The modern inbox is a hostile environment. Every morning, millions of Americans engage in a ruthless digital purge; they swipe left on generic newsletters and mass promotions that fail to respect their time or current needs. If your marketing strategy relies on blasting the same message to your entire list at a scheduled time, you are actively contributing to that noise. You are also leaving a significant amount of revenue on the table. The era of generic “batch-and-blast” is effectively dead. The era of behavioral email marketing has taken its place.
Table of Contents
Success in the current digital landscape is no longer about guessing when to speak; it is about listening. It is about letting the customer’s actions dictate the timing, tone, and content of the conversation. By leveraging email automation triggers, sophisticated marketers can deploy messages that land exactly when a user signals intent. This approach transforms the email channel from a megaphone into a responsive conversation.
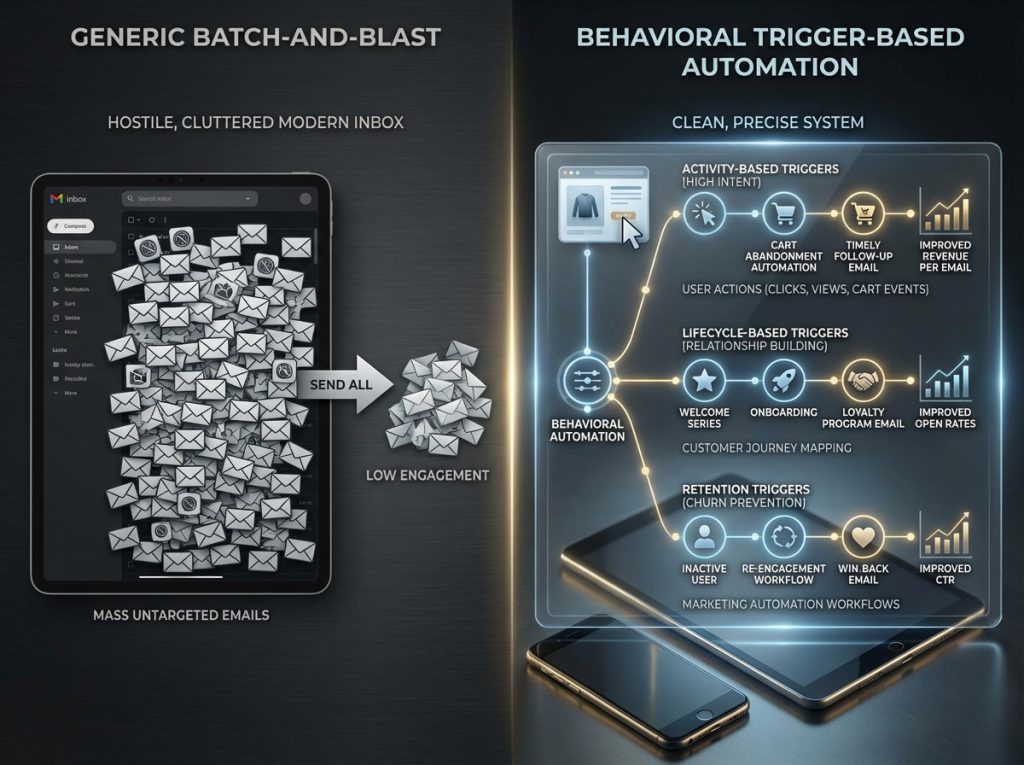
The difference in performance is not marginal. It is transformative. Industry data consistently reveals that automated email campaigns drive exponentially more revenue per email than non-automated ones. Furthermore, behavioral triggers—emails fired based on specific user actions—generate significantly higher open rates and click-through rates compared to standard scheduled campaigns.
This guide is a comprehensive deep dive into the mechanics of high-performance email strategy. We will dissect the three critical categories of triggers: Activity-Based Triggers (High Intent), Lifecycle-Based Triggers (Relationship Building), and Retention Triggers (Churn Prevention). We will explore advanced customer journey mapping, the technical implementation of cart abandonment solutions, and the precise marketing automation workflows required to maximize Email marketing ROI for years to come.
Core Concept: The Anatomy of Behavioral Email Marketing and Automation
To truly master this discipline, one must look beneath the surface of the software. Behavioral email marketing is not merely a feature in your ESP (Email Service Provider). It is a methodology that combines data science with consumer psychology.
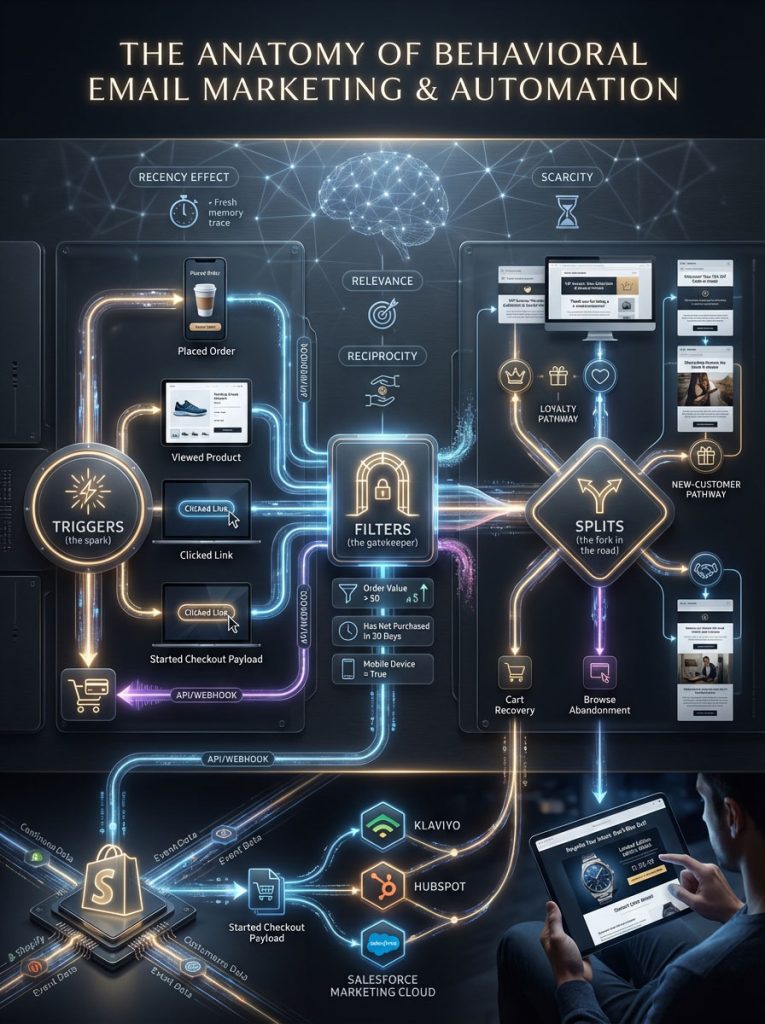
Distinguishing Between Triggers, Filters, and Splits in Automation
Many marketers fail because they conflate a trigger with a filter. Understanding the technical architecture of email automation triggers is the first step toward conversion rate optimization (CRO).
The Trigger is the spark. This is the event that initiates the workflow. It is binary; it either happened, or it didn’t. Examples include “Placed Order,” “Viewed Product,” or “Clicked specific link.” Without a clear trigger, automation cannot begin.
The Filter is the gatekeeper. This is the logic applied immediately after the trigger to qualify the user. For instance, a user might trigger a “Post-Purchase Flow,” but a filter set to “Order Value > $0” ensures that users who merely downloaded a free ebook do not receive the “Thank you for buying” email. Filters protect your brand from sending irrelevant content that leads to high unsubscribe rates.
The Split is the fork in the road. This is where dynamic content personalization happens. A conditional split might ask: “Has this user purchased before?” If yes, they go down Branch A which focuses on loyalty messaging. If no, they go down Branch B which focuses on introduction and brand storytelling.
Leading platforms like Klaviyo, HubSpot, and Salesforce Marketing Cloud utilize APIs and Webhooks to process this data in real-time. When a user creates a “Started Checkout” event on an e-commerce platform like Shopify, a webhook instantly transmits that data payload (items, price, image URL) to the ESP. This allows the automation to fire within seconds, ensuring the message arrives while the user is still psychologically engaged.
The Psychology of Relevance and Timing in User Engagement
Why do behavioral triggers outperform manual campaigns by such a wide margin? The answer lies in Robert Cialdini’s principles of influence; specifically Reciprocity and Scarcity; combined with the “Recency Effect.”
A standard newsletter is irrelevant to the vast majority of its recipients at the moment it arrives. However, a browse abandonment flow arriving two hours after a user viewed a specific pair of boots is hyper-relevant. The user is still thinking about the boots. The neural pathway is still active. By injecting a reminder with dynamic product blocks showing those exact boots, you are reducing the cognitive load required to return and purchase. This alignment of message and mindset is the “secret sauce” of high user engagement metrics.
Type 1: Activity-Based Triggers for High Intent Acquisition and Revenue Recovery
The first category of triggers focuses on immediate user actions. These are your “Revenue Rescue” workflows. These users are active; they are browsing; and they have high commercial intent. Your goal here is to remove friction and facilitate the transaction.

Implementing Cart Abandonment Solutions to Recover Lost Revenue
The abandoned cart email is the single most profitable workflow in eCommerce history. However, the standard “You forgot something” approach is outdated. To dominate the market, you need advanced cart abandonment solutions that utilize segmentation and psychological framing.
The Multi-Stage Drip Campaign Strategy:
Email 1: The Service Nudge (45 Minutes – 1 Hour Delay)
The goal here is customer service, not sales. The subject line might read: “Was there a problem checking out?” The content should ask if they had technical issues or needed help with payment methods. Display the cart contents clearly using dynamic product blocks. Do not offer a discount yet. You want to capture full margin from high-intent buyers who simply got distracted.
Email 2: The Social Proof Injection (12 – 24 Hours Delay)
The goal here is to build trust. If the user hasn’t bought yet, they might be doubting the product quality. The content should say: “See what others are saying about this item.” Pull in 5-star reviews specifically for the category or product in the cart. This addresses the “fear of regret” that often causes abandonment.
Email 3: The Scarcity and Incentive (48 Hours Delay)
The goal here is conversion at any cost. The content should warn: “Your cart is expiring.” Now is the time to offer a 10% discount or free shipping to close the deal.
Advanced Segmentation Tip:
Do not treat all carts equally. Split your flow based on Cart Value. For a cart value over $200, alert your customer support team to reach out personally via a concierge approach. For a cart value under $50, stick to an automated flow with a small coupon.
Deploying Browse Abandonment Flows for The “Invisible” Lead
Cart abandonment captures users who almost bought. Browse abandonment triggers capture users who were “just looking.” This is a massive, often untapped segment of potential revenue.
The Trigger Logic:
The event is “Viewed Product.” The filter is “Added to Cart zero times” AND “Placed Order zero times” since starting the session. The timing is typically a 2 hour delay.
Example Scenario:
A user visits MobileFun and looks at three different iPhone cases but leaves. Two hours later, they receive an email: “Still looking for protection?” The email displays the last case they viewed, plus two “Best Seller” alternatives. This strategy keeps the brand top-of-mind without being aggressive. To execute this, you must have first-party cookies active to track the user and link their browsing behavior to their email profile.
Search Abandonment Strategies for High-Intent Shoppers
A user who utilizes your on-site search bar converts at significantly higher rates than a user who simply browses navigation menus. They know exactly what they want. If they search but don’t buy, this is a critical behavioral trigger.
The Strategy:
If a user searches for “Winter Waterproof Boots” and leaves, trigger an email featuring your “Top Rated Waterproof Boots.”
Subject Line: “We found what you were looking for.”
This level of dynamic content personalization feels like a helpful shopping assistant rather than a marketing bot. It proves you are paying attention to their specific needs.
Leveraging Checkout Abandonment for Critical Conversion Failures
Checkout abandonment is distinct from cart abandonment. This trigger fires when a user enters their information on the checkout page but fails to complete the payment. This indicates a critical failure; perhaps their card was declined, or they were surprised by shipping costs.
The Strategy:
Send this email within 15 to 30 minutes. Focus entirely on trust and logistics. Display “Secure Payment” badges. Reiterate your return policy. Offer a direct link to customer support. The intent here is to reassure the user that their transaction will be safe and easy.
Benchmarking High-Intent Activity Triggers
The following table illustrates the comparative performance of high-intent activity triggers based on industry averages. Use this to benchmark your own user engagement metrics.
| Trigger Type | Intent Signal Strength | Recommended Delay | Content Strategy | Avg. Open Rate | Avg. Conversion Rate |
| Cart Abandonment | Extremely High | 1 Hour | Service Reminder + Social Proof + Discount | 45% – 50% | 3.5% – 5.0% |
| Browse Abandonment | Medium | 2 – 4 Hours | “Did you see this?” + Recommended Alternatives | 35% – 40% | 1.0% – 2.5% |
| Search Abandonment | Medium-High | 1 – 3 Hours | Curated search results based on keywords | 38% – 42% | 1.5% – 3.0% |
| Checkout Abandonment | Critical | 15 – 30 Mins | Trust badges + Payment reassurance + Support Link | 50% – 60% | 4.0% – 8.0% |
Type 2: Lifecycle-Based Triggers for Customer Journey Mapping and Nurturing
While activity triggers capture immediate demand, lifecycle-based triggers are designed to nurture the relationship over time. These workflows align with customer journey mapping; moving a user from “Awareness” to “Advocacy.”
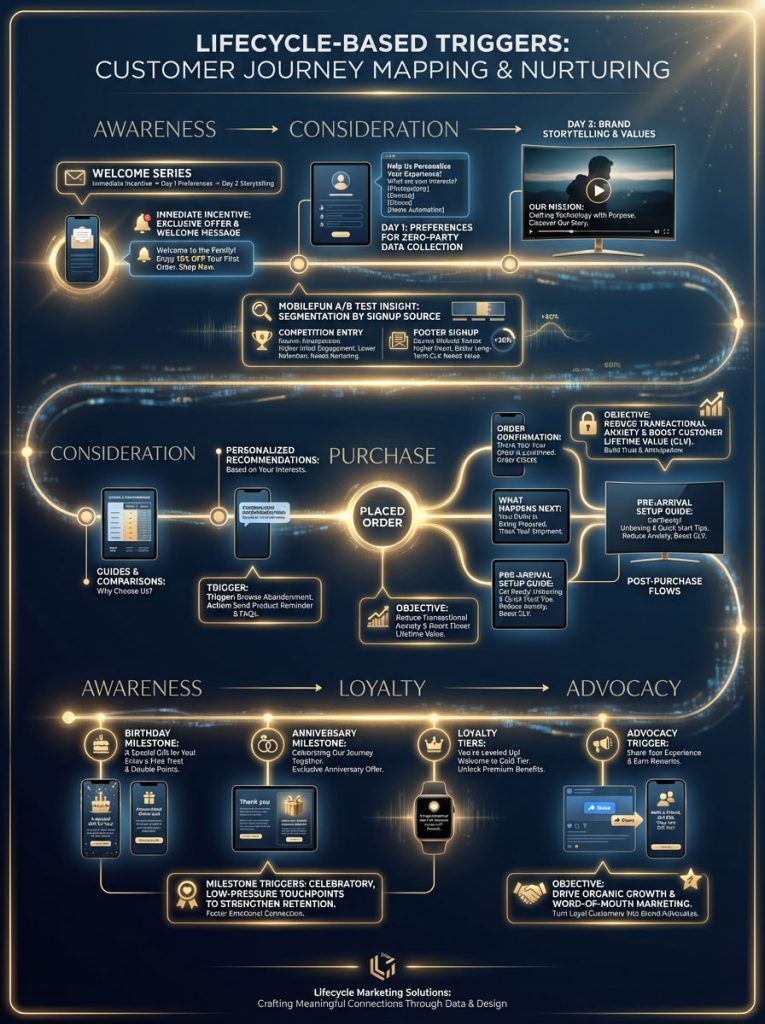
Optimizing The Welcome Series for Long-Term Value and Onboarding
The Welcome Series is the most frequently sent automation; yet it is often the most under-optimized. It typically generates significantly higher open rates and click rates than a standard newsletter. This is your prime opportunity to set expectations and gather data.
The “Onboarding” Approach:
Do not just deliver a coupon code and disappear. Use the welcome flow to collect preferences (Zero-Party Data) that will fuel future segmentation.
Email 1 (Immediate): Delivery of the sign-up incentive (PDF, Discount Code).
Email 2 (Day 1): Ask for preferences. “What are you interested in? Men’s, Women’s, or Kids?”
Email 3 (Day 3): Brand storytelling. Why do you exist? What are your values?
MobileFun Case Study Insight:
By utilizing A/B testing on their welcome sequence, MobileFun discovered that splitting their flow based on the source of the signup (e.g., Competition Entry vs. Footer Signup) drastically improved quality. Competition entrants needed more brand education to convert; while footer signups were ready to buy immediately.
Mastering Post-Purchase Flows to Reduce Transactional Anxiety
For B2B and SaaS companies, the post-purchase (or post-signup) phase is critical. This is where onboarding happens. For eCommerce, the moment a customer enters their credit card details, they experience “Transactional Anxiety.” Did it work? When will it arrive? Is this a scam?
The “Peace of Mind” Trigger:
The trigger is “Placed Order.” The content should be an Order Confirmation plus a “What happens next” guide.
Expansion: For products requiring setup (like tech gadgets or skincare), send a “How to use” guide to arrive before the package does. This builds excitement and reduces returns and customer support tickets. This is a prime example of boosting Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) through service.
Leveraging Milestone Marketing and Drip Campaign Strategy
People love to be celebrated. Milestone triggers leverage dates to create engagement. These emails require zero sales pressure but often result in high conversion because they feel like a gift.
Key Milestone Triggers:
Birthdays: Collect birth dates in your welcome series or via a pop-up. Send a “Treat yourself” email.
Anniversaries: “It’s been 1 year since your first order.”
Loyalty Tiers: “You’ve just unlocked VIP status.”
These triggers should be part of a broader drip campaign strategy that prioritizes retention. By acknowledging the user’s history with the brand, you validate their loyalty; making them less likely to switch to a competitor.
Type 3: Retention and Re-engagement Triggers to Prevent Churn
In the highly competitive US market, acquiring a new customer is 5x to 25x more expensive than retaining an existing one. Retention triggers are your defensive line. They utilize predictive analytics in email to identify when a user is drifting away.
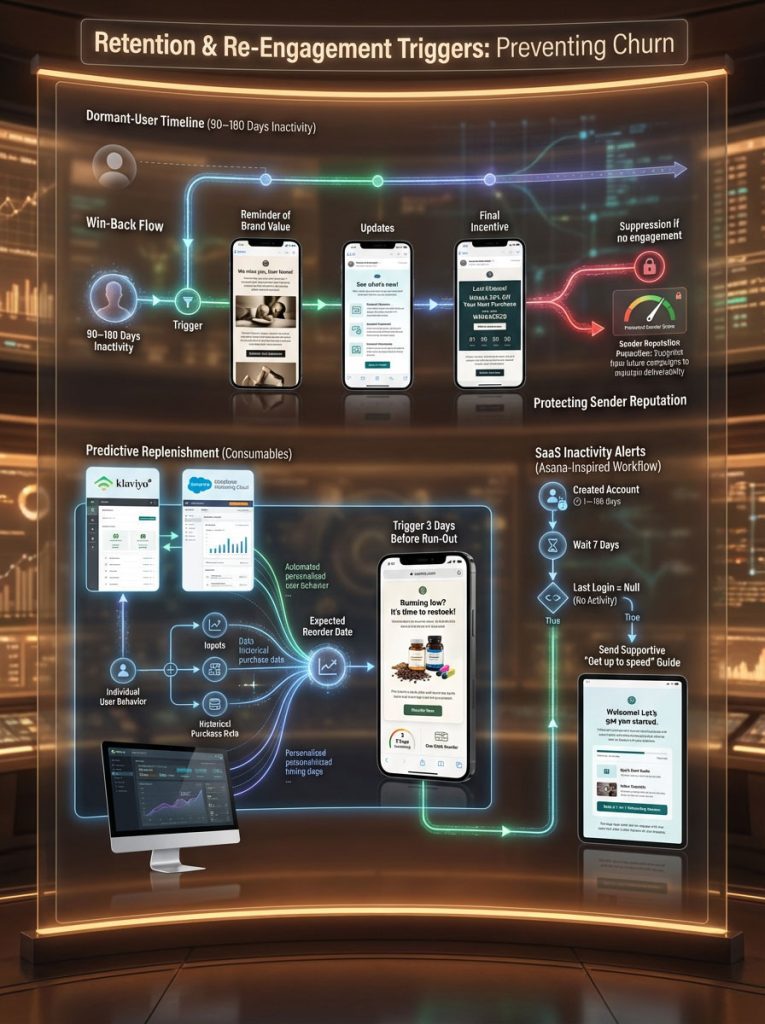
Executing The Win-Back Flow to Reactivate Dormant Users
A user is considered “dormant” or “at-risk” if they haven’t opened or clicked an email in a specific timeframe (e.g., 90 days) or haven’t purchased in a lifecycle-relevant period (e.g., 180 days).
The Strategy:
You must interrupt their pattern of inactivity.
Subject Line Ideas: “Is this goodbye?”, “We’ve made some changes,” “Come back for 20% off.”
The Content: Remind them of what they liked about your brand. Show them what is new.
The Ultimatum: If they don’t engage with the win-back flow, move them to a suppression list. Sending emails to unengaged users hurts your sender reputation and deliverability. Reducing churn with re-engagement trigger emails is vital for maintaining a healthy list hygiene.
Leveraging Predictive Analytics in Email for Replenishment
For consumable products such as coffee, shampoo, or dog food, predictive analytics in email is a game-changer.
The Algorithm:
If a customer buys a 1lb bag of coffee that typically lasts 3 weeks, a standard timer might be inaccurate. Klaviyo and Salesforce Marketing Cloud use algorithms to calculate the specific “Expected Date of Next Order” for that individual based on their past purchase cadence.
The Trigger: Fire email 3 days before the predicted run-out date.
Subject Line: “Running low?”
This timeliness creates a friction-free reordering process; significantly increasing Customer Lifetime Value (CLV).
Setting Inactivity Alerts and Churn Risk in SaaS
For B2B and SaaS platforms, engagement is not just about buying; it is about logging in. If a daily user suddenly stops logging in, that is a massive red flag.
Asana Case Study Example:
Asana utilizes “inactivity triggers.” If a user creates an account but doesn’t log in for 7 days, they trigger a “Get up to speed” email. This email doesn’t scold the user; it offers a “5-minute quick start guide” or a template to make getting started easier.
The Logic: Created Account > Wait 7 Days > Filter: Last Login = Null.
These marketing automation workflows catch the user at the moment they are losing interest; pulling them back into the ecosystem.
Advanced Strategy: Technical Implementation and Optimization
Strategy without execution is hallucination. To make these email automation triggers work, you need a robust technical setup and a commitment to data hygiene.
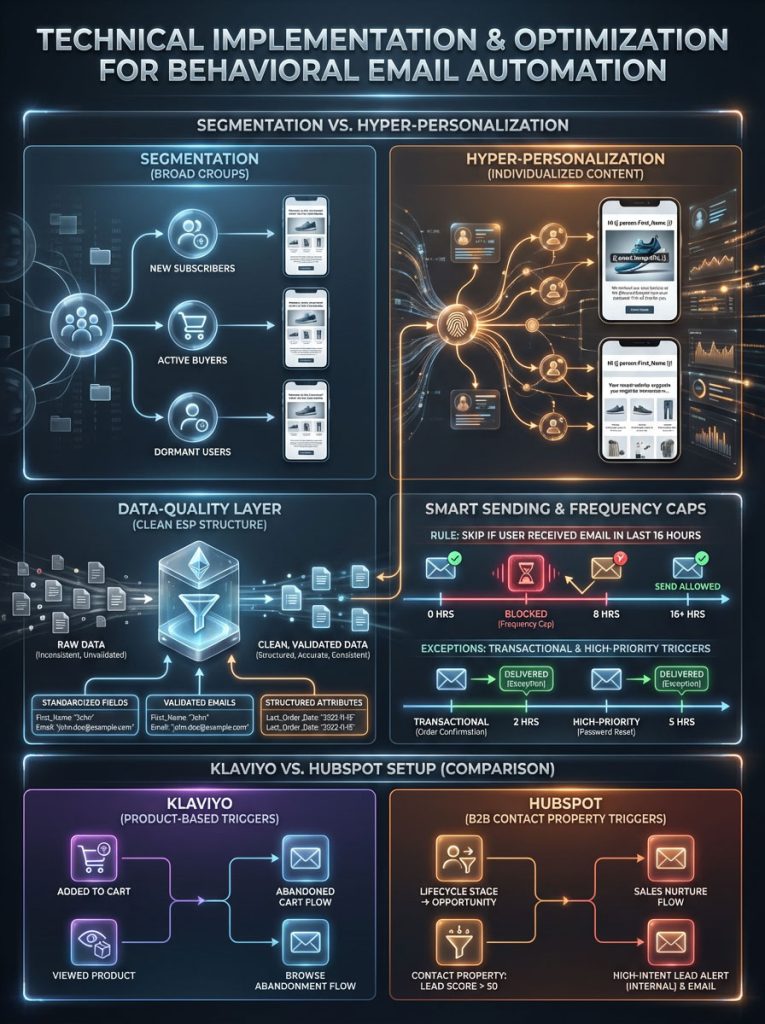
Mastering Email Segmentation Best Practices vs. Hyper-Personalization
There is a fundamental difference between email segmentation best practices and true personalization.
Segmentation is sending an email to “All Women in California.”
Hyper-Personalization is sending an email to “Sarah in California” showing the “Red Dress” she viewed yesterday in her size.
To achieve this, you need to utilize dynamic content personalization tags (e.g., {{ event.ImageURL }} or {{ person.First_Name }}). This requires a clean data structure within your ESP.
Smart Sending and Managing Frequency Caps
One of the biggest risks of automated email campaigns is “over-sending.” If a user triggers a browse abandonment flow; signs up for the newsletter; and has a birthday all in one week, they could receive 10 emails. This leads to fatigue and unsubscribes.
You must utilize Smart Sending windows. This feature is standard in tools like Klaviyo and Omnisend.
Rule: “Skip this email if the user has received another email in the last 16 hours.”
Exception: Transactional emails (Receipts) and high-priority alerts (Cart Abandonment) should bypass Smart Sending.
Platform-Specific Setup: How to Set Up Behavioral Email Triggers in Klaviyo vs. HubSpot
Ranking for specific “how-to” queries requires understanding the nuances of the platform.
Klaviyo (eCommerce): Best for product-based triggers. Focus on “Metric” triggers like “Added to Cart” and “Viewed Product.”
HubSpot (B2B): Best for page-view and form-fill triggers. Focus on “Contact Property” triggers like “Lifecycle Stage changed to Opportunity.”
Compliance, Deliverability, and the Legal Landscape
In the USA, email marketing is regulated by the CAN-SPAM Act; with additional pressure from GDPR (Europe) and CCPA (California) for global businesses. Understanding the legal distinction between message types is critical for Email deliverability protocols.

Navigating the Difference Between Transactional and Behavioral Emails
Mixing these two categories can lead to legal trouble and poor inbox placement. Transactional emails are functional; Behavioral emails are commercial.
The table below outlines the critical distinctions you must respect to ensure your strategy remains compliant and your emails remain in the primary inbox.
| Feature | Transactional Email | Behavioral (Marketing) Email |
| Primary Definition | Facilitates an agreed-upon transaction or updates a customer about an ongoing service. | Advertises a commercial product or service to generate sales or engagement. |
| Common Examples | Order confirmation, Password reset, Shipping notification, Legal policy update. | Abandoned cart reminder, Welcome series, Win-back offer, Newsletter, Birthday discount. |
| Trigger Mechanism | System-generated immediately following a user’s completed action. | User-generated based on behavioral cues (browsing) or lack of action (inactivity). |
| Consent Requirement | Implied Consent: No opt-in needed as it is essential for the service. | Explicit Consent: User must have opted-in to receive marketing (checked a box). |
| Unsubscribe Link | Not required (and often discouraged to prevent users from missing critical info). | Mandatory by federal law (CAN-SPAM). Must be clear and functional for 30 days. |
| Sender Reputation | High deliverability; often sent from a dedicated transactional IP address. | Subject to promotional filtering; reputation depends on engagement and spam complaints. |
| Routing Priority | Critical priority (Real-time delivery). | Standard priority (Queued delivery). |
Ensuring Deliverability with SPF, DKIM, and DMARC
Even the best behavioral triggers are useless if they land in the spam folder. To ensure high email sender reputation, you must authenticate your domain.
SPF (Sender Policy Framework): A DNS record that lists the IP addresses authorized to send email on your behalf.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail): An encryption key that verifies the email has not been altered in transit.
DMARC: A policy that tells ISPs (like Gmail or Yahoo) what to do if an email fails SPF or DKIM checks.
Major inbox providers enforce strict requirements. If you do not have these protocols set up, your automated email campaigns will be blocked.
Summary & Key Takeaways
The transition from manual campaigns to behavioral email marketing is the single most effective lever for increasing Email marketing ROI. By shifting your focus from “What do I want to say?” to “What is the customer doing?”, you align your business with the natural flow of user intent.

Audit Your Activity Triggers: Ensure you have cart abandonment solutions, browse abandonment, and search abandonment flows active. These are your revenue safety nets.
Map Your Lifecycle: Use the welcome series and post-purchase flows to gather data and reduce anxiety; improving Customer Lifetime Value (CLV).
Automate Retention: Set up win-back and replenishment flows using predictive analytics in email to stop churn before it starts.
Respect the Inbox: Use Smart Sending and proper segmentation to deliver value, not noise.
If you are not using these email automation triggers, you are voluntarily lowering your conversion rates. The technology is accessible; the data is clear; and the ROI is proven. It is time to let the behavior drive the strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the single most effective behavioral trigger for eCommerce revenue?
Without question, the abandoned cart flow is the highest revenue-generating trigger. Because the user has already selected items and initiated checkout, their intent is at its peak. Implementing a 3-part sequence with dynamic product blocks and social proof can recover 10-15% of otherwise lost sales.
How do I strictly set up behavioral email triggers in Klaviyo?
To set up a trigger in Klaviyo, go to the “Flows” section and select “Create Flow.” Choose a metric-based trigger such as “Started Checkout.” Crucially, you must add a Trigger Filter (e.g., Value > $0) and a Profile Filter (e.g., Has not been in this flow in the last 7 days) to prevent spamming. Finally, add your time delays and email content.
What is the fundamental difference between transactional and behavioral emails?
Transactional emails are functional messages (receipts, password resets) necessary for the service and do not require opt-in. Behavioral emails are marketing messages (abandoned cart, recommendations) designed to sell and strictly require explicit opt-in consent and an unsubscribe link under the CAN-SPAM Act.
How can re-engagement trigger emails effectively reduce churn?
Re-engagement triggers (Win-Backs) reduce churn by identifying users who are drifting away before they leave permanently. By detecting “0 opens in 90 days” and triggering a high-value offer or emotional appeal (“We miss you”), you can reactivate a portion of these users, which is significantly cheaper than acquiring new ones.
What are the best real-world examples of B2B behavioral triggers?
Top B2B triggers include:
Whitepaper Follow-up: “Here is the PDF you requested + a related case study.”
Pricing Page Frenzy: Alerting sales when a lead views the pricing page more than 3 times.
Feature Activation: Nudging a SaaS user who hasn’t used a core feature during their trial.
How does behavioral segmentation differ from demographic segmentation?
Demographic segmentation targets who someone is (Age 30, Female, New York). Behavioral segmentation targets what they do (Visited site 5 times, bought Red Shoes, Abandoned Cart). Behavioral data is historically 10x more predictive of purchase intent because it reflects real-time desire rather than static identity.
What is the ideal time delay for a browse abandonment email?
The industry “sweet spot” is 2 hours. Sending sooner (e.g., 20 minutes) can feel intrusive; as if the brand is stalking the user. Waiting longer than 4 hours allows the user’s purchase intent (and memory of the product) to fade.
Are behavioral emails compliant with GDPR and CCPA?
Yes, but only if you have properly collected consent. You cannot fire behavioral triggers based on cookies if the user declined cookie tracking. You also cannot send marketing emails to users who only provided their email for a transactional receipt, unless they also checked a “Subscribe to Newsletter” box.
How much does behavioral email automation software cost?
Pricing is tiered by contact count. Small businesses might use Klaviyo or Mailchimp for $20 to $100 per month. Mid-market companies might use HubSpot Pro or Omnisend for $800 to $1,500 per month. Enterprise-grade solutions like Salesforce Marketing Cloud can cost over $3,000 per month. The Email marketing ROI from automation usually covers these costs within the first month.
Why are my behavioral emails going to spam?
The most common reasons are poor sender reputation (sending to unengaged users), authentication issues (missing SPF/DKIM records), using spam-trigger words (e.g., “FREE”, “CASH”) excessively, or overwhelming the user with too many emails in a short window.
What is a “dynamic product block” in email marketing?
A dynamic product block is a script in your email template that queries your e-commerce platform. It automatically pulls the image, title, price, and URL of the specific product a user interacted with. This allows one email template to serve thousands of different product recommendations personally.
How do I calculate the ROI of an automated email campaign?
Use this formula: (Attributed Revenue – (Software Cost + Setup Cost)) / (Software Cost + Setup Cost) * 100. Most ESPs utilize a 5-day attribution window, meaning if a user clicks an email and buys within 5 days, the revenue is credited to that flow.
Disclaimer: The content provided in this article regarding email marketing strategies, data privacy, and compliance (including CAN-SPAM, GDPR, and CCPA) is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. Regulations vary by jurisdiction and are subject to change. Marketers should consult with their own legal counsel to ensure their automation workflows comply with all applicable local, state, and federal laws.
References:
- Omnisend. The Impact of Automation on E-commerce Revenue: Annual Report.
- Klaviyo. Email Benchmarks and Trends for eCommerce.
- HubSpot. State of Marketing Automation: B2B and B2C Insights.
- Federal Trade Commission. CAN-SPAM Act: A Compliance Guide for Business.









