digital realm. For marketers, content creators, and AI specialists, this massive expansion of computational power is not an abstract concept—it is the engine that will drive the next generation of tools and strategies that define their careers.
What More Compute Power Actually Means for Your AI Toolkit
More infrastructure isn’t just about making existing tools run faster; it’s about enabling entirely new capabilities. The development of this new Ann Arbor hyperscale data center directly translates to tangible advancements for AI users:
- More Powerful Models: The ability to train larger, more complex models will lead to AI that can understand nuance, generate higher-quality content, and perform multi-modal tasks like creating video from text with unprecedented realism.
- Lower API Costs: As infrastructure scales and becomes more efficient, the cost-per-query for using AI models through APIs is likely to decrease over time, making advanced AI accessible to smaller businesses and individual creators.
- Specialized and Fine-Tuned AI: With more compute available, there will be a greater capacity for creating fine-tuned models tailored to specific industries or tasks, such as AI assistants for legal research, medical diagnostics, or hyper-personalized marketing campaigns.
Digital marketing leaders should be planning their technology stacks and talent development with these future capabilities in mind. The future of AI infrastructure in the American Midwest is directly linked to the future of their toolkits.
The Rise of the Midwest AI Corridor vs. Traditional Tech Hubs
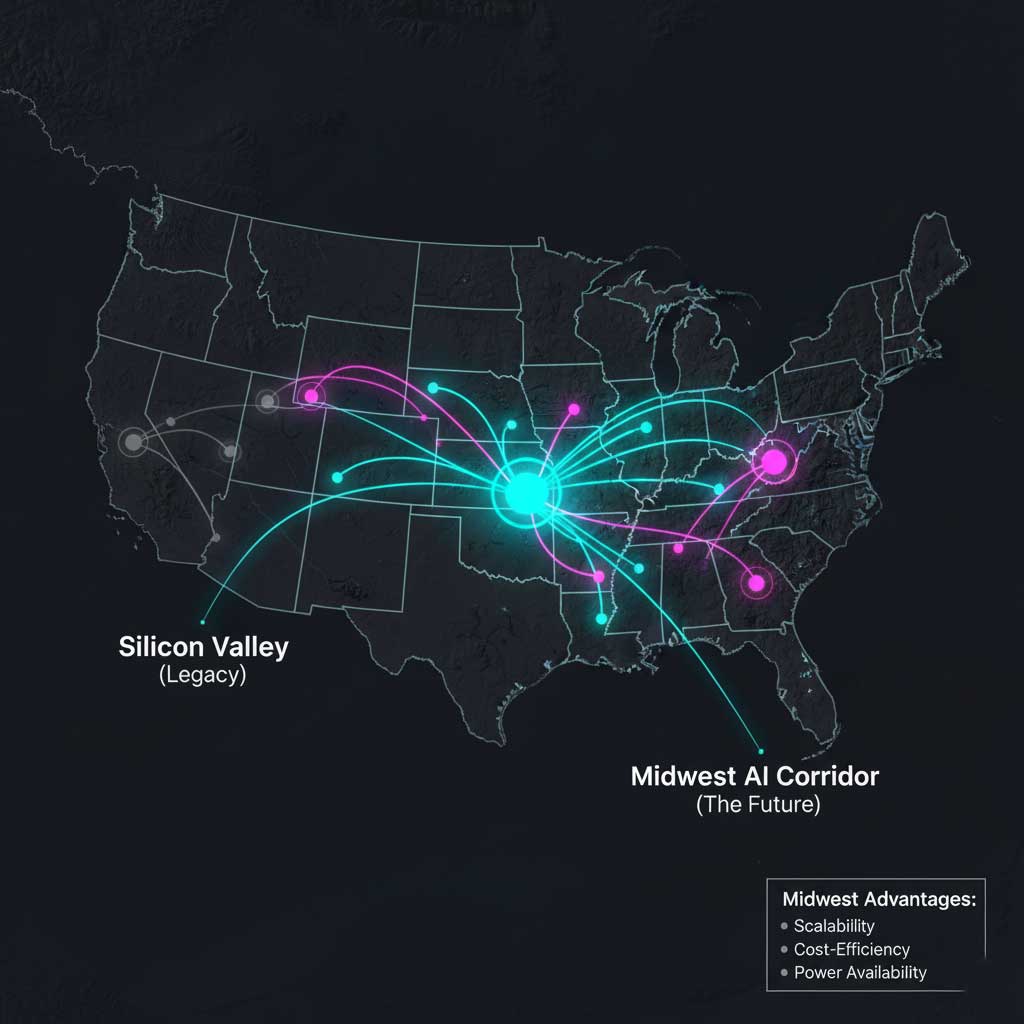
For decades, the tech world has revolved around Silicon Valley and Northern Virginia’s “Data Center Alley.” However, the immense land and power requirements of AI are forcing a geographic shift. The Michigan AI development hub is a key anchor in the emerging “Midwest AI Corridor,” which includes significant investments in Ohio and Indiana. This strategic shift is driven by clear economic and logistical advantages.
| Factor | Silicon Valley (CA) | Data Center Alley (VA) | Emerging Midwest Hub (MI/OH) |
| Land & Construction Cost | Extremely High | High | Moderate to Low |
| Energy Cost & Availability | High / Grid Strain | Moderate / Grid Congestion | Lower / More Available Capacity |
| Government Incentives | Limited | Established & Competitive | Aggressive & Expanding |
| Talent Pool | Highly Concentrated & Expensive | Strong & Established | Growing & More Affordable |
| Key Advantage | Proximity to Tech HQs | Proximity to Government/East Coast | Scalability & Cost-Efficiency |
This table illustrates why the future of AI infrastructure in the American Midwest is so bright. The region offers a sustainable and scalable model for growth that traditional hubs can no longer provide, making it a critical part of the national strategy for AI infrastructure projects USA.
The ESG Imperative: Navigating the Sustainability Conversation in AI
The immense hyperscale data center energy consumption has placed the AI industry under intense scrutiny from an Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) perspective. The initial local opposition in Saline Township, driven by concerns over energy and water use, highlights a growing trend.
Professionals in the AI space can no longer ignore the environmental impact of hyperscale AI data centers. The OpenAI data center Michigan is proactively addressing this with its commitment to sustainable data center cooling solutions. The project will utilize a closed-loop cooling system, which continuously recycles water for cooling servers. This technology reduces daily water consumption to a level comparable to a standard office building, a stark contrast to traditional data centers that can consume millions of gallons of water per day.
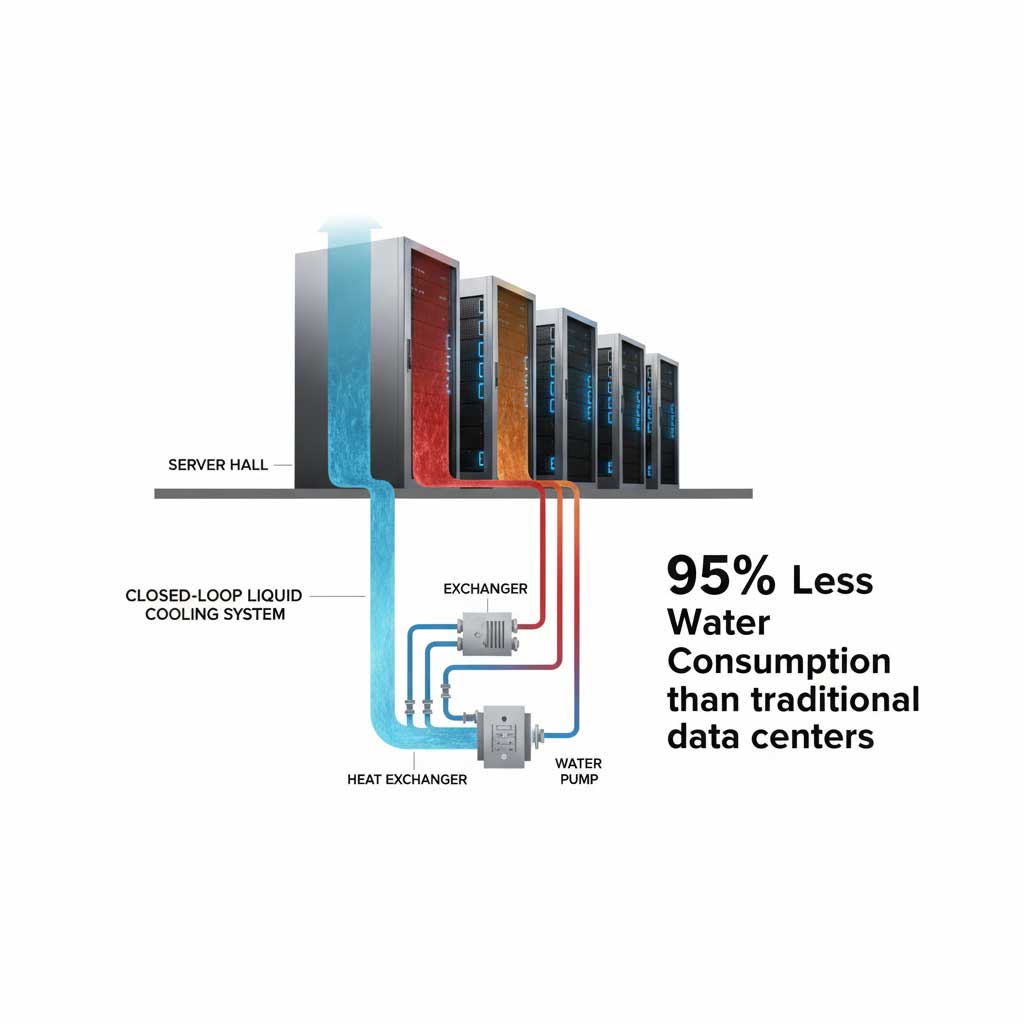
Understanding and communicating these sustainable practices is becoming a critical skill for marketers and brand managers in the tech industry. As customers and investors alike demand greater environmental responsibility, proving the sustainability of your AI pipeline will be a key competitive differentiator.
The Cloud Wars Supercharged: Comparing the AI Infrastructure Giants
The Project Stargate Michigan facility will not operate in a vacuum. It is a critical asset within the larger ecosystem of cloud computing, where giants like Oracle, Microsoft, Google, and Amazon are locked in a fierce battle for AI supremacy. The partnership between OpenAI and Oracle is a strategic power play designed to challenge the established market leaders. The choice of Oracle AI infrastructure Michigan is a significant vote of confidence in their high-performance computing capabilities.

This competition is good news for AI professionals, as it drives innovation and lowers costs. Understanding the key players and their unique strengths is essential for making informed decisions about which platform to build on.
| Cloud Platform | Key AI Services | Partnership with Major AI Labs | Key Differentiator | Recommended For |
| Oracle Cloud (OCI) | OCI Generative AI, Supercluster | Exclusive Cloud for OpenAI | High-performance computing for massive-scale model training at lower cost. | Enterprises needing dedicated, high-power compute for custom AI models. |
| Microsoft Azure | Azure AI, Azure OpenAI Service | Deep integration & investment in OpenAI | Seamless integration with Microsoft’s enterprise software suite (Office 365, Teams). | Businesses heavily invested in the Microsoft ecosystem. |
| Google Cloud (GCP) | Vertex AI, Gemini | Developer of its own models (Gemini) | Leading-edge AI/ML research and powerful data analytics tools (BigQuery). | Data-first companies focused on analytics and custom model development. |
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | Amazon Bedrock, SageMaker | Partner with Anthropic (Claude) | Broadest market share and most extensive portfolio of cloud services. | Organizations needing a wide variety of tools and maximum scalability. |
The decision to build the Related Digital data center Saline on Oracle AI infrastructure Michigan underscores Oracle’s successful push to capture the most demanding AI workloads, positioning them as a critical player in the future of the industry.
Summary & Key Takeaways: A Foundation for the Future of AI
The Massive OpenAI Data Center in Michigan is far more than a large construction project. It is a foundational piece of infrastructure that will enable the next wave of AI innovation, directly impacting everything from enterprise software to creative content generation. This venture is a clear indicator of the strategic direction of the entire tech industry.

This project signifies a strategic shift towards more powerful, geographically diverse, and increasingly sustainable AI development. For AI and marketing professionals, it promises access to more capable and efficient tools while demanding a greater awareness of the complex economic and environmental systems that power them. The Michigan technology investment seen here is a blueprint for the future.
The key takeaways are clear:
- Scale is the New Frontier: The future of AI is dependent on massive-scale, purpose-built infrastructure like the Ann Arbor hyperscale data center.
- The Midwest is a Power Player: The region has emerged as a critical hub for data center development, offering a scalable and cost-effective alternative to traditional tech centers.
- Sustainability is Non-Negotiable: The partnership between DTE Energy and the commitment to sustainable data center cooling solutions set a new standard for responsible industrial development.
The future of AI isn’t just being written in code; it’s being built with concrete and steel in places like Saline Township, Michigan. This is a game-changing project that will reverberate through the digital world for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is OpenAI really building a data center in Michigan?

Yes, OpenAI, in partnership with Oracle and Related Digital, is building a massive hyperscale data center campus in Saline Township, near Ann Arbor, Michigan, as a key site for its “Project Stargate.”
What is Project Stargate and its connection to Michigan?

Project Stargate is OpenAI’s multi-billion-dollar national initiative to build the supercomputing infrastructure required for developing next-generation AI. The Michigan site is a critical component of this plan.
Why is this data center important for digital marketers and AI users?

This massive increase in computing power will enable the development of faster, more sophisticated, and potentially more affordable AI tools, directly impacting the capabilities of platforms like ChatGPT, DALL-E, and other generative AI services.
How will the facility’s massive 1.4 GW energy demand be met?

DTE Energy will supply the power. Crucially, the data center is funding its own infrastructure upgrades, including a large-scale battery storage system, to ensure grid stability and prevent rate increases for existing residents.
What are the main economic benefits of the OpenAI data center for Michigan?

The project is expected to create over 4,400 jobs (construction and permanent), inject billions into the economy, and establish Michigan as a central hub in the growing “Midwest AI Corridor.”
What sustainable technologies will the data center use?

To minimize its environmental footprint, the facility will utilize a closed-loop cooling system, which significantly reduces water consumption compared to traditional data center cooling methods.
Why did OpenAI and its partners choose the Midwest over a traditional tech hub?

The Midwest offers strategic advantages like lower land and energy costs, a skilled workforce, and strong government incentives, making it an ideal location for cost-effective, large-scale infrastructure projects.
How does this Oracle partnership affect the cloud computing landscape?

It solidifies Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) as a premier platform for high-performance AI computing, intensifying its competition with Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and AWS for dominance in the AI infrastructure market.
What is the total investment in the OpenAI Project Stargate Michigan facility?

While exact figures are part of a broader national strategy, the investment for the Saline Township site and its related infrastructure is estimated to be in the multi-billion-dollar range, making it the largest economic project in Michigan’s history.
How was the community’s initial opposition to the data center resolved?
After initial concerns led to a rezoning denial, a settlement was reached that included a $14 million community benefits agreement. This fund will support local services, schools, and farmland preservation, addressing community needs while allowing the project to move forward.
What is the timeline for the Ann Arbor hyperscale data center?

Construction is slated to begin in 2026, with the facility expected to become operational in phases over the following years, pending final approvals from regulatory bodies like the Michigan Public Service Commission.
Will this data center only be used by OpenAI?

While built as a cornerstone for OpenAI’s needs, its development on Oracle’s cloud infrastructure means it enhances the overall capacity of OCI, potentially serving other high-performance computing clients and contributing to the broader cloud ecosystem.